Java數組的運用詳解
一,數組的含義:
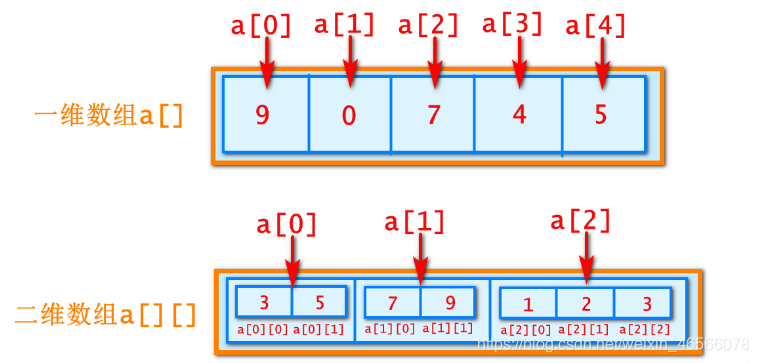
一維數組:相同數據類型的元素的集合。
二位數組:存放數組的數組,也就是說數組裡存的還是數組的數據形式。
二,數組的創建
一維數組
1,動態初始化
數據類型[] 數組名 = new 數據類型[數組長度];
例:int[] a = new int[5];
2,靜態初始化
數據類型[] 數組名 = {數組0,數組1,數組2,數組3,…};
例:int[] b = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
數據類型[] 數組名 = {數組0,數組1,數組2,數組3,…};
例:int[] c = {1,2,3,4,5}
二位數組
數據類型[][] 數組名 = {數組1,數組2,…};
例:int[][] a = {{3,5},{7,9},{1,2}};
三,數組遍歷
一維數組遍歷
int [] arr={1,2,3,4,5};
for(int a = 0; a < arr.length; a++){
System.out.print(arr[a]);
}
運行結果:
12345
Arrays工具類中toString靜態方法遍歷
int [] arr={1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(arr));
運行結果:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
二維數組遍歷
int Arr[][]={{5,7,15},{8,4,11},{3,6,13}};
for (int i = 0; i < Arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < Arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(Arr[i][j]+" ");
}
}
運行結果:
5 7 15 8 4 11 3 6 13
Arrays工具類中deepToString靜態方法遍歷
int b[][]={{5,7,15},{8,4,11},{3,6,13}};
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(b));
運行結果:
[[5, 7, 15], [8, 4, 11], [3, 6, 13]]
四,Arrays.deepToString()與Arrays.toString()的區別
Arrays.deepToString()主要用於數組中還有數組的情況,而Arrays.toString()則相反,對於Arrays.toString()而言,當數組中有數組時,不會打印出數組中的內容,隻會以地址的形式打印出來。
例:
int a[][]={{5,7,15},{8,4,11},{3,6,13}};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
int b[][]={{1,2,3},{8,4,11},{3,6,13}};
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(b));
運行結果:
[[I@da2dbb, [I@176fe71, [I@fb509a]
[[1, 2, 3], [8, 4, 11], [3, 6, 13]]
五,Java中Arrays類的常用方法
Arrays類位於 java.util 包中,主要包含瞭操作數組的各種方法。
Arrays.fill(); //填充數組
int[] a = new int[5];//新建一個大小為5的數組 Arrays.fill(a,4);//給所有值賦值4 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); int[] b = new int[5];//新建一個大小為5的數組 Arrays.fill(b, 2,4,1);//給第2位(0開始)到第4位(不包括)賦值6 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
運行結果:
[4, 4, 4, 4, 4]
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0]
Arrays.sort(); //數組排序
1,數字排序
int[] a = new int[] { 4, 1, 3, -2, 10 };
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
運行結果:
[-2, 1, 3, 4, 10]
2,字符串排序,先大寫後小寫
String[] a = new String[] { "a", "b", "C" };
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
運行結果:
[C, a, b]
3,嚴格按字母表順序排序,也就是忽略大小寫排序 CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
String[] a = new String[] { "a", "b", "C" };
Arrays.sort(a, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
運行結果:
[a, b, C]
4,反向排序, Collections.reverseOrder()
String[] a = new String[] { "a", "b", "C" };
Arrays.sort(a, Collections.reverseOrder());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
運行結果:
[a, b, C]
5,忽略大小寫反向排序 (先忽略大小寫,再反向排序)
String[] a = new String[] { "a", "B", "c","D" };
Arrays.sort(a, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
Collections.reverse(Arrays.asList(a));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
運行結果:
[D, c, B, a]
6,選擇數組指定位置進行排序
int[] a = {3,2,1,8,6,5,4,7};
Arrays.sort(a,0,3);//給第0位(0開始)到第3位(不包括)排序
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(a));
運行結果:
[1, 2, 3, 8, 6, 5, 4, 7]
Arrays.toString(); //將數組中的內容全部打印出來
int[] a = {3,2,1,5,4};
System.out.println(a);//直接將數組打印輸出
String str = Arrays.toString(a); // Arrays類的toString()方法能將數組中的內容全部打印出來
System.out.println(str);
運行結果:
[I@da2dbb
[3, 2, 1, 5, 4]
Arrays.equals(); //比較數組元素是否相等
int[] arr1 = {1,2,3};
int[] arr2 = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(arr1,arr2));
System.out.println(arr1.equals(arr2));
運行結果:
true
false
因為equals比較的是兩個對象的地址,不是裡面的數,而Arrays.equals重寫瞭equals,所以,這裡能比較元素是否相等。
Arrays.copyOf();//復制數組
int[] a= {3, 7, 2, 1};
int[] b=Arrays.copyOf(arr6, 4); //指定新數組的長度
int[] c=Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 1, 3); //隻復制從索引[1]到索引[3]之間的元素(不包括索引[3]的元素)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c));
運行結果:
[3, 7, 2, 1]
[7, 2]
數組中是否包含某一個值
String[] array={"aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","eee"};
String a="aaa";
String b="fff";
if (Arrays.asList(array).contains(a)) {
System.out.println("1");
}else {
System.out.println("2");
}
if (Arrays.asList(array).contains(b)) {
System.out.println("1");
}else {
System.out.println("2");
}
運行結果:
1
2
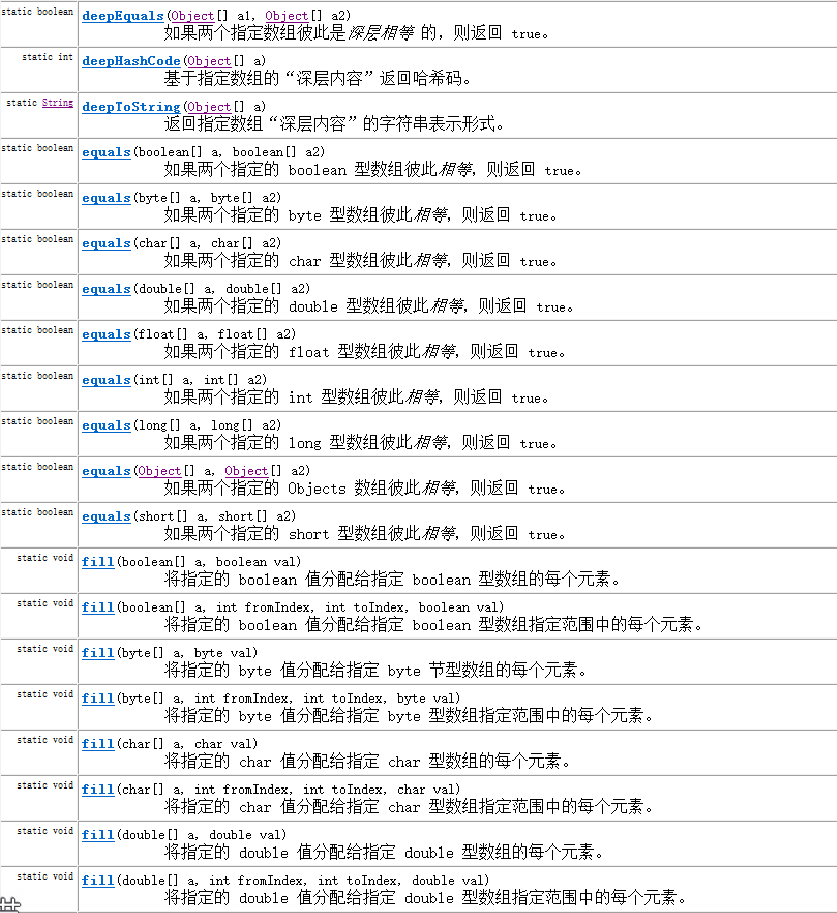
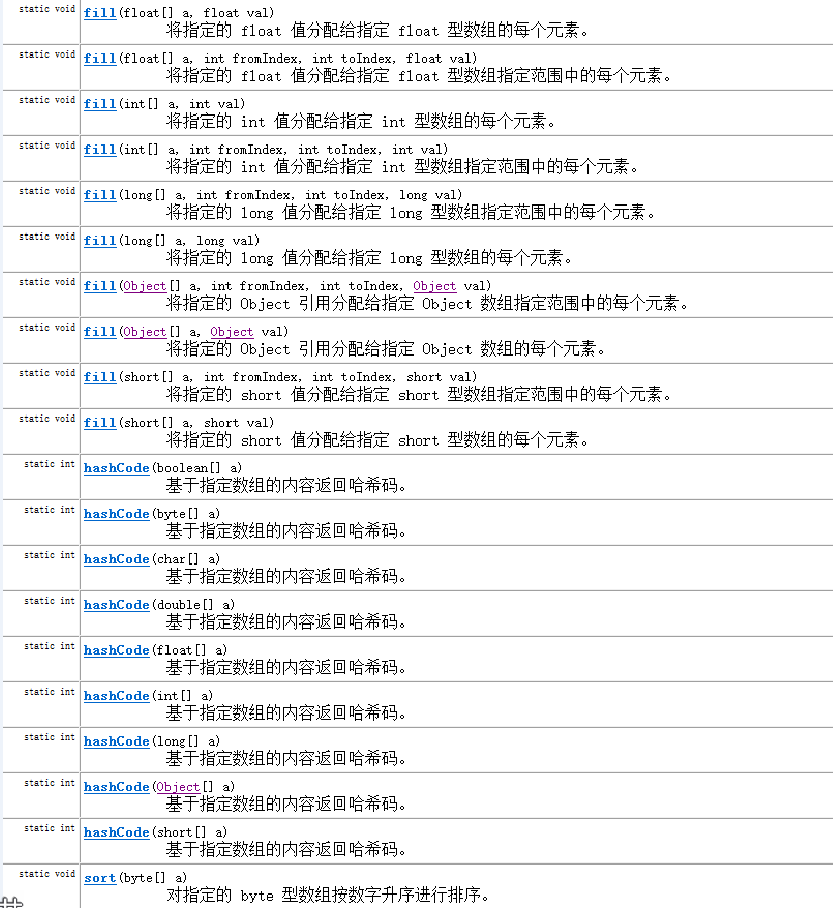
其它方法,詳情見JAVA JDK_API




六,數組去重
1,利用set的特性去重
int[] arr11 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0,3,2,4,5,6,7,4,32,2,1,1,4,6,3};
Set<Integer> set2=new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr11.length; i++) {
set2.add(arr11[i]);
}
System.out.println(set2);
int[] arr12 = new int[set2.size()];
int j=0;
for (Integer i:set2) {
arr12[j++]=i;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr12));
運行結果:
[0, 32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
[0, 32, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
2,用List集合實現
int[] str = {5, 6, 6, 6, 8, 8, 7,4};
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i=0; i<str.length; i++) {
if(!list.contains(str[i])) {
list.add(str[i]);
}
}
System.out.println("去除重復後的list集合"+list);
運行結果:
[5, 6, 8, 7, 4]
3,用hashSet或者TreeSet實現
Integer[] nums = { 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 8, 8, 7, 11, 12, 12 };
HashSet hset = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(nums));
//TreeSet<Integer> hset = new TreeSet<Integer>(Arrays.asList(nums));
Iterator i = hset.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
System.out.print(i.next());
}
運行結果:
56781112
4,用List和set實現
int[] nums = { 5, 6, 6, 6, 8, 8, 7 };
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i : nums)
numList.add(i);
Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
numSet.addAll(numList);
System.out.println(numSet);
運行結果:
[5, 6, 7, 8]
七,數組刪除,增加元素
刪除數組中其中一個元素
String [] str = {"Java", "C++", "Php", "C#", "Python"};//刪除php
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i=0; i<str.length; i++) {
list.add(str[i]);
}
list.remove(2); //list.remove("Php")
String[] newStr = list.toArray(new String[1]); //返回一個包含所有對象的指定類型的數組
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newStr));
運行結果:
[Java, C++, C#, Python]
在數組中增加一個元素
String [] str = {"Java", "C++", "Php", "C#", "Python"};//增加ruby
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i=0; i<str.length; i++) {
list.add(str[i]);
}
list.add(2, "ruby");
String[] newStr = list.toArray(new String[1]); //返回一個包含所有對象的指定類型的數組
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newStr));
運行結果:
[Java, C++, ruby, Php, C#, Python]
八,數組與List相互轉換
數組轉 List ,使用 JDK 中 java.util.Arrays 工具類的 asList 方法
String[] strs = new String[] {"aaa", "bbb", "ccc"};
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(strs);
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
List 轉數組,使用 List 的toArray方法。無參toArray方法返回Object數組,傳入初始化長度的數組對象,返回該對象數組
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("aaa", "bbb", "ccc");
String[] array = list2.toArray(new String[list2.size()]);
for (String s : array) {
System.out.println(s);
}
總結
本篇文章就到這裡瞭,希望能給你帶來幫助,也希望您能夠多多關註WalkonNet的更多內容!
推薦閱讀:
- java中Map、Set、List的簡單使用教程(快速入門)
- Java打印數組的三種方法整理
- Java 基礎–Arrays工具類詳解
- Java中Arrays數組工具類的基本使用詳解
- 一篇文章帶你入門java集合