jackson json序列化實現首字母大寫,第二個字母需小寫
jackson json序列化首字母大寫,第二個字母需小寫
有這樣一個類:
@Setter
@Getter
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategy.UpperCamelCaseStrategy.class)
public class Student {
private String bName;
}
序列化後,希望首字母大寫,如下面的測試代碼:
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws IOException {
Student test = new Student();
test.setBName("234234");
String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(test);
Assert.assertEquals("{\"BName\":\"234234\"}", s);
}
可實際運行後,結果與希望不一樣:
org.junit.ComparisonFailure:
Expected :{“BName”:”234234″}
Actual :{“Bname”:”234234″}
jackson在序列化時把第二個大寫字母n轉成瞭小寫,這是為什麼呢?
以下是跟蹤源碼的過程:
直接找到:com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.introspect.POJOPropertiesCollector#collectAll這個方法:

執行完_addFields(props)方法後:

執行完_addMethods(props)方法後:

一個是bName,一個是bname;
第一個bName取的是字段的名稱,
第二個bname是取的它的set方法:
public static String okNameForIsGetter(AnnotatedMethod am, String name,
boolean stdNaming)
{
if (name.startsWith("is")) { // plus, must return a boolean
Class<?> rt = am.getRawType();
if (rt == Boolean.class || rt == Boolean.TYPE) {
return stdNaming
? stdManglePropertyName(name, 2)
: legacyManglePropertyName(name, 2);
}
}
return null;
}
根據stdNaming來決定這個name是以什麼標準輸出,默認的是false;
stdManglePropertyName 就是原始輸出。
legacyManglePropertyName 就是規范輸出。
下面的代碼就是規范輸出:
protected static String legacyManglePropertyName(final String basename, final int offset)
{
final int end = basename.length();
if (end == offset) { // empty name, nope
return null;
}
// next check: is the first character upper case? If not, return as is
char c = basename.charAt(offset);
char d = Character.toLowerCase(c);
if (c == d) {
return basename.substring(offset);
}
// otherwise, lower case initial chars. Common case first, just one char
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(end - offset);
sb.append(d);
int i = offset+1;
for (; i < end; ++i) {
c = basename.charAt(i);
d = Character.toLowerCase(c);
if (c == d) {
sb.append(basename, i, end);
break;
}
sb.append(d);
}
return sb.toString();
}
主要邏輯在for循環中,去除set後,第一個字母小寫,
第二字母小寫後,與第二個字母比較,如果都是小寫,則直接接上,返回,
如果第二字母大寫,就如我們的這種情況,就以小寫的情況,接上,再去找下一個字母,直到找到小寫字母為止。
意思就是為瞭滿足駝峰命名規則,要規范輸出。
如果我們的字段命名正如它的規范的話,props是隻有一條記錄的,因為:名稱相同,就不插入瞭,由於咱們的名稱不同,所以就有兩條記錄。
protected POJOPropertyBuilder _property(Map<String, POJOPropertyBuilder> props,
String implName)
{
POJOPropertyBuilder prop = props.get(implName);
if (prop == null) {
prop = new POJOPropertyBuilder(_config, _annotationIntrospector, _forSerialization,
PropertyName.construct(implName));
props.put(implName, prop);
}
return prop;
}
可是我們輸出中隻有一條,沒有bName這條,
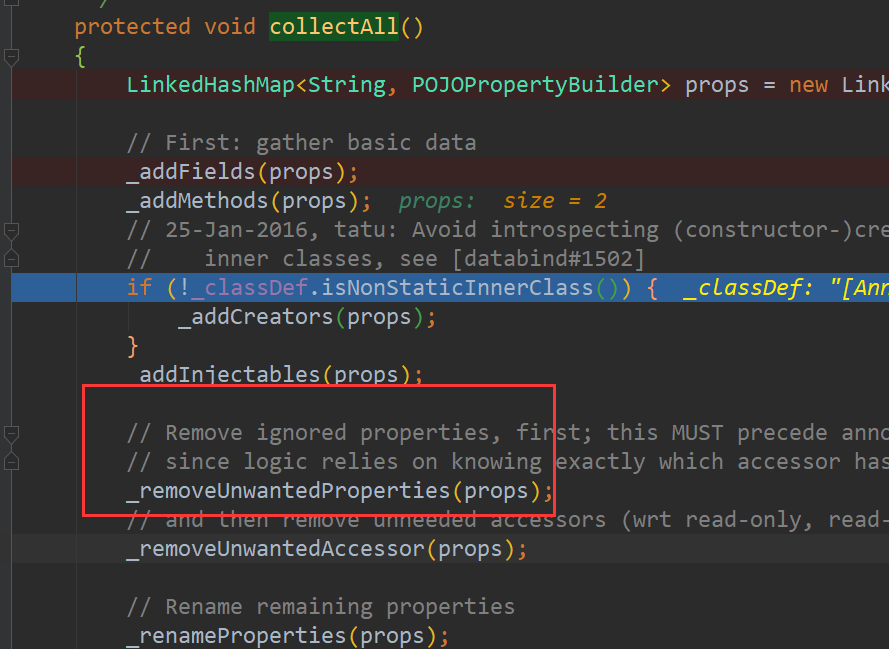
其實在是這裡把第一條刪除瞭。因為:

這些屬性為空,導致這個字段不可見:
protected void _removeUnwantedProperties(Map<String, POJOPropertyBuilder> props)
{
Iterator<POJOPropertyBuilder> it = props.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
POJOPropertyBuilder prop = it.next();
// First: if nothing visible, just remove altogether
if (!prop.anyVisible()) {
it.remove();
continue;
}
// Otherwise, check ignorals
if (prop.anyIgnorals()) {
// first: if one or more ignorals, and no explicit markers, remove the whole thing
if (!prop.isExplicitlyIncluded()) {
it.remove();
_collectIgnorals(prop.getName());
continue;
}
// otherwise just remove ones marked to be ignored
prop.removeIgnored();
if (!prop.couldDeserialize()) {
_collectIgnorals(prop.getName());
}
}
}
}
隻剩第二記錄bname,再首字母大寫,所以就是Bname瞭。
解決方案:
第一個就是JsonProperty
@Setter
@Getter
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategy.UpperCamelCaseStrategy.class)
public class Student {
@JsonProperty("BName")
private String bName;
}
測試結果如下:
org.junit.ComparisonFailure:
Expected :{“BName”:”234234″}
Actual :{“Bname”:”234234″,”BName”:”234234″}
雖然生成瞭BName,但是Bname仍在(加瞭JsonProperty就visable瞭)。
第二個就是配置
objectMapper的MapperFeature.USE_STD_BEAN_NAMIN如上文提到瞭,非規范化輸出。
如下代碼:
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws IOException {
Student test = new Student();
test.setBName("234234");
objectMapper.configure(MapperFeature.USE_STD_BEAN_NAMING, true);
String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(test);
Assert.assertEquals("{\"BName\":\"234234\"}", s);
}
第三個方案:重寫PropertyNamingStrategy:
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws IOException {
Student test = new Student();
test.setBName("234234");
//objectMapper.configure(MapperFeature.USE_STD_BEAN_NAMING, true);
objectMapper.setPropertyNamingStrategy(new PropertyNamingStrategy() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// 反序列化時調用
@Override
public String nameForSetterMethod(MapperConfig<?> config,
AnnotatedMethod method, String defaultName) {
return method.getName().substring(3);
}
// 序列化時調用
@Override
public String nameForGetterMethod(MapperConfig<?> config,
AnnotatedMethod method, String defaultName) {
return method.getName().substring(3);
}
});
String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(test);
Assert.assertEquals("{\"BName\":\"2342344\"}", s);
}
修改objectMapper的配置,要註意對其他功能的影響。
以上為個人經驗,希望能給大傢一個參考,也希望大傢多多支持WalkonNet。
推薦閱讀:
- 新手瞭解java 類,對象以及封裝基礎知識
- 分析jackjson的安全漏洞CVE-2019-14379
- Java中的getClass()以及getName()方法使用
- 詳解Java-Jackson使用
- Java如何重寫object類的equals方法詳解