SpringBoot2.x 集成 Thymeleaf的詳細教程
一、Thymeleaf簡介
Thymeleaf是面向Web和獨立環境的現代服務器Java模板引擎,能夠處理HTML,XML,JavaScript,CSS甚至純文本。
Thymeleaf旨在提供一個優雅的、高度可維護的創建模板的方式。為瞭實現這一目標,Thymeleaf建立在自然模板的概念上,將其邏輯註入到模板文件中,不會影響模板設計原型。這改善瞭設計的溝通,彌合瞭設計和開發團隊之間的差距。
Thymeleaf從設計之初就遵循Web標準——特別是HTML5標準,如果需要,Thymeleaf允許創建完全符合HTML5驗證標準的模板。
二、集成Thymeleaf
通過Maven新建一個名為springboot-thymeleaf的項目。
1.引入依賴
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Thymeleaf 起步依賴 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok插件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.8</version>
</dependency>
2.編寫配置文件
spring:
thymeleaf:
# 在構建URL時用於查看名稱的前綴,默認為classpath:/templates/
prefix: classpath:/templates/
# 在構建URL時附加到視圖名稱的後綴,默認為.html
suffix: .html
# 模板模式,默認為HTML
mode: HTML
# 模板文件編碼,默認為UTF-8
encoding: UTF-8
# 是否啟用模板緩存,默認為true,表示啟用,false不啟用
cache: false
# 在呈現模板之前是否檢查模板存在與否,默認為true
check-template: true
# 是否檢查模板位置存在與否,默認為true
check-template-location: true
更多的配置可以查看ThymeleafProperties類:

3.準備模板
首先按照配置文件中配置的模板前綴在resources下創建一個templates目錄,用於存放模板。然後創建如下名為hello.html的模板:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello Thymeleaf</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span th:text="${hello}">th:text文本替換會轉義html標簽,不解析html</span>
</div>
<hr/>
<div>
<span th:utext="${hello}">th:utext文本替換不會轉義html標簽,會解析html</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<html>標簽中的xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org聲明使用Thymeleaf標簽。th:text屬性會計算表達式的值將結果設置為標簽的標簽體。但它會轉義HTML標簽,HTML標簽會直接顯示在瀏覽器上。th:utext屬性不會轉義HTML標簽,HTML標簽會被瀏覽器解析。${hello}是一個變量表達式,它包含一個OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)的表達式,它會從上下文中獲取名為hello的變量,然後在模板上進行渲染。
4.Controller層
創建Controller並將模板中要獲取的變量設置到Model對象中,如果Controller類上使用的是@Controller註解,則可以返回跟模板名稱相同的字符串(不包括前綴和後綴),視圖解析器會解析出視圖具體地址並生成視圖,然後返回給前端控制器進行渲染:
package com.rtxtitanv.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
/**
* @author rtxtitanv
* @version 1.0.0
* @name com.rtxtitanv.controller.ThymeleafController
* @description ThymeleafController
* @date 2021/7/3 19:23
*/
@Controller
public class ThymeleafController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("hello", "<h1>Hello Thymeleaf</h1>");
return "hello";
}
}
運行項目,瀏覽器訪問http://localhost:8080/hello,發現數據成功渲染到模板:
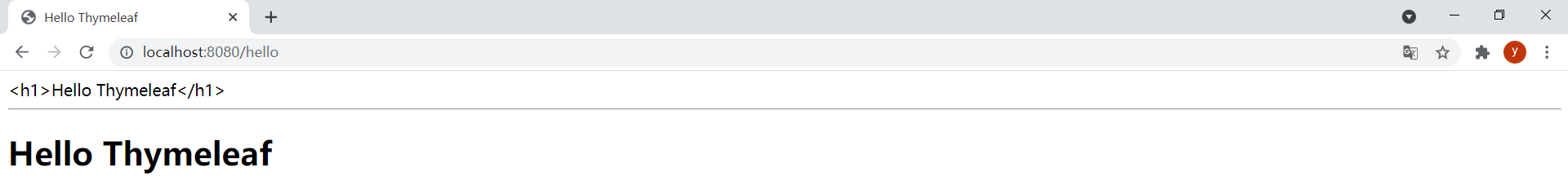
如果Controller類上使用的是@RestController註解,則需要將視圖添加到ModelAndView對象中並返回:
package com.rtxtitanv.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
/**
* @author rtxtitanv
* @version 1.0.0
* @name com.rtxtitanv.controller.TestController
* @description TestController
* @date 2021/7/3 19:43
*/
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public ModelAndView hello() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("hello");
modelAndView.addObject("hello", "<h1>hello thymeleaf</h1>");
return modelAndView;
}
}
運行項目,瀏覽器訪問http://localhost:8080/test/hello,發現數據成功渲染到模板:

三、Thymeleaf常用語法
1.標準表達式
(1)變量表達式
${}表達式實際上是在上下⽂中包含的變量的映射上執行的OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)對象。例如:${session.user.name}。
在Spring MVC啟用的應用程序中,OGNL將被替換為SpringEL,但其語法與OGNL相似(實際上,在大多數常見情況下完全相同)。
模板variable.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>變量表達式</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>變量表達式:${}</p>
<div>
<p>id: <span th:text="${user.id}"></span></p>
<p>username: <span th:text="${user.username}"></span></p>
<p>password: <span th:text="${user.password}"></span></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
User實體類:
package com.rtxtitanv.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* @author rtxtitanv
* @version 1.0.0
* @name com.rtxtitanv.model.User
* @description User
* @date 2021/7/3 19:37
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
}
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/variable")
public String variable(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "趙雲", "qwe123"));
return "variable";
}
效果:
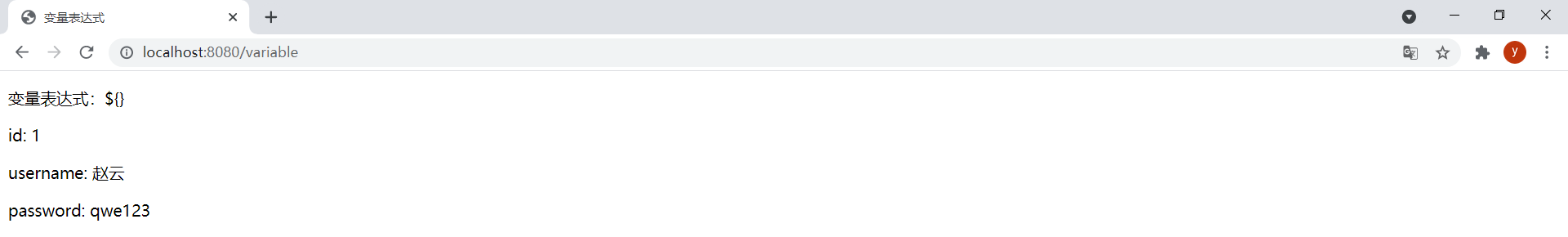
在${}表達式中還可以使用基本對象和工具類對象。這些對象都以#開頭。基本對象:
#ctx:上下文對象。#vars:上下文變量。#locale:上下文區域設置。#request:(僅在Web Contexts中)HttpServletRequest對象。#response:(僅在Web上下⽂中)HttpServletResponse對象。#session:(僅在Web上下⽂中)HttpSession對象。#servletContext:(僅在Web上下⽂中)ServletContext對象。
工具類對象:
#execInfo:有關正在處理的模板的信息。#messages:用於在變量表達式中獲取外部化消息的方法,與使用#{}語法獲取的方式相同。#uris:轉義URL/URI部分的方法。#conversions:執行配置的轉換服務的方法。#dates:java.util.Date對象的方法。#calendars:類似於#dates,但對應java.util.Calendar對象。#numbers:用於格式化數字對象的方法。#strings:字符串對象的方法。#objects:一般對象的方法。#bools:佈爾相關方法。#arrays:Array的方法。#lists:List的方法。#sets:Set的方法。#maps:Map的方法。#aggregates:在數組或集合上創建聚合的方法。#ids:處理可能重復的id屬性的方法。
這些對象的詳細方法可以查看官方文檔:https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html#appendix-a-expression-basic-objects。
(2)選擇表達式(星號語法)
星號語法*{}計算所選對象而不是整個上下文的表達式。也就是說,隻要沒有選定的對象(選定對象為th:object屬性的表達式結果),$和*語法就會完全相同。
模板asterisk.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>選擇表達式(星號語法)</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>*語法</p>
<div th:object="${user}">
<p>id: <span th:text="*{id}"></span></p>
<p>username: <span th:text="*{username}"></span></p>
<p>password: <span th:text="*{password}"></span></p>
</div>
<p>$語法</p>
<div>
<p>id: <span th:text="${user.id}"></span></p>
<p>username: <span th:text="${user.username}"></span></p>
<p>password: <span th:text="${user.password}"></span></p>
</div>
<p>$和*混合使用</p>
<div th:object="${user}">
<p>id: <span th:text="*{id}"></span></p>
<p>username: <span th:text="${user.username}"></span></p>
<p>password: <span th:text="*{password}"></span></p>
</div>
<p>對象選擇到位時所選對象將作為#object表達式變量可⽤於$表達式</p>
<div th:object="${user}">
<p>id: <span th:text="${#object.id}"></span></p>
<p>username: <span th:text="${user.username}"></span></p>
<p>password: <span th:text="*{password}"></span></p>
</div>
<p>沒有執⾏對象選擇時$和*語法等效</p>
<div>
<p>id: <span th:text="*{user.id}"></span></p>
<p>username: <span th:text="*{user.username}"></span></p>
<p>password: <span th:text="*{user.password}"></span></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/asterisk")
public String star(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "趙雲", "qwe123"));
return "asterisk";
}
效果:
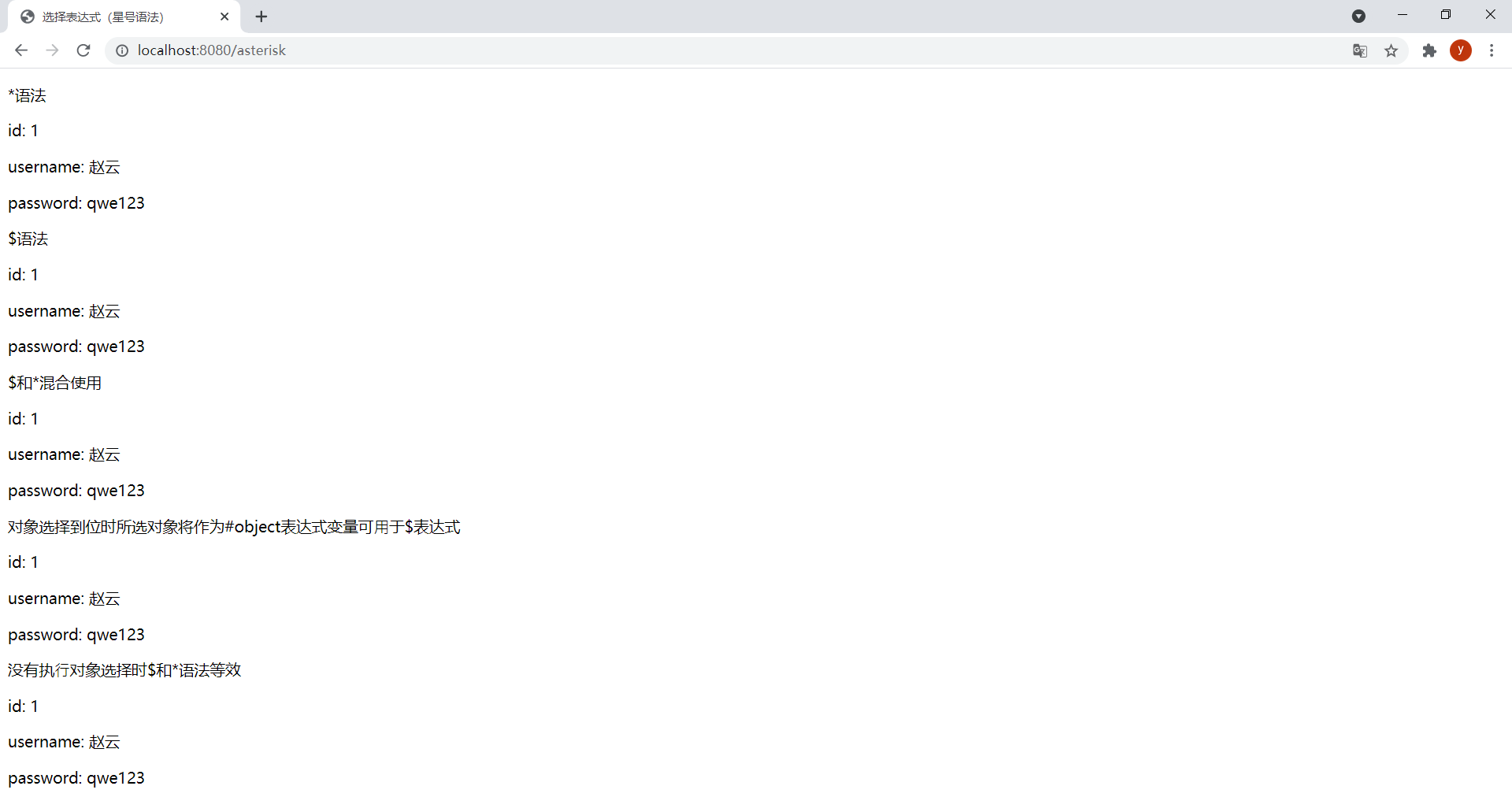
(3)URL表達式
URL表達式的語法為@{}。使用th:href屬性可以對鏈接進行渲染。
模板url.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>URL表達式</title>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li><a href="user/one.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" th:href="@{/user/one(id=${user.id})}" rel="external nofollow" >設置單個參數</a></li>
<li><a href="user/list.html" rel="external nofollow" th:href="@{/user/list(username=${user.username},password=${user.password})}" rel="external nofollow" >設置多個參數</a></li>
<li><a href="user/one.html" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" th:href="@{/user/one/{id}(id=${user.id})}" rel="external nofollow" >URL路徑中也允許使⽤變量模板(rest風格參數)</a></li>
<li><a href="user/update.html" rel="external nofollow" th:href="@{${url}(id=${user.id})}" rel="external nofollow" >URL基數也可以是計算另⼀個表達式的結果</a></li>
<li><a href="store/user/update.html" rel="external nofollow" th:href="@{'/store'%20+%20${url}(id=${user.id})}" rel="external nofollow" >url基數也可以是計算另⼀個表達式的結果</a></li>
</ol>
<hr/>
<!-- th:action設置表單提交地址 -->
<form id="login-form" th:action="@{/hello}">
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
註意:
th:href屬性會計算要使用的URL並將該值設置為<a>標簽的href屬性。URL中允許使用表達式的URL參數,設置多個參數將以,分隔。
URL路徑中也可以使用變量模板,即可以設置rest風格的參數。
/開頭的相對URL將自動以應用上下文名稱為前綴。如果cookie未啟用或還未知道,可能會在相對URL中添加;jsessionid=...後綴以便保留會話。這被稱為URL重寫。
th:href屬性允許在模板中有一個靜態的href屬性,這樣在直接打開原型模板時,模板鏈接可以被導航。
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/url")
public String url(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "趙雲", "qwe123"));
model.addAttribute("url", "/user/update");
return "url";
}
效果:
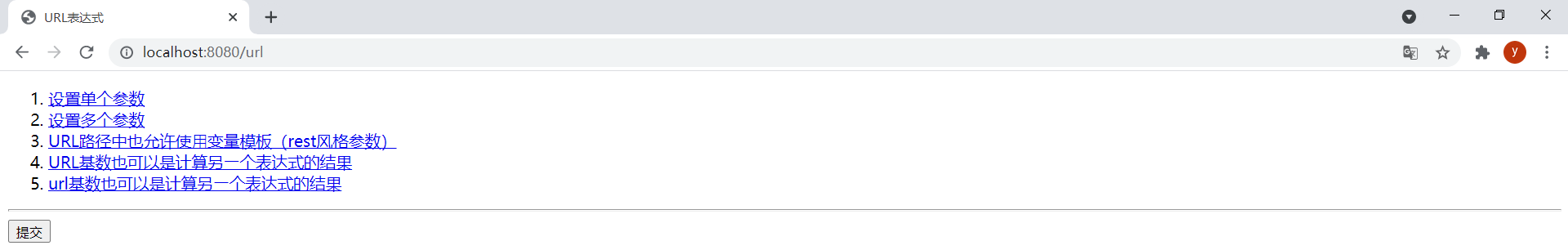
從上到下依次點擊5個鏈接和提交表單的結果:
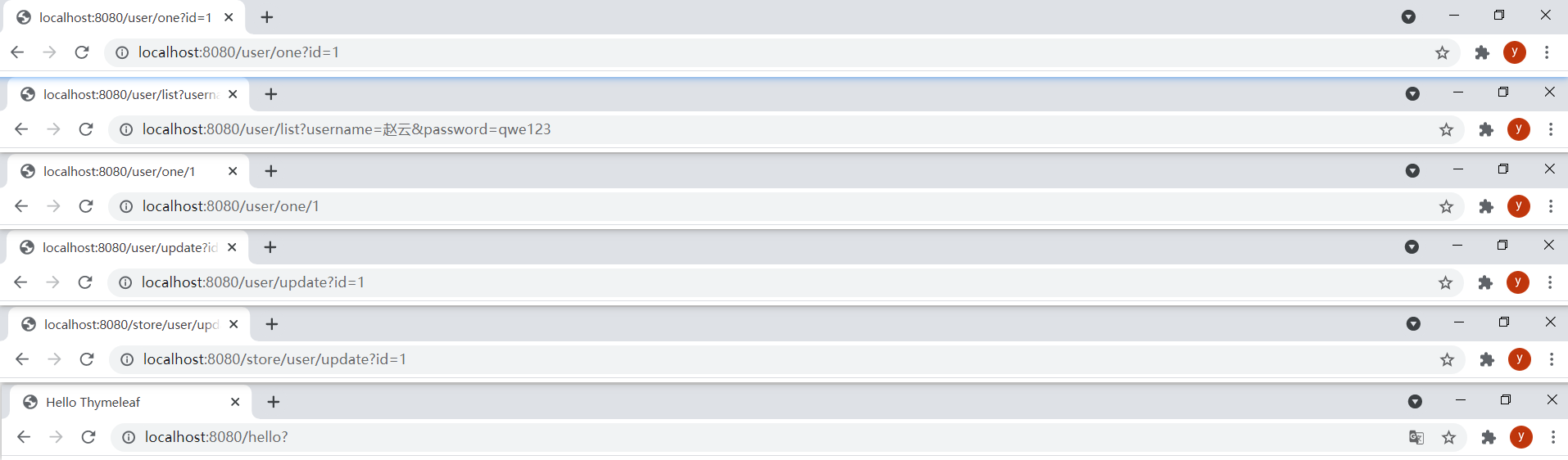
(4)字面量
字面量(Literals)分為:
- 文本文字(Text literals):包含在單引號之間的字符串,可以包含任何字符,其中的單引號需要\’轉義。
- 數字字面量(Number literals):數字。
- 佈爾字面量(Boolean literals):包含true和false。
- null字面量(The null literal):null。
- 文本符號(Literal tokens):數字,佈爾和null字面量實際是文本符號的特殊情況,文本符號不需要引號包圍,隻允許使用字母(A-Z和a-z)、數字(0-9)、括號、點(.)、連字符(-)和下劃線(_)。
模板literal.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>字面量</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<p><span>文本文字:</span><span th:text="'Hello World'">⽂本文字隻是包含在單引號之間的字符串,可以包含任何字符,其中的單引號需要\'轉義</span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>數字字面量:</span><span th:text="2020 + 1">數字字面量就是數字</span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>佈爾字面量:</span><span th:if="${flag} == false">佈爾字⾯量包含true和false</span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>null字面量:</span><span th:if="${flag} != null">Thymeleaf標準表達式語法中也可以使⽤null字⾯量</span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>文本符號:</span><span th:text="Hello_.-._World">數字,佈爾和null字面量實際上是⽂本符號的特殊情況</span></p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/literal")
public String literal(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("flag", false);
return "literal";
}
效果:
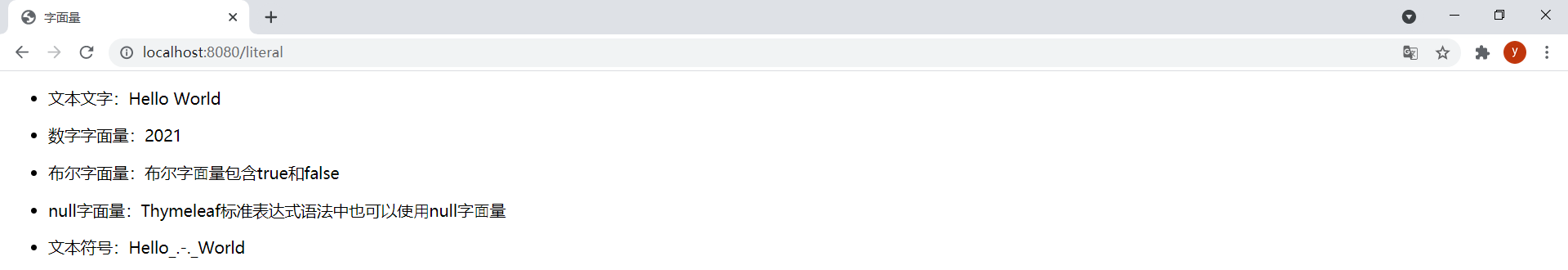
(5)文本操作
這裡的文本操作包含:
- 追加文本(Appending texts),即字符串連接:無論是文本常量還是表達式結果都可以使用
+運算符進行拼接。 - 字面替換(Literal substitutions):字面替換可以輕松地對包含變量值的字符串進行格式化,而不需要在字面後加
+,這些替換必需用|包圍。使用字面替換也可以實現和追加文本相同的效果。
模板text.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>文本操作(字符串連接)</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<p><span>方式1(+):</span><span th:text="'username: ' + ${user.username} + ', password: ' + ${user.password}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>方式2(|):</span><span th:text="|username: ${user.username}, password: ${user.password}|"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<!-- 隻有變量或消息表達式(${},*{},#{})才允許包含在||中 -->
<p><span>方式3(+與|混合):</span><span th:text="'username: ' + ${user.username} + |, password: ${user.password}|"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>方式4(#strings.concat):</span><span th:text="${#strings.concat('username: ', user.username, ', password: ', user.password)}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>方式5(#strings.append):</span><span th:text="${#strings.append('username: ' + user.username, ', password: ' + user.password)}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>方式6(#strings.prepend):</span><span th:text="${#strings.prepend(', password: ' + user.password, 'username: ' + user.username)}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>方式7(#strings.arrayJoin):</span><span th:text="${#strings.arrayJoin(new String[] {'username: ', user.username, ', password: ', user.password}, '')}"></span></p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/text")
public String text(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "趙雲", "qwe123"));
return "text";
}
效果:
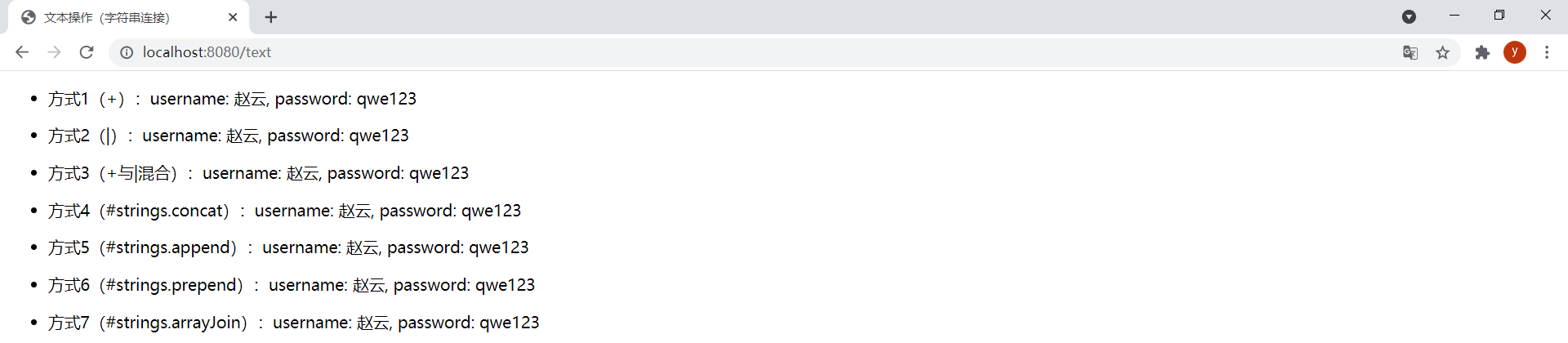
(6)運算符
運算符:
- 算數運算符:
+、-、*、/(div)、%(mod)。 - 比較運算符:
>(gt)、<(lt)、>=(ge)、<=(le)。 - 等值運算符:
==(eq)、!=(ne)。 - 佈爾運算符:
and、or、!(not)。
模板operation.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>運算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="|x=${x}, y=${y}|"></p>
<p>算術運算符:+、-、*、/(div)、%(mod)</p>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<p><span>(y + x % 3) * (y - x / 2) :</span><span th:text="(${y} + ${x} % 3) * (${y} - ${x} / 2)"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<!-- 運算符也可以在OGNL變量表達式本身中應⽤(這種情況下由OGNL解析執⾏,⽽不是Thymeleaf標準表達式引擎來解析執⾏) -->
<p><span>(x * 5 + 8 div y) mod (x - y) :</span><span th:text="${(x * 5 + 8 div y) mod (x - y)}"></span></p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<p>比較和等值運算符:>(gt)、<(lt)、>=(ge)、<=(le)、==(eq)、!=(ne)</p>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<p><span>x > 5:</span><span th:text="${x} > 5"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>y le 2:</span><span th:text="${y le 2}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>(x * y) < 50:</span><span th:text="${(x * y) < 50}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>y ge x:</span><span th:text="${y} ge ${x}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>x == y:</span><span th:text="${x == y}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>x ne y:</span><span th:text="${x} ne ${y}"></span></p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<p>佈爾運算符:and、or、!(not)</p>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<p><span>y lt x and -x gt -y:</span><span th:text="${y} lt ${x} and ${-x} gt ${-y}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>-x <= -y or y >= x:</span><span th:text="${-x <= -y or y >= x}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>!(x != y):</span><span th:text="${!(x != y)}"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>not (x eq y):</span><span th:text="${not (x eq y)}"></span></p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/operation")
public String operator(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("x", 10);
model.addAttribute("y", 3);
return "operation";
}
效果:
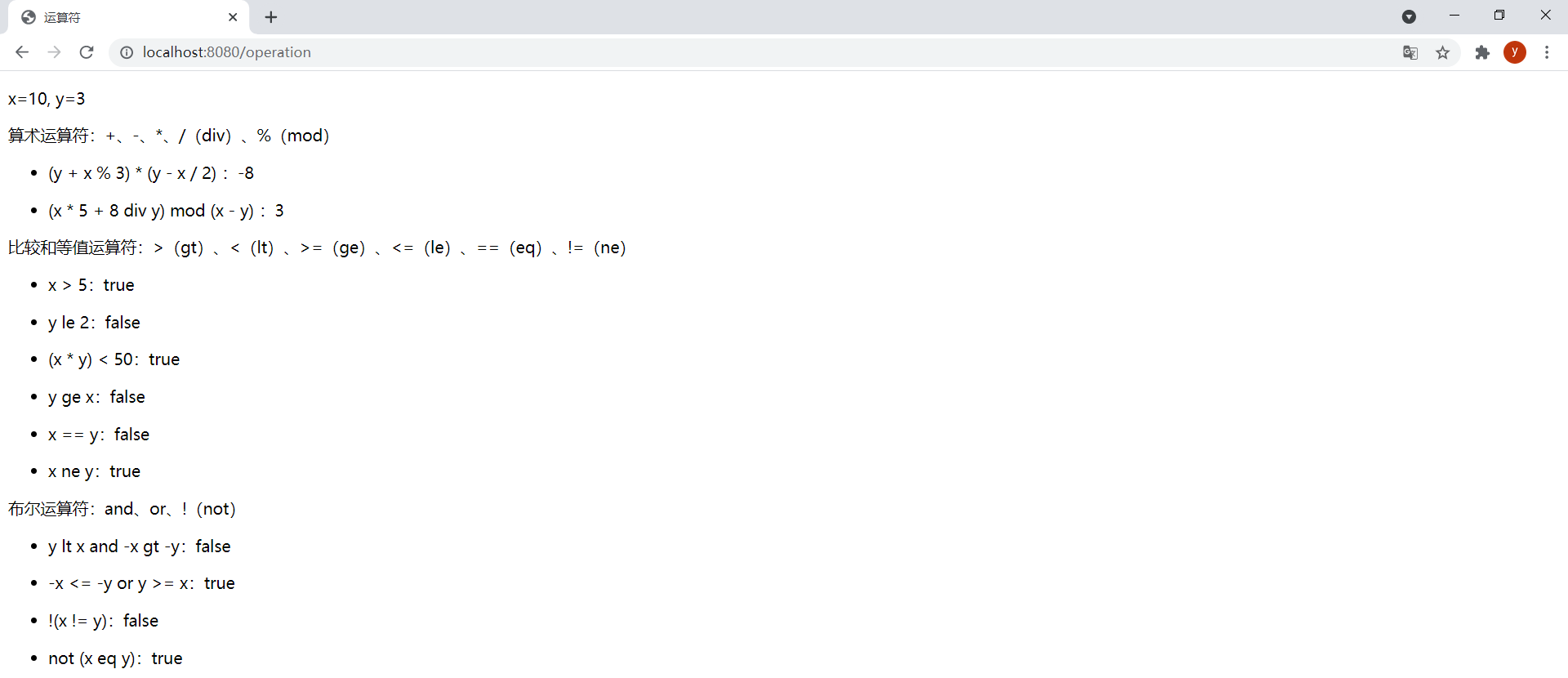
(7)條件表達式
條件表達式:
- If-then:
(if) ? (then)。if表達式結果為true,則條件表達式結果為then表達式結果,否則為null。 - If-then-else:
(if) ? (then) : (else)。if表達式結果為true,則條件表達式結果為then表達式結果,否則為else表達式結果。 - Default(默認表達式):
(value) ?: (defaultvalue)。value不為null,則結果為value,否則結果為defaultvalue。
模板conditional-expr.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>條件表達式、默認表達式、_符號</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="|grade: ${grade}, age: ${age}|"></p>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<!-- (if) ? (then) : (else) -->
<p><span>成績是否及格:</span><span th:text="${grade >= 60} ? '及格' : '不及格'"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<!-- (if) ? (then),else表達式可以省略,在這種情況下,如果條件為false,則返回null值 -->
<p><span>成績是否是正常數據:</span><span th:text="${grade >= 0 and grade <= 100} ? '正常數據'"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<!-- 條件表達式可以使⽤括號嵌套 -->
<p><span>成績對應的級別:</span><span th:text="${grade >= 0 and grade <= 100} ? (${grade >= 60} ? (${grade} >= 70 ? (${grade >= 90} ? '優' : '良') : '差') : '不及格') : '無效數據'"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<!-- 默認表達式 第一個表達式結果不為null,則結果使用第一個表達式的值,結果為null,則使用第二個表達式 -->
<p><span>年齡:</span><span th:text="${age} ?: '沒有年齡數據'"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<p><span>默認表達式嵌套示例:</span><span th:text="${age} ?: (${grade} ?: '年齡和成績數據都不存在')"></span></p>
</li>
<li>
<!-- _符號指定表達式不處理任何結果,這允許開發⼈員使⽤原型⽂本作為默認值 -->
<p><span>年齡:</span><span th:text="${age} ?: _">沒有年齡數據</span></p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/conditional/expr")
public String conditionExpr(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("grade", 85);
model.addAttribute("age", null);
return "conditional-expr";
}
效果:
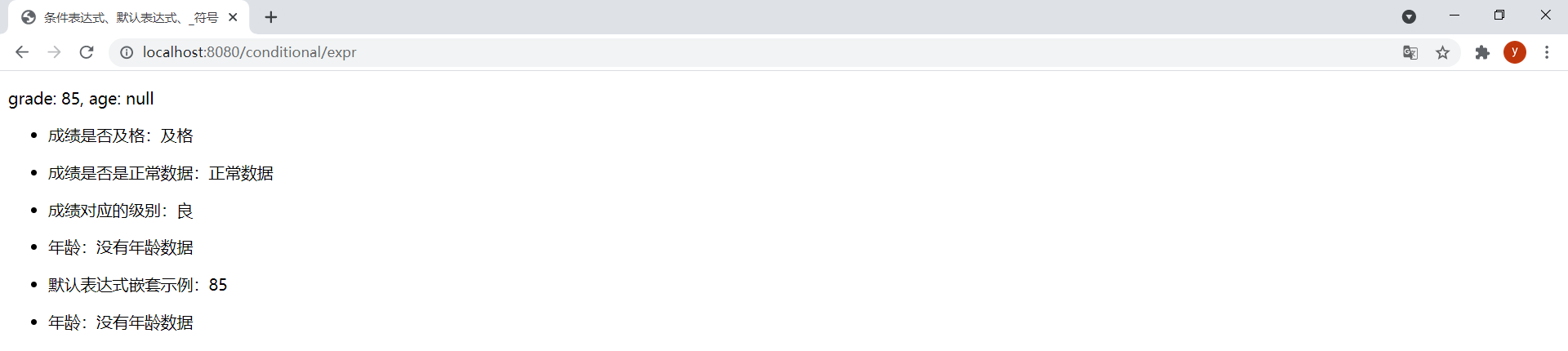
grade設置為-1,age設置為20。效果如下:

2.設置屬性
使用th:attr屬性可以設置標簽的任何屬性值,th:attr隻需要通過一個表達式將值賦給對應的屬性,並且還可以通過,分隔的形式設置多個屬性值。不過使用th:attr設置屬性不太優雅,所以用的不多,一般使用其他th:*屬性的形式設置指定屬性,例如要設置value屬性,可以使用th:value,要設置action屬性,可以使用th:action,要設置href屬性,可以使用th:href,具體都有哪些屬性可以這樣設置可以參考官方文檔。
th:attrprepend和th:attrappend可以給屬性設置前綴和後綴。Thymeleaf標準方言中還有兩個特定的附加屬性th:classappend和th:styleappend,用於將CSS的class或style樣式追加到元素中,而不覆蓋現有屬性。
HTML中有佈爾屬性這個概念,佈爾屬性沒有值,並且一旦這個佈爾屬性存在則意味著屬性值為true。但是在XHTML中,這些屬性隻取它本身作為屬性值。例如checked屬性。Thymeleaf標準方言允許通過計算條件表達式的結果來設置這些屬性的值,如果條件表達式結果為true,則該屬性將被設置為其固定值,如果評估為false,則不會設置該屬性。
Thymeleaf支持使用HTML5自定義屬性語法data-{prefix}-{name}來處理模板,這不需要使用任何命名空間。Thymeleaf使這種語法自動適用於所有的方言(不僅僅是標準的方法)。
模板attr.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>設置屬性</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>設置單個任何屬性:<input type="submit" value="提交" th:attr="value=${success}"></p>
<!-- th:attr可以以逗號分隔的形式來設置多個屬性值 -->
<p>設置多個任何屬性:<input type="submit" value="提交" th:attr="value=${success},class='btn btn-primary'"></p>
<p>設置單個指定屬性:<input type="submit" value="提交" th:value="${success}"></p>
<p>設置多個指定屬性:<input type="submit" value="提交" th:value="${success}" th:class="'btn btn-primary'"></p>
<!-- th:attrappend設置後綴 -->
<p>設置屬性後綴:<input type="submit" value="提交" th:attrappend="value=${' ' + success}"></p>
<!-- th:attrprepend設置前綴 -->
<p>設置屬性前綴:<input type="submit" value="提交" th:attrprepend="value=${success + ' '}"></p>
<!-- th:classappend追加class樣式 -->
<p>追加class樣式:<input type="submit" value="提交" class='btn btn-primary' th:classappend="'btn-warning'"></p>
<!-- th:styleappend追加style樣式 -->
<p>追加style樣式:<input type="submit" value="提交" style="text-align: left" th:styleappend="'color: green'"></p>
<!-- 如果條件表達式結果為true,則該屬性將被設置為其固定值,如果結果為false,則不會設置該屬性 -->
<p>設置佈爾屬性checked:<input type="checkbox" name="active" th:checked="${active}"></p>
<!--
data-{prefix}-{name}語法是在HTML5中編寫⾃定義屬性的標準⽅式,不需要使⽤任何命名空間
Thymeleaf使這種語法自動適用於所有的方言(不僅僅是標準的方法)
-->
<p>使用HTML5自定義屬性語法來處理模版:<span data-th-text="${success}"></span></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/attr")
public String attr(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("success", "成功");
model.addAttribute("active", true);
return "attr";
}
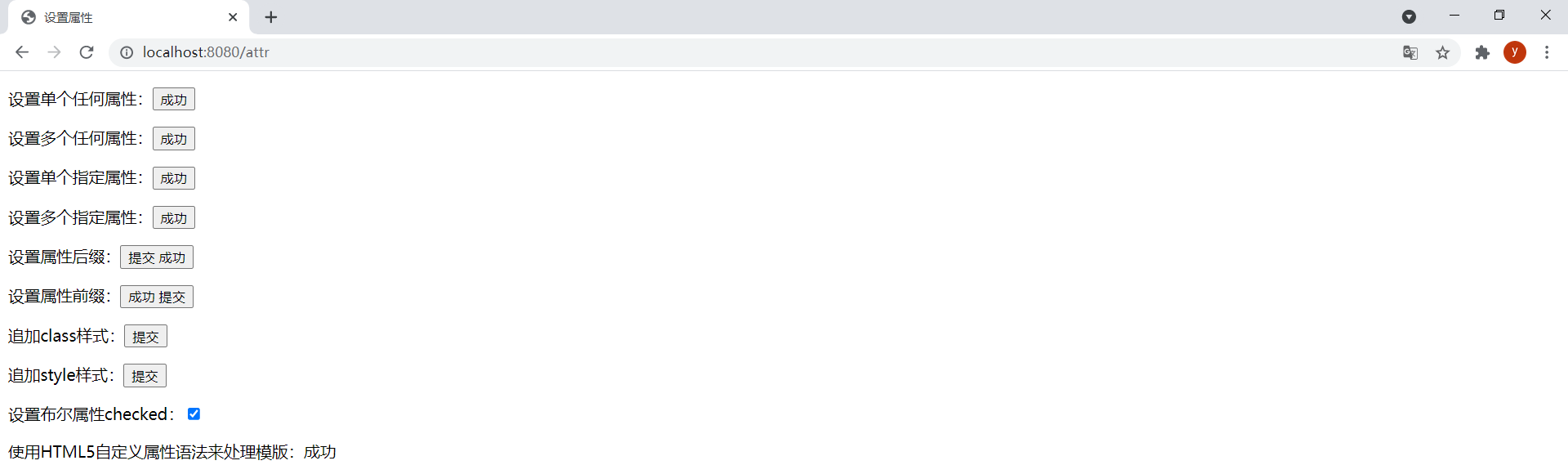
效果:
f12查看源碼可見屬性設置成功:
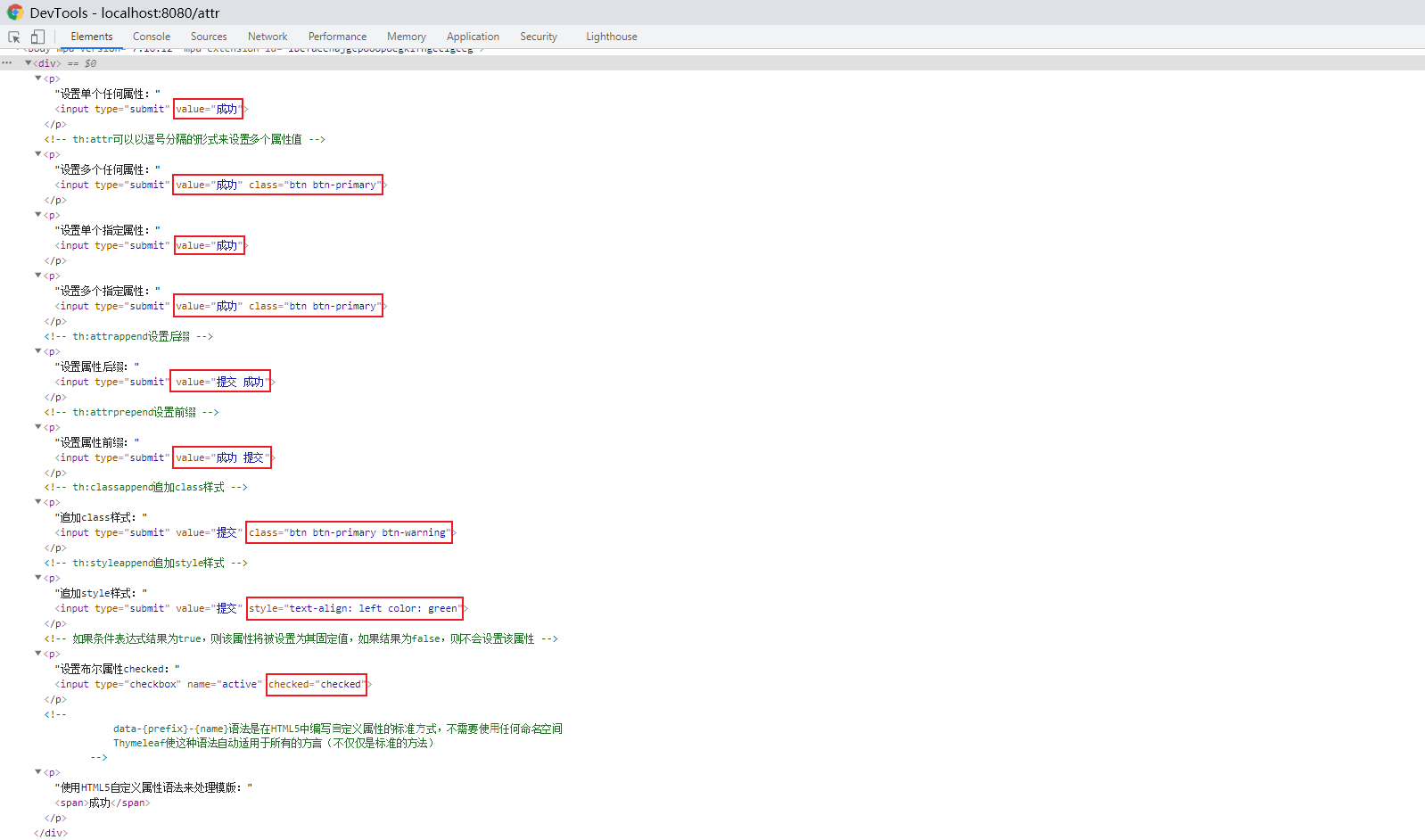
active設置為false。checkbox沒有選中,查看源碼也沒有設置checked屬性:

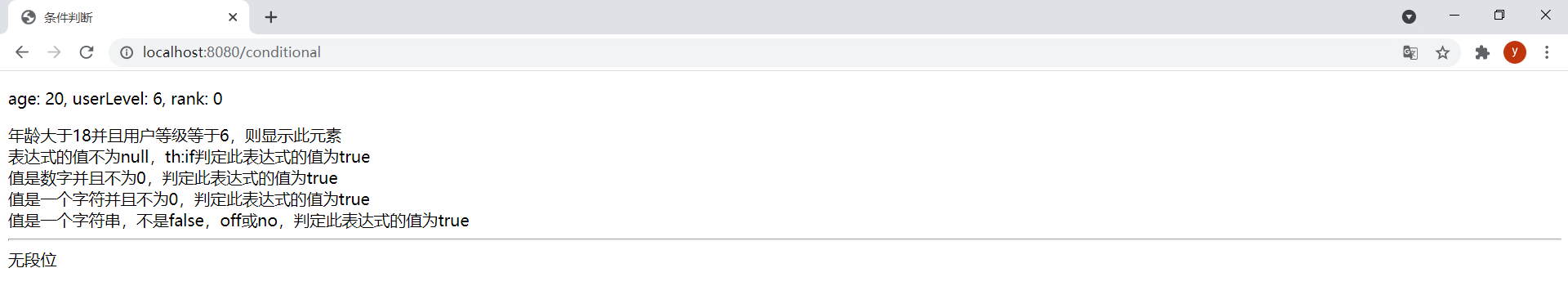
3.條件判斷
th:if屬性可以通過判斷一個條件是否滿足,來決定是否將模板片段顯示在結果中,隻有滿足條件才將模板片段顯示在結果中。而th:unless屬性則正好與th:if屬性相反。通過th:switch和th:case可以在模板中使用一種與Java中的Swicth語句等效的結構有條件地顯示模板內容。
模板conditional.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>條件判斷</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="|age: ${age}, userLevel: ${userLevel}, rank: ${rank}|"></p>
<div th:if="${age} >= 18 and ${userLevel} eq 6">
<span>年齡大於18並且用戶等級等於6,則顯示此元素</span>
</div>
<div th:unless="!(${age} < 18 or ${userLevel} ne 6)">
<span>與if條件判斷相反,年齡小於18或用戶等級不等於6,則顯示此元素</span>
</div>
<div th:if="'null'">
<span>表達式的值不為null,th:if判定此表達式的值為true</span>
</div>
<div th:if="null">
<span>表達式的值為null,th:if判定此表達式的值為false</span>
</div>
<div th:if="${age}">
<span>值是數字並且不為0,判定此表達式的值為true</span>
</div>
<div th:if="0">
<span>值是數字但為0,判定此表達式的值為false</span>
</div>
<div th:if="A">
<span>值是一個字符並且不為0,判定此表達式的值為true</span>
</div>
<div th:if="'string'">
<span>值是一個字符串,不是false,off或no,判定此表達式的值為true</span>
</div>
<div th:if="'false'">
<span>值是字符串false,判定此表達式的值為false</span>
</div>
<div th:if="'off'">
<span>值是字符串off,判定此表達式的值為false</span>
</div>
<div th:if="'no'">
<span>值是字符串no,判定此表達式的值為false</span>
</div>
<hr/>
<div th:switch="${rank}">
<span th:case="1">青銅</span>
<span th:case="2">白銀</span>
<span th:case="3">黃金</span>
<span th:case="4">鉑金</span>
<span th:case="5">鉆石</span>
<span th:case="6">王者</span>
<span th:case="*">無段位</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
註意:
th:if屬性不僅僅以佈爾值作為判斷條件。它將按照以下規則判定指定的表達式值為true:如果表達式的值不為null。(如果表達式的值為null,
th:if判定此表達式的值為false。)
如果值為佈爾值,則為true。如果值是數字且不為0。
如果值是一個字符且不為0。如果值是一個字符串,不是”false”,“off”或”no”。
如果值不是佈爾值,數字,字符或字符串。
同一個Switch語句中隻要第一個
th:case的值為true,則其他的th:case屬性將被視為false。Switch語句的default選項指定為th:case=“*”。
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/conditional")
public String condition(Model model) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age", 10);
map.put("userLevel", 6);
map.put("rank", 5);
model.addAllAttributes(map);
return "conditional";
}
效果:
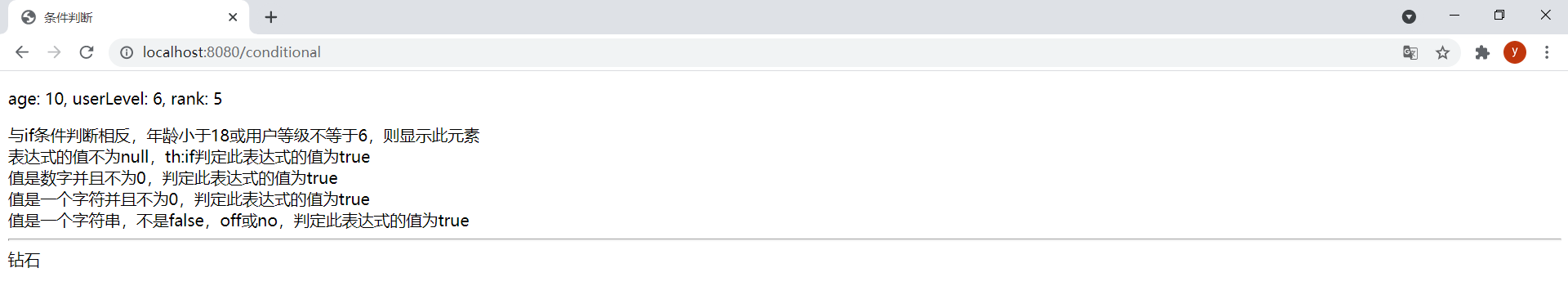
age設置為20,userLevel設置為6,rank設置為0。效果如下:
4.循環迭代
使用th:each屬性可以迭代以下對象:
- 任何實現
java.util.Iterable接口的對象。 - 任何實現
java.util.Enumeration接口的對象。 - 任何實現
java.util.Iterator接口的對象。其值將被迭代器返回,不需要在內存中緩存所有值。 - 任何實現
java.util.Map接口的對象。迭代map時,迭代變量將是java.util.Map.Entry類型。 - 任何數組。
- 任何其將被視為包含對象本身的單值列表。
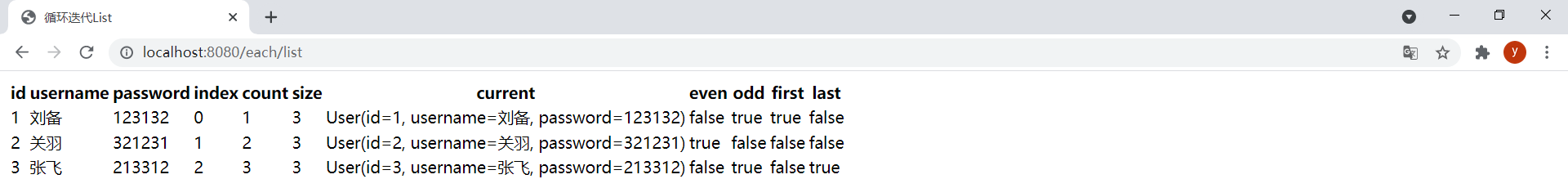
(1)迭代List
模板each-list.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>循環迭代List</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>password</th>
<th>index</th>
<th>count</th>
<th>size</th>
<th>current</th>
<th>even</th>
<th>odd</th>
<th>first</th>
<th>last</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- ${users}為迭代表達式或被迭代變量,userStat為狀態變量,user為迭代變量 -->
<tr th:each="user,userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.password}"></td>
<!-- 當前迭代索引,從0開始 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.index}"></td>
<!-- 當前迭代索引,從1開始 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.count}"></td>
<!-- 被迭代變量中元素總數 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.size}"></td>
<!-- 每次迭代的迭代變量 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.current}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是奇數,從0算起 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.even}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是偶數,從0算起 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.odd}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是第一個 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.first}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是最後一個 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.last}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
狀態變量是在使用
th:each時Thymeleaf提供的一種用於跟蹤迭代狀態的機制。狀態變量在th:each屬性中通過在迭代變量之後直接寫其名稱來定義,用,分隔。與迭代變量一樣,狀態變量的作用范圍也是th:each屬性所在標簽定義的代碼片段中。如果沒有顯式地設置狀態變量,Thymeleaf總是會創建一個名為迭代變量名加上Stat後綴的狀態變量。
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/each/list")
public String eachList(ModelMap model) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User(1L, "劉備", "123132"));
users.add(new User(2L, "關羽", "321231"));
users.add(new User(3L, "張飛", "213312"));
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "each-list";
}
效果:
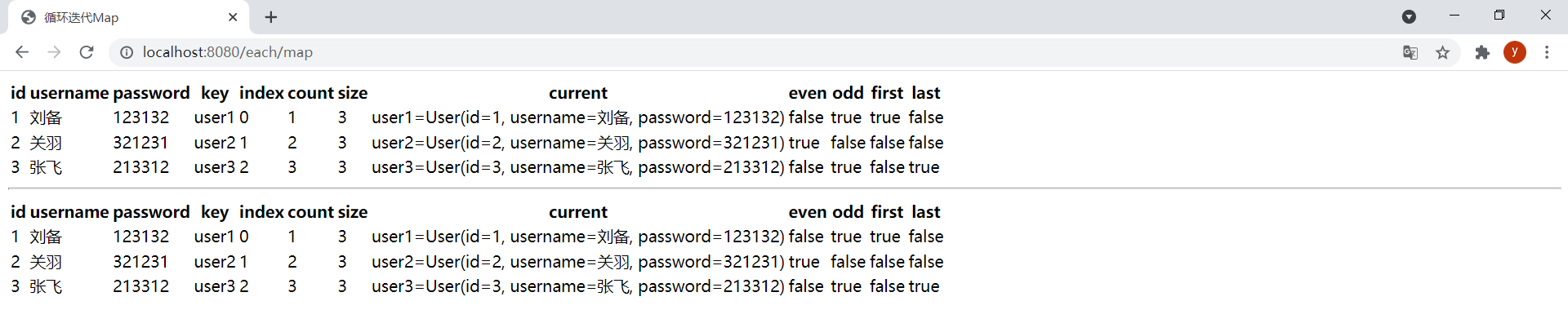
(2)迭代Map
模板each-map.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>循環迭代Map</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>password</th>
<th>key</th>
<th>index</th>
<th>count</th>
<th>size</th>
<th>current</th>
<th>even</th>
<th>odd</th>
<th>first</th>
<th>last</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="map,mapStat : ${userMap}">
<td th:text="${mapStat.current.value.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.current.value.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.current.value.password}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.current.key}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.size}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.current}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.even}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.odd}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.first}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.last}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<hr/>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>password</th>
<th>key</th>
<th>index</th>
<th>count</th>
<th>size</th>
<th>current</th>
<th>even</th>
<th>odd</th>
<th>first</th>
<th>last</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="map,mapStat : ${userMap}">
<td th:text="${map.value.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${map.value.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${map.value.password}"></td>
<td th:text="${map.key}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.size}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.current}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.even}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.odd}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.first}"></td>
<td th:text="${mapStat.last}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/each/map")
public String eachMap(Model model) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("user1", new User(1L, "劉備", "123132"));
map.put("user2", new User(2L, "關羽", "321231"));
map.put("user3", new User(3L, "張飛", "213312"));
model.addAttribute("userMap", map);
return "each-map";
}
效果:
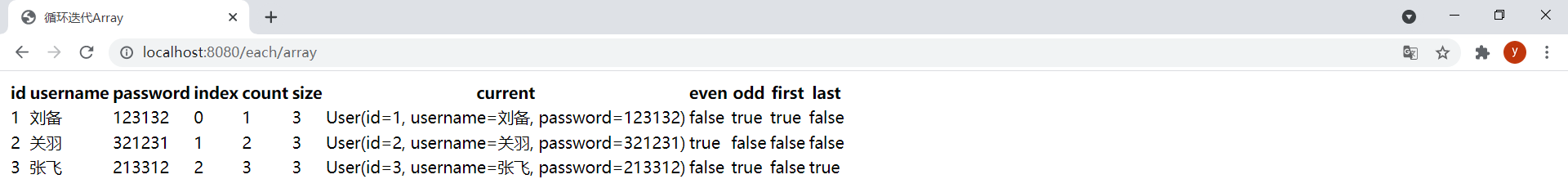
(3)迭代Array
模板each-array.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>循環迭代Array</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>username</th>
<th>password</th>
<th>index</th>
<th>count</th>
<th>size</th>
<th>current</th>
<th>even</th>
<th>odd</th>
<th>first</th>
<th>last</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- ${users}為迭代表達式或被迭代變量,userStat為狀態變量,user為迭代變量 -->
<tr th:each="user,userStat : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.password}"></td>
<!-- 當前迭代索引,從0開始 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.index}"></td>
<!-- 當前迭代索引,從1開始 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.count}"></td>
<!-- 被迭代變量中元素總數 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.size}"></td>
<!-- 每次迭代的迭代變量 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.current}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是奇數,從0算起 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.even}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是偶數,從0算起 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.odd}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是第一個 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.first}"></td>
<!-- 佈爾值,當前迭代是否是最後一個 -->
<td th:text="${userStat.last}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/each/array")
public String eachArray(Model model) {
User[] users = {new User(1L, "劉備", "123132"), new User(2L, "關羽", "321231"), new User(3L, "張飛", "213312")};
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "each-array";
}
效果:
5.模板佈局
(1)引用模板片段
th:fragment屬性可以用來定義模板片段,th:insert、th:replace和th:include(Thymeleaf3.0不再推薦使用)屬性可以引用模板片段。
首先創建一個名為footer.html的模板文件用來包含模板片段,然後定義一個名為copy1的片段:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>footer</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="copy1">
© 2021
</div>
</body>
</html>
然後在名為layout.html的模板中引用該片段:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>引用模板片段</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:insert="~{footer :: copy1}"></div>
<div th:replace="~{footer :: copy1}"></div>
<div th:include="~{footer :: copy1}"></div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/layout")
public String layout(Model model) {
return "layout";
}
效果:

引用模板片段語法中的~{}是可選的,以下代碼與之前的等價:
<div th:insert="footer :: copy1"></div> <div th:replace="footer :: copy1"></div> <div th:include="footer :: copy1"></div>
效果:
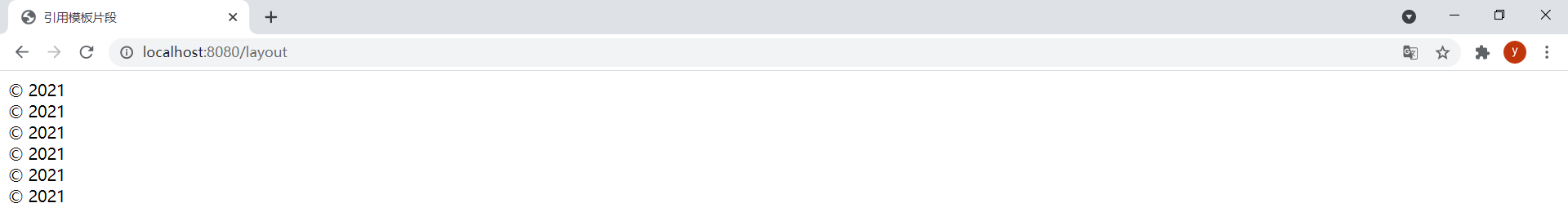
th:insert、th:replace和th:include都能引用模板片段,直接在頁面中還看不出三者的區別。為瞭更明顯地看出區別,在footer.html模板中新增以下片段:
<footer th:fragment="copy2" >
© 2020-2023
</footer>
然後在layout.html模板中分別使用th:insert、th:replace和th:include進行引用:
<div th:insert="footer :: copy2">th:insert將指定片段插⼊到指定宿主標簽的標簽體中</div> <div th:replace="footer :: copy2">th:replace實際上⽤指定的⽚段替換其宿主標簽</div> <div th:include="footer :: copy2">th:include隻插⼊此⽚段的內容到指定宿主標簽的標簽體中</div>
效果:
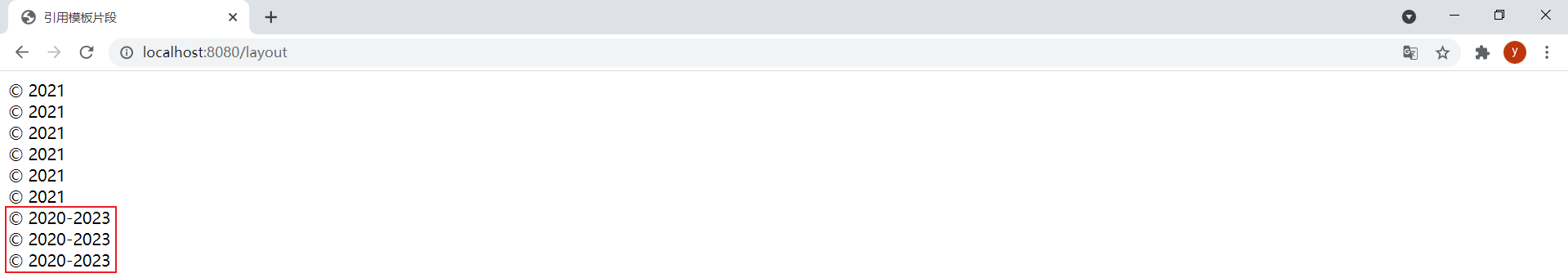
按F12查看源碼可以看出區別:

所以三者區別為:
th:insert將指定片段插入到指定宿主標簽的標簽體中。th:replace實際上用指定的片段替換其宿主標簽。th:include隻插入此片段的內容到指定宿主標簽的標簽體中。
引用模板片段的規范語法有以下三種格式:
~{templatename::selector}:包含在名為templatename的模板上通過指定的selector匹配的片段。selector可以隻是一個片段名稱。~{templatename}:包含名為templatename的整個模板。~{::selector}或~{this::selector}:包含在同一模板中與指定selector匹配的片段。如果在表達式出現的模板上沒有找到,模板調用(插入)的堆棧會向最初處理的模板(root)遍歷,直到selector在某個層次上匹配。
templatename和selector都可以是表達式。模板片段中可以包含任何th:*屬性,一旦在目標模板中引用瞭片段,這些屬性將被計算並且它們能夠引用目標模板中定義的任何上下文變量。
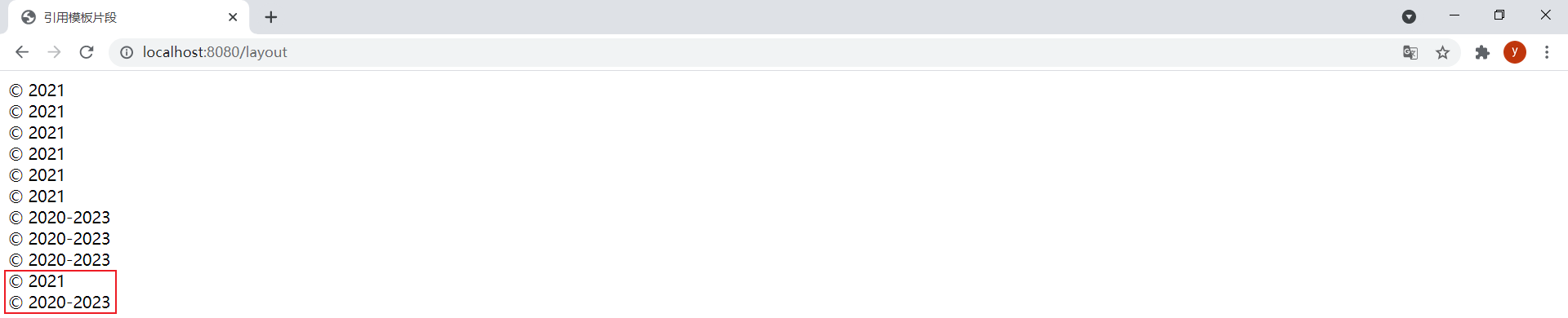
通過th:replace="~{footer}"可以引用整個footer.html:
<div th:replace="~{footer}">引用名為footer的整個模板</div>
效果:
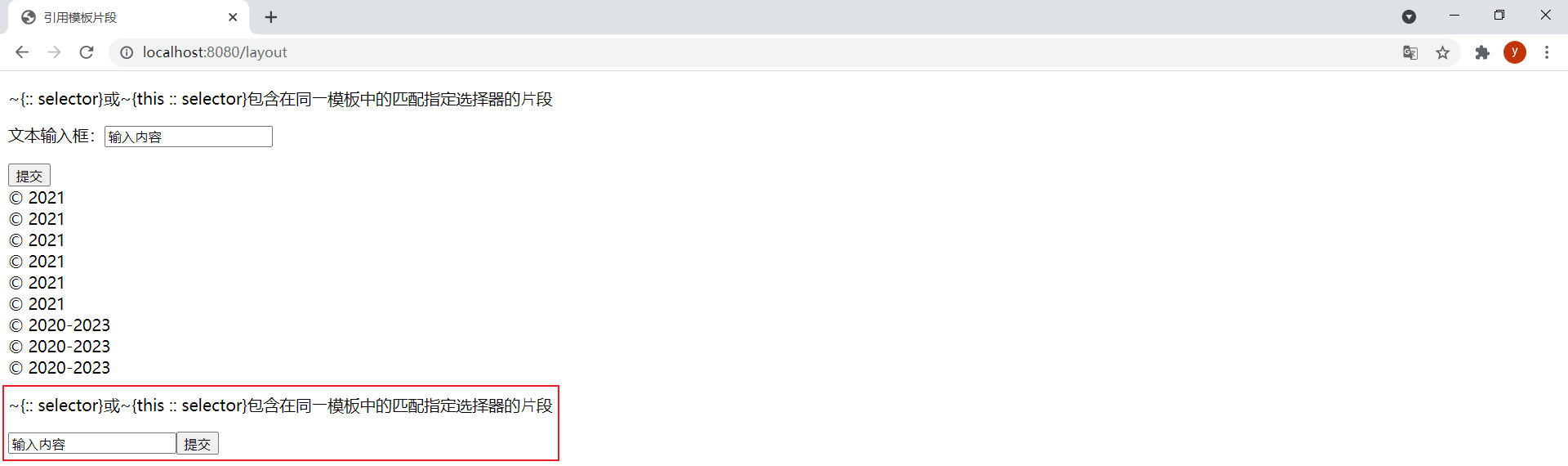
在layout.html模板中新增以下幾個片段:
<div th:fragment="frag">
<p>~{:: selector}或~{this :: selector}包含在同⼀模板中的匹配指定選擇器的⽚段</p>
</div>
<div>
<p>文本輸入框:<input type="text" value="輸入內容"></p>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
在layout.html模板中引用frag和input片段:
<div th:insert="~{:: frag}">引用當前模板中的片段</div>
<div th:insert="~{this :: input}">引用當前模板中的片段</div>
效果:
selector寫成一個條件表達式,可以通過條件來決定引用的片段:
<div th:insert="~{footer :: (${flag} ? copy1 : copy2)}">模板名和選擇器都可以是表達式</div>
將變量flag設置到Model中:
model.addAttribute("flag", true);
效果:
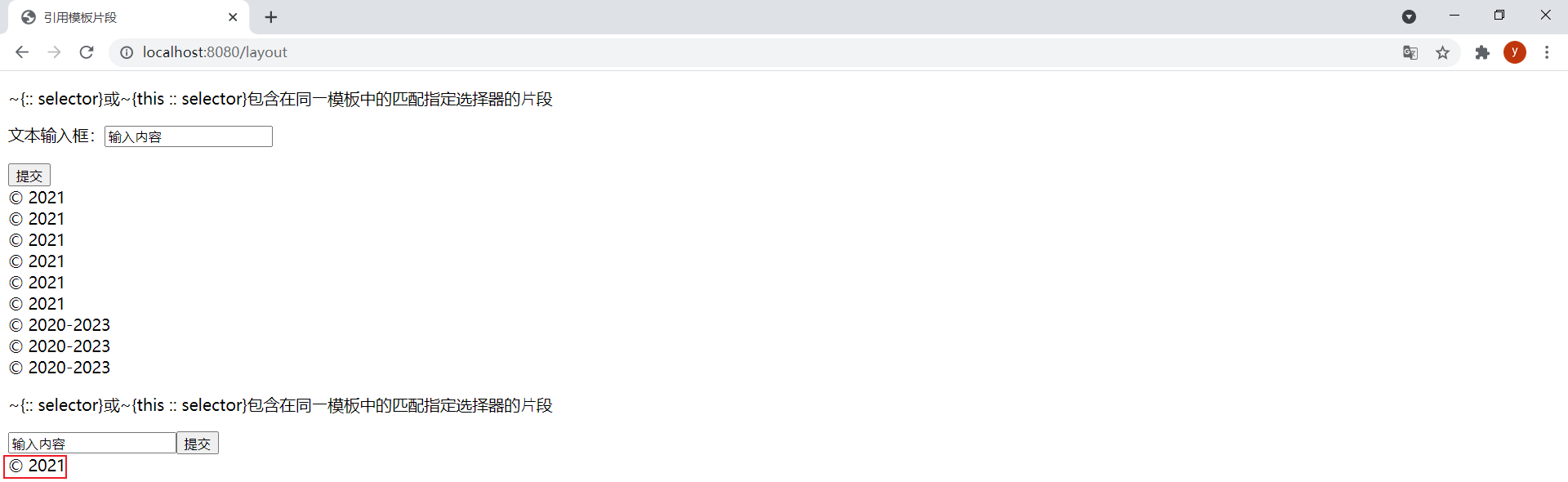
flag設置為fasle時的效果:

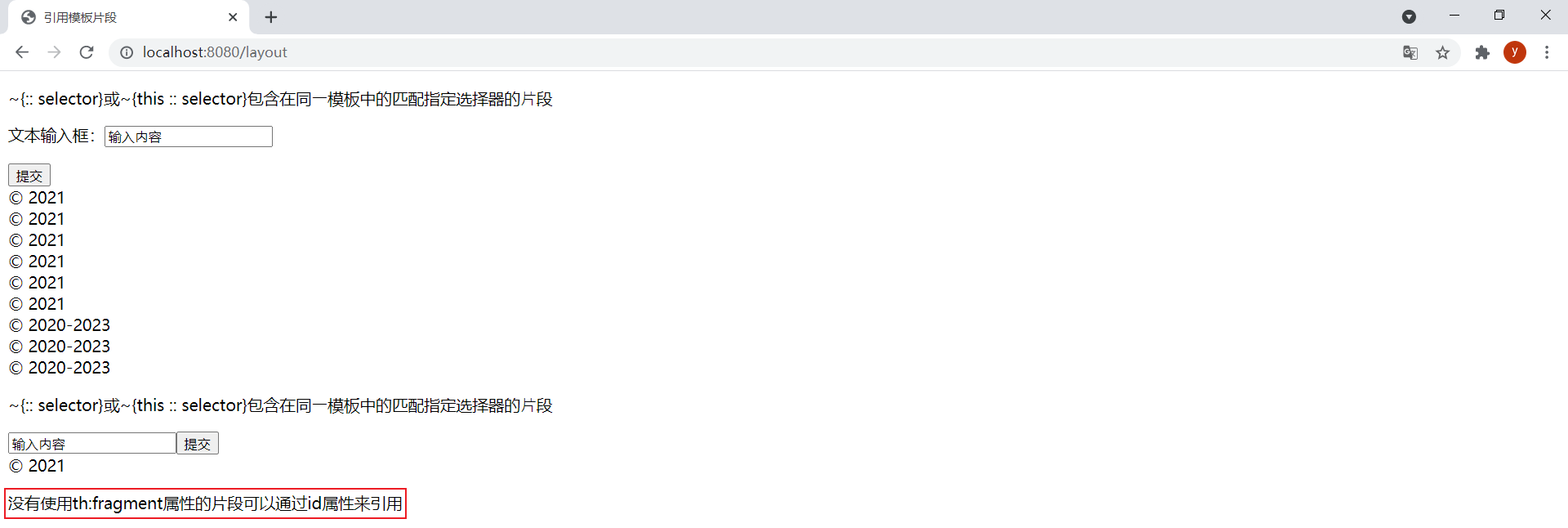
由於標簽選擇器的強大功能,沒有使用th:fragment屬性的片段可以通過id屬性來引用。在footer.html模板中新增以下片段:
<div id="copy-section">
<p>沒有使用th:fragment屬性的片段可以通過id屬性來引用</p>
</div>
在layout.html模板中引用該片段:
<div th:insert="~{footer :: #copy-section}">可以通過id屬性來引⽤沒有th:fragment屬性的⽚段</div>
效果:
(2)參數化的模板片段
th:fragment定義的片段可以指定一組參數。在footer.html模板中新增以下片段:
<div th:fragment="frag (var1,var2)">
<p th:text="${var1} + ' - ' + ${var2}">th:fragment定義的⽚段可以指定⼀組參數</p>
</div>
在layout.html模板中分別用以下兩種語法引用該片段:
<!-- 引用定義瞭參數的模板片段的兩種語法 -->
<div th:insert="footer :: frag (${var1},${var2})">引用定義瞭參數的模板片段語法1</div>
<div th:insert="footer :: frag (var1=${var1},var2=${var2})">引用定義瞭參數的模板片段語法2,可以改變參數順序</div>
將變量var1和var2設置到Model中:
model.addAttribute("var1", "參數1");
model.addAttribute("var2", "參數2");
效果:

即使片段沒有定義參數,也可以調用片段中的局部變量。在footer.html模板中新增以下片段:
<div th:fragment="frag2">
<p th:text="${var1} + ' * ' + ${var2}">沒有定義參數的模板片段</p>
</div>
在layout.html模板中分別通過以下語法調用片段中的局部變量:
<!-- 沒有定義參數的模板片段中的局部變量,可以使用以下語法調用,以下兩種寫法等價 -->
<div th:insert="footer :: frag2 (var1=${var1},var2=${var2})">沒有定義參數的模板片段中的局部變量的調用語法1</div>
<div th:insert="footer :: frag2" th:with="var1=${var1},var2=${var2}">沒有定義參數的模板片段中的局部變量的調用語法2</div>
引用定義參數的模板片段的兩種語法中,第一種語法不能調用沒有定義參數的片段中的局部變量,隻有第二種語法能調用。
註意:片段的局部變量規范 – 無論是否具有參數簽名 – 都不會導致上下文在執行前被清空。片段仍然能訪問調用模板中正在使用的每個上下文變量。
效果:

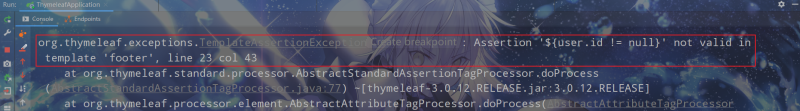
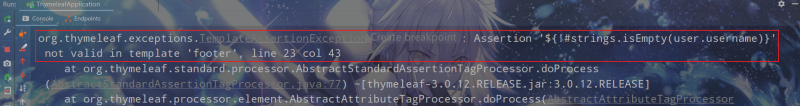
使用th:assert可以進行模板內部斷言,它可以指定逗號分隔的表達式列表,如果每個表達式的結果都為true,則正確執行,否則引發異常。在footer.html模板中新增以下片段:
<div th:fragment="assert-test (user)" th:assert="${user.id != null},${!#strings.isEmpty(user.username)},${!#strings.isEmpty(user.password)}">
<p th:text="${#strings.toString(user)}">⽤th:assert進⾏模版內部斷⾔ </p>
</div>
在layout.html模板中引用該片段:
<!-- 引用帶有斷言的模板片段 -->
<div th:insert="footer :: assert-test (${user})"></div>
將變量user設置到Model中:
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "趙雲", "qwe123"));
效果:

隻將id設置為null,訪問模板出現以下異常:
隻將username設置為空,訪問模板出現以下異常:
隻將password設置為空,訪問模板出現以下異常:

(3)靈活佈局
通過片段表達式不僅可以指定文本類型、數字類型、對象類型的參數,還可以指定標記片段作為參數。這種方式可以使模板佈局變得非常靈活。
下面進行一個頁面佈局的簡單模擬測試,首先在templates下新建一個layout目錄,用於存放一些組件模板。
layout/footer.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>footer</title>
</head>
<body>
<footer th:fragment="footer">
<h1>模板佈局頁面頁腳</h1>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
layout/header.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>header</title>
</head>
<body>
<header th:fragment="header">
<h1>模板佈局頁面頭部</h1>
</header>
</body>
</html>
layout/left.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>left</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="left">
<h1>模板佈局頁面左側菜單</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
在templates下新建一個基礎模板base.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:fragment="common_header (title)">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title th:replace="${title}">common title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="common_div (header,left,footer)">
<div th:replace="${header}"><h1>common header</h1></div>
<div th:replace="${left}"><h1>common left</h1></div>
<p>common content</p>
<div th:replace="${footer}"><h1>common footer</h1></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
然後在名為layout-home.html的模板中引用base.html中的片段:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head th:replace="base :: common_header(~{:: title})">
<title>模板佈局主頁</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:replace="base :: common_div (~{layout/header :: header},~{layout/left :: left},~{layout/footer :: footer})"></div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/layout/home")
public String layoutHome(Model model) {
return "layout-home";
}
效果:
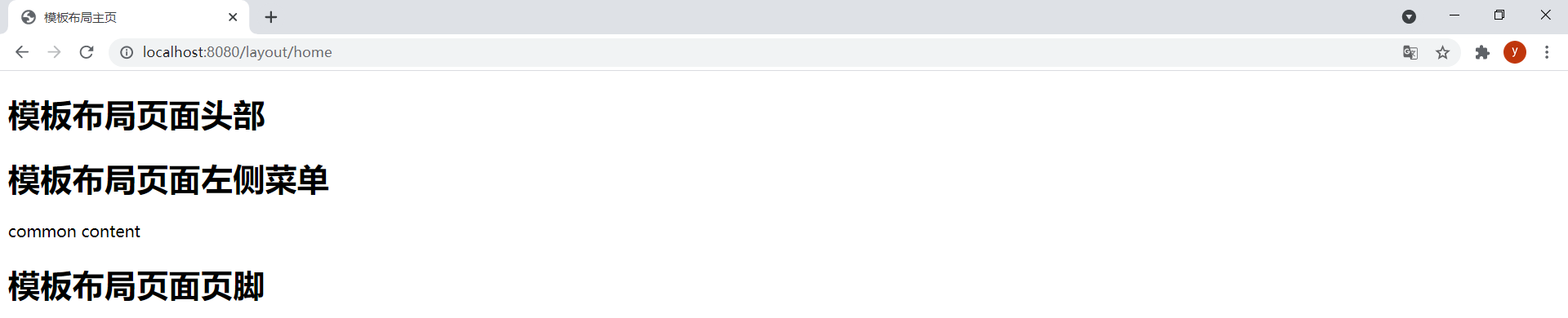
使用特殊片段表達式~{}可以指定沒有標記。在layout-home.html中通過以下代碼引用base.html中的片段:
<div th:replace="base :: common_div (~{layout/header :: header},~{layout/left :: left},~{})"></div>
效果:

_符號也可以用作片段參數。在layout-home.html中通過以下代碼引用base.html中的片段:
<div th:replace="base :: common_div (~{layout/header :: header},~{layout/left :: left},_)"></div>
_符號導致common_div片段中的th:replace="${footer}"不被執行,從而該div標簽使用原型文本。
效果:
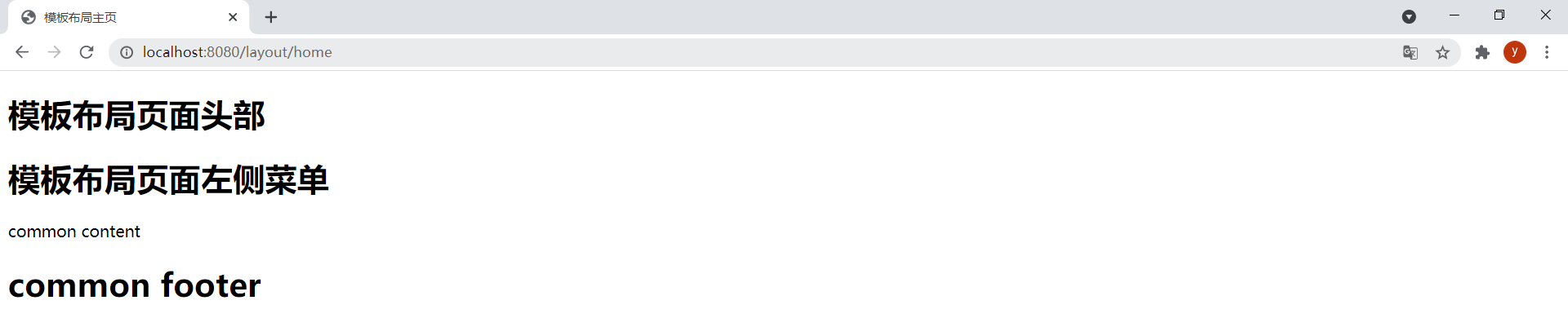
~{}和_符號可以通過簡單優雅的方式實現執行片段的條件插入。在layout-home.html中通過以下代碼引用base.html中的片段:
<div th:replace="base :: common_div (${condition} ? ~{layout/header :: header} : ~{},${condition} ? ~{layout/left :: left} : ~{},${condition} ? ~{layout/footer :: footer} : ~{})"></div>
參數中的每一個
condition條件可以根據實際業務需求靈活控制。這裡為瞭測試方便,都使用的相同條件。
將變量condition設置到Model中:
model.addAttribute("condition", false);
效果:

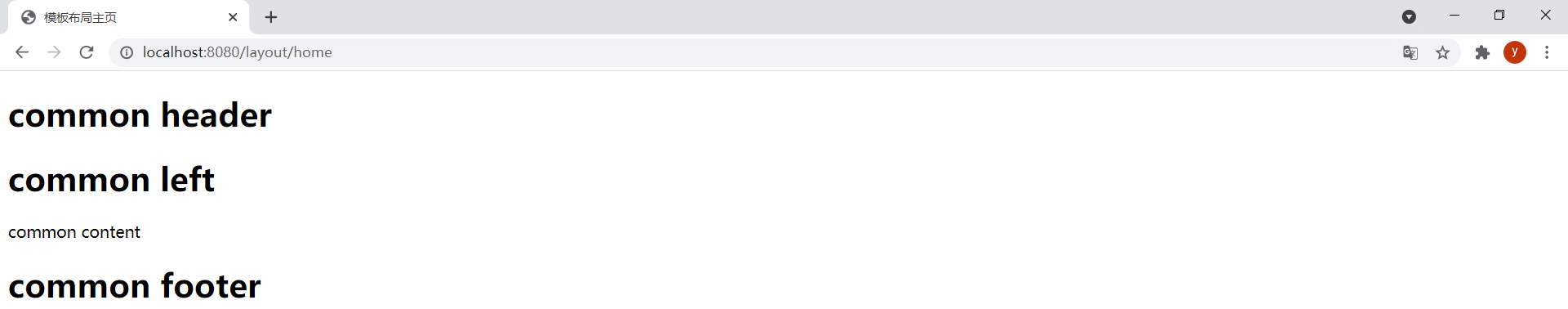
在layout-home.html中通過以下代碼引用base.html中的片段:
<div th:replace="base :: common_div (${condition} ? ~{layout/header :: header} : _,${condition} ? ~{layout/left :: left} : _,${condition} ? ~{layout/footer :: footer} : _)"></div>
效果:
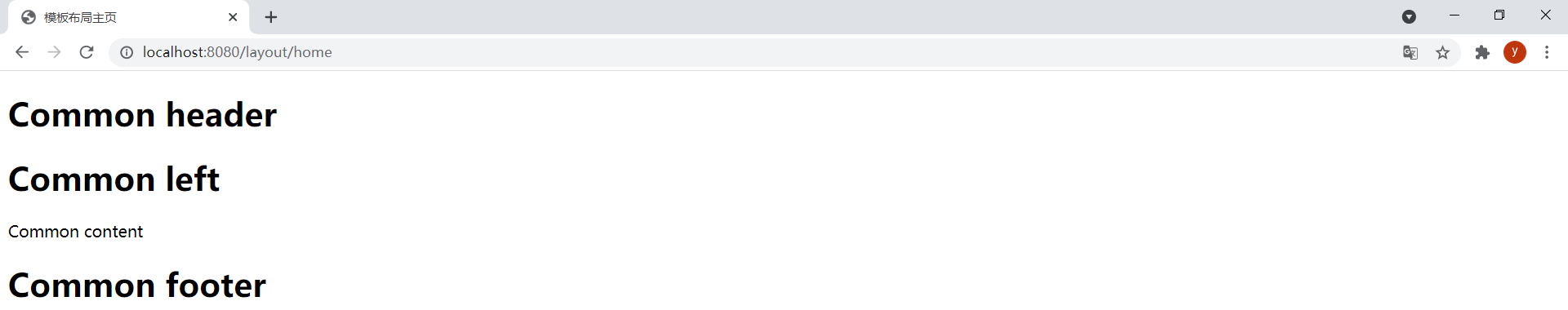
條件也可以不在參數中進行判斷,還在common_div片段的th:replace屬性中進行判斷。在layout-home.html中通過以下代碼引用base.html中的片段:
<div th:replace="base :: common_div (~{layout/header :: header},~{layout/left :: left},~{layout/footer :: footer},${condition})"></div>
base.html中的common_div片段:
<div th:fragment="common_div (header,left,footer,condition)">
<div th:replace="${condition} ? ${header} : _"><h1>Common header</h1></div>
<div th:replace="${condition} ? ${left}: _"><h1>Common left</h1></div>
<p>Common content</p>
<div th:replace="${condition} ? ${footer}: _"><h1>Common footer</h1></div>
</div>
效果:
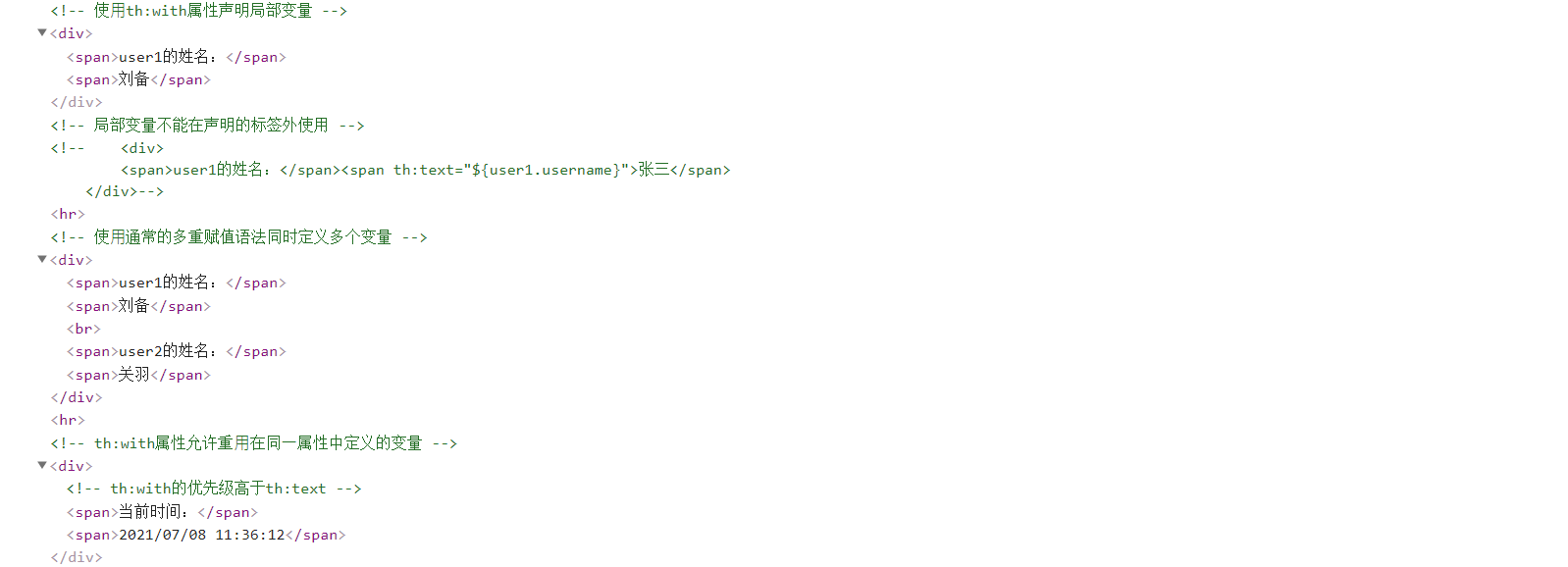
6.局部變量
Thymeleaf的局部變量是指定義在模板片段中的變量,該變量的作用域為所在模板片段。th:each中的迭代變量就是一個局部變量,作用域為th:each所在的標簽范圍,可用於該標簽內優先級低於th:each的任何其他th:*屬性,可用於該標簽的任何子元素。使用th:with屬性可以聲明局部變量。
在local.html模板中使⽤th:with屬性聲明局部變量:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>局部變量</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 使⽤th:with屬性聲明局部變量 -->
<div th:with="user1=${users[0]}">
<span>user1的姓名:</span><span th:text="${user1.username}"></span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/local")
public String local(Model model) {
User[] users = {new User(1L, "劉備", "123132"), new User(2L, "關羽", "321231"), new User(3L, "張飛", "213312")};
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "local";
}
效果:

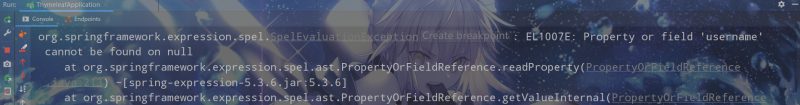
局部變量隻能在聲明的標簽內使用。在local.html模板中新增以下內容:
<!-- 局部變量不能在聲明的標簽外使用 -->
<div>
<span>user1的姓名:</span><span th:text="${user1.username}">張三</span>
</div>
訪問模板會報錯:
可以同時定義多個局部變量。在local.html模板中新增以下內容:
<!-- 使⽤通常的多重賦值語法同時定義多個變量 -->
<div th:with="user1=${users[0]},user2=${users[1]}">
<span>user1的姓名:</span><span th:text="${user1.username}"></span>
<br/>
<span>user2的姓名:</span><span th:text="${user2.username}"></span>
</div>
效果:

th:with屬性允許重⽤在同⼀屬性中定義的變量。在local.html模板中新增以下內容:
<!-- th:with屬性允許重⽤在同⼀屬性中定義的變量 -->
<div>
<!-- th:with的優先級高於th:text -->
<span>當前時間:</span><span th:with="now=${#calendars.createNow()}" th:text="${#calendars.format(now, 'yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss')}"></span>
</div>
效果:

7.屬性優先級
多個th:*屬性在同一個標簽中的執行順序由優先級決定。所有Thymeleaf屬性都定義瞭一個數字優先級,以確定瞭它們在標簽中執行的順序,數字越小優先級越高:
| Order | Feature | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fragment inclusion | th:insert th:replace |
| 2 | Fragment iteration | th:each |
| 3 | Conditional evaluation | th:if th:unless th:switch th:case |
| 4 | Local variable definition | th:object th:with |
| 5 | General attribute modification | th:attr th:attrprepend th:attrappend |
| 6 | Specific attribute modification | th:value th:href th:src ... |
| 7 | Text (tag body modification) | th:text th:utext |
| 8 | Fragment specification | th:fragment |
| 9 | Fragment removal | th:remove |
優先級意味著屬性位置發生變化,也會得出相同的結果。
8.註釋和塊
(1)標準HTML/XML註釋
標準HTML/XML註釋<!-- -->可以在Thymeleaf模板中的任何地方使用。這些註釋中的任何內容都不會被Thymeleaf處理,並將逐字復制到結果中。
這裡直接運行項目訪問local.html模板,查看模板源碼可見HTML註釋沒有被處理,保持原樣:
(2)ThymeLeaf解析器級註釋
解析器級註釋塊<!--/* */-->在Thymeleaf解析時會將<!--/和*/-->之間的所有內容從模板中刪除。當此模板靜態打開時,這些註釋塊可用於顯示代碼。
修改local.html模板的其中一個註釋為如下內容:
<!--/* <div>
<span>user1的姓名:</span><span th:text="${user1.username}">張三</span>
</div>*/-->
查看源碼可見註釋已從模板中刪除:

(3)Thymeleaf專有註釋
Thymeleaf允許定義特殊註釋塊<!--/*/ /*/-->,在Thymeleaf解析時會將<!--/*/和/*/-->標記刪除,但不刪除標記之間的內容。當此模板靜態打開時,會顯示註釋標記。
修改local.html模板的其中一個註釋為如下內容:
<!--/*/ <div th:with="user1=${users[0]}">
<span>user1的姓名:</span><span th:text="${user1.username}"></span>
</div>/*/-->
查看源碼發現隻刪除瞭標記部分,中間的內容保留:

(4)th:block標簽
th:block標簽是Thymeleaf標準方言中唯一的元素處理器。th:block是一個允許模板開發者指定想要的任何屬性的屬性容器,Thymeleaf會執行這些屬性並讓這個塊消失,但它的內容保留。
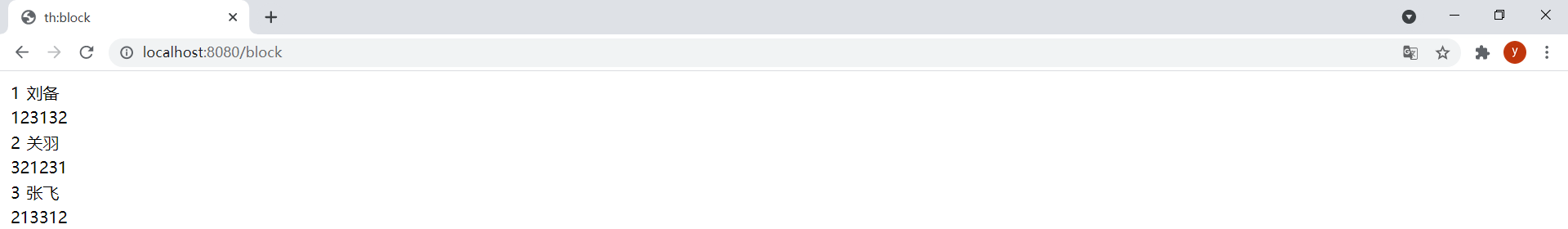
模板block.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>th:block</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<th:block th:each="user : ${users}">
<tr>
<td th:text="${user.id}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">root</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" th:text="${user.password}">root</td>
</tr>
</th:block>
</table>
</body>
</html>
使用
th:block可以輕松地迭代同級標簽,例如在<table>中為每個迭代元素創建多個<tr>時使用th:block就很簡單。
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/block")
public String block(Model model) {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User(1L, "劉備", "123132"));
users.add(new User(2L, "關羽", "321231"));
users.add(new User(3L, "張飛", "213312"));
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "block";
}
效果:
查看源碼:

在和原型註釋塊結合時很有用:
<table>
<!--/*/ <th:block th:each="user : ${users}"> /*/-->
<tr>
<td th:text="${user.id}">1</td>
<td th:text="${user.username}">root</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" th:text="${user.password}">root</td>
</tr>
<!--/*/ </th:block> /*/-->
</table>
效果:

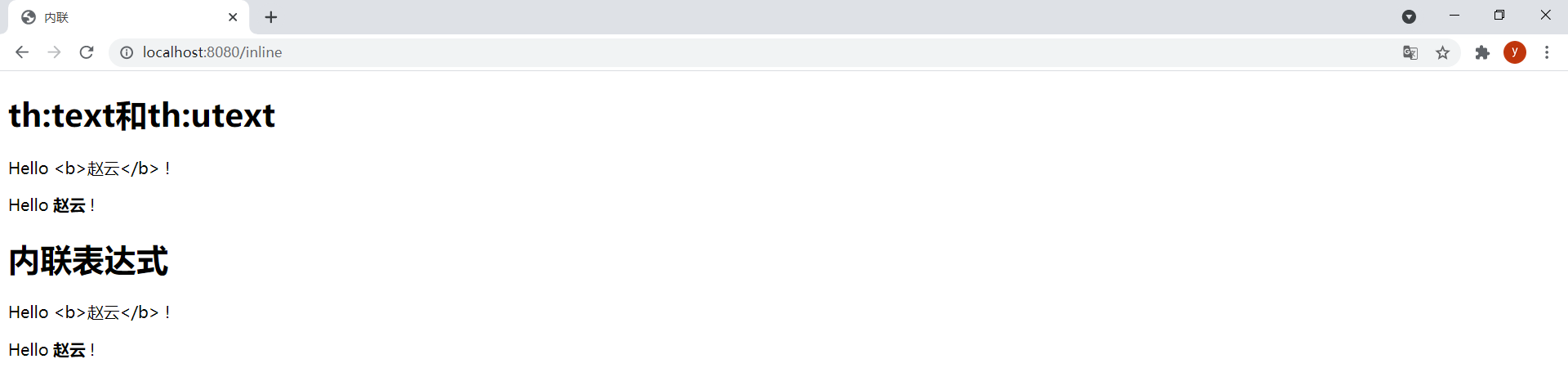
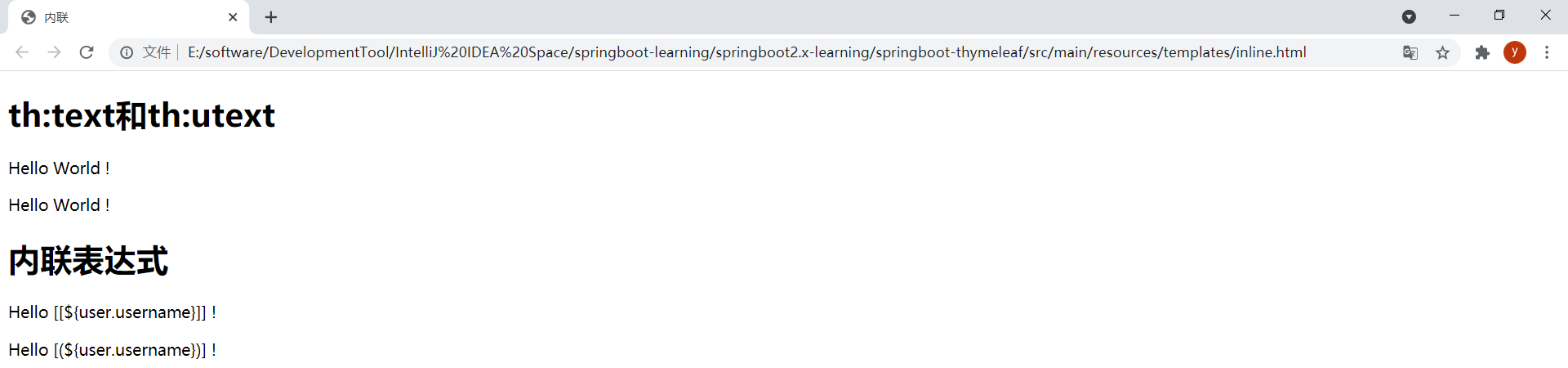
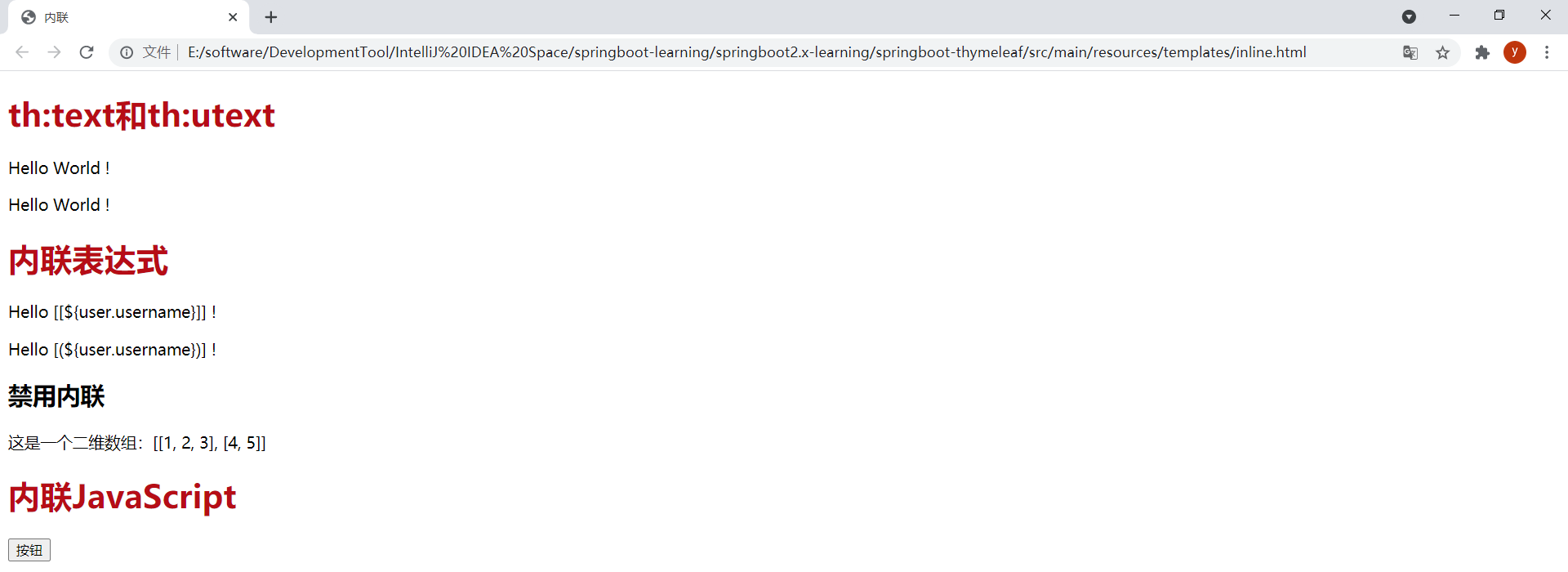
9.內聯 (1)內聯表達式
[[]]或[()]中的表達式為內聯表達式,可以直接將表達式寫入HTML文本。任何在th:text或th:utext屬性中使用的表達式都可以出現在[[]]或[()]中。[[]]等價於th:text,會轉義html標簽;[()]等價於th:utext,不會轉義html標簽。
模板inline.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>內聯</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>th:text和th:utext</h1>
<p>Hello <span th:text="${user.username}">World</span> !</p>
<p>Hello <span th:utext="${user.username}">World</span> !</p>
<h1>內聯表達式</h1>
<!-- 會轉義html標簽,等價於th:text -->
<p>Hello [[${user.username}]] !</p>
<!-- 不會轉義html標簽,等價於th:utext -->
<p>Hello [(${user.username})] !</p>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/inline")
public String inline(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "<b>趙雲</b>", "this is \"pass\" word"));
return "inline";
}
效果:
註意,靜態打開模板文件時,內聯表達式會顯示出來,這樣就無法將其作為原型設計瞭。靜態打開inline.html模板的效果如下:
在有些情況下可能需要禁用內聯,比如需要輸出[[]]序列時。通過th:inline="none"可以禁用內聯。在模板inline.html中新增以下內容:
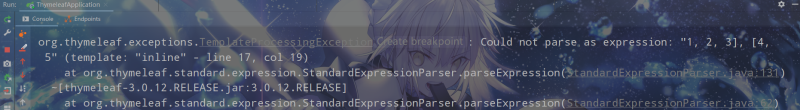
<p>這是一個二維數組:[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]</p>
訪問模板時會報如下錯誤:
在剛才的代碼中增加禁用內聯:
<h2>禁用內聯</h2> <p th:inline="none">這是一個二維數組:[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]</p>
效果:

(2)內聯JavaScript
使用th:inline="javascript"啟用內聯JavaScript。
在模板inline.html中新增以下內容:
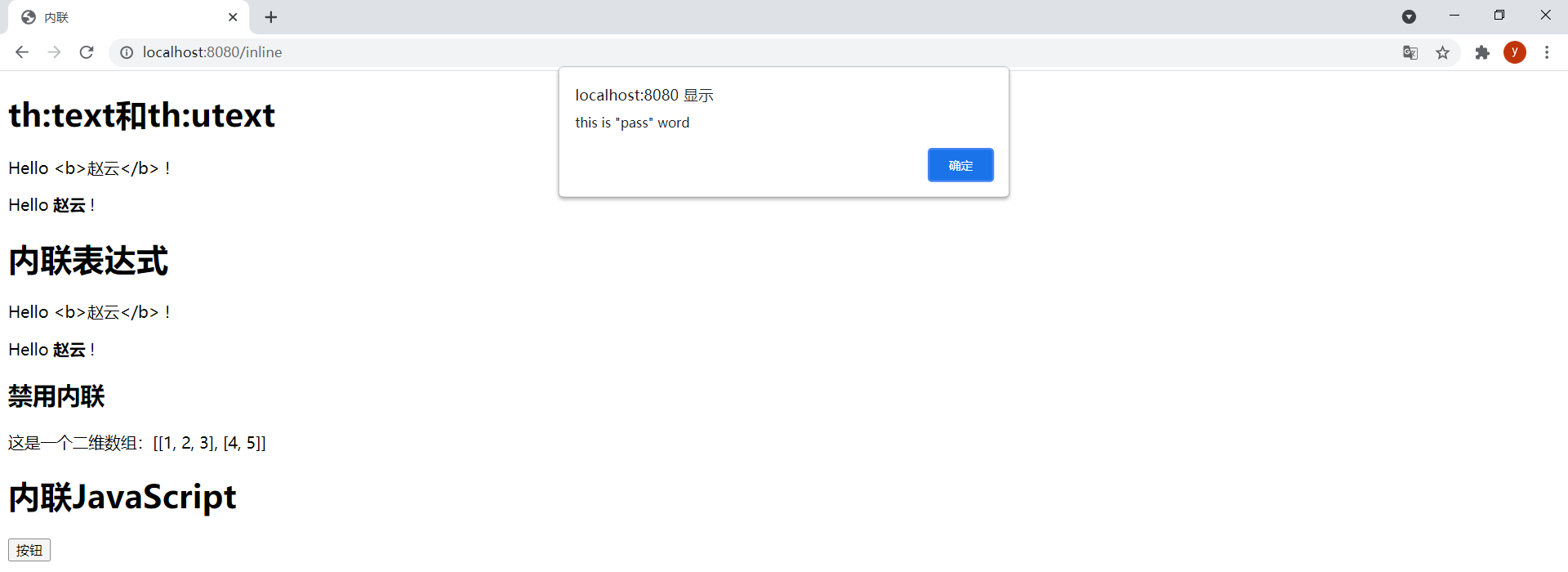
<h1>內聯JavaScript</h1>
<div>
<span><button onclick="showPassword()">按鈕</button></span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" th:inline="javascript">
let password = [[${user.password}]];
console.log("password:", password);
function showPassword() {
alert(password);
}
</script>
效果:
查看源碼,可見輸出的字符串進行瞭轉義,是格式正確的JavaScript字符串,因為使用[[]]在輸出${user.password}表達式的時候進行瞭轉義:

查看Console中打印的日志:

註釋掉let password = [[${user.password}]];,新增let password = [(${user.password})];。查看源碼,由於[()]不會進行轉義,可見輸出的字符串沒有轉義,是格式錯誤的JavaScript代碼:

查看Console,發現有語法錯誤:

如果通過附加內聯表達式的方式來構建腳本的一部分,可能會需要輸出未轉義的字符串,所以這個功能也很有用。
內聯JavaScript可以通過在註釋中包含內聯表達式作為JavaScript自然模板。下面註釋掉let password = [(${user.password})];,新增如下代碼:
// 在JavaScript註釋中包含(轉義)內聯表達式,Thymeleaf將忽略在註釋之後和分號之前的所有內容
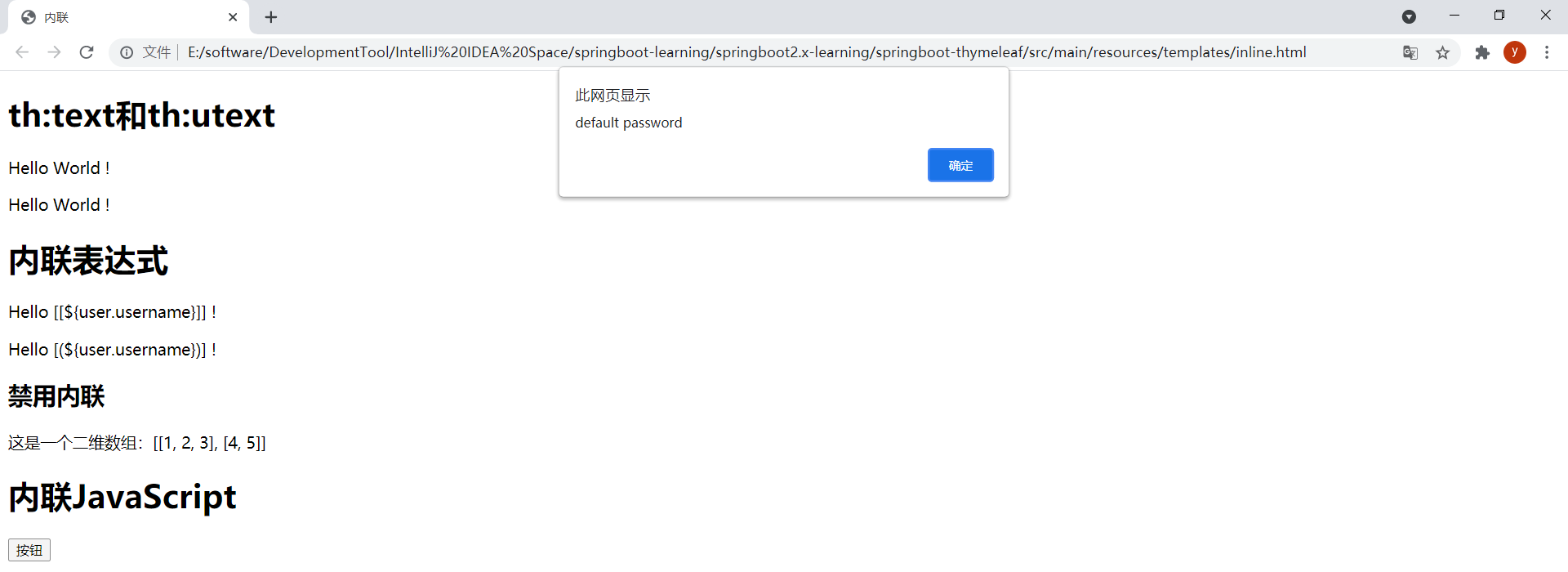
let password = /*[[${user.password}]]*/ "default password";
查看源碼:

查看Console中打印的日志:

發現"default password"確實被忽略瞭。以靜態方式打開模板時變量password的值就為"default password"瞭:


JavaScript內聯表達式結果不限於字符串,還會自動地將Strings、Numbers、Booleans、Arrays、Collections、Maps、Beans(有getter和setter方法)這些對象序列化為JavaScript對象。下面在Controller中新增以下代碼:
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("user1", new User(1L, "劉備", "123132"));
map.put("user2", new User(2L, "關羽", "321231"));
map.put("user3", new User(3L, "張飛", "213312"));
model.addAttribute("userMap", map);
script標簽內新增以下代碼,Thymeleaf會將userMap對象轉換為JavaScript對象:
// userMap為一個Map對象,Thymeleaf會將其轉換為JavaScript對象
let userMap = /*[[${userMap}]]*/ null;
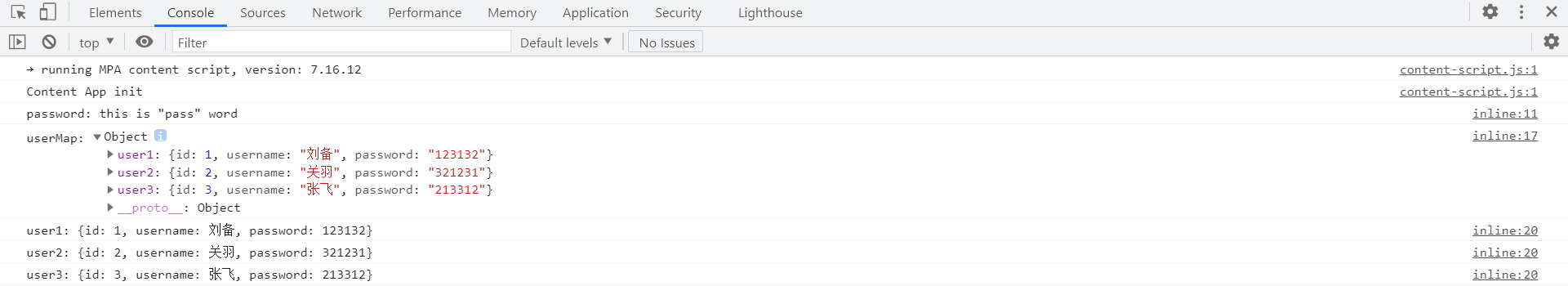
console.log("userMap:", userMap);
// 遍歷userMap
for (let key in userMap) {
console.log(key + ": " + "{id: " + userMap[key].id
+ ", username: " + userMap[key].username + ", password: " + userMap[key].password + "}");
}
查看源碼發現Thymeleaf已經將其轉換為JavaScript對象:
查看Console中打印的日志:
(3)內聯CSS
使用th:inline="css"啟用內聯CSS。
在模板inline.html中新增以下內容:
<style type="text/css" th:inline="css">
[[${element}]] {
text-align: [[${align}]];
color: [[${color}]];
}
</style>
將變量element、align和color設置到Model中:
model.addAttribute("element", "h1");
model.addAttribute("align", "center");
model.addAttribute("color", "#2876A7");
訪問模板,對齊生效,顏色未生效:

查看源碼,發現color的值多瞭一個\:

這是由於[[]]會進行轉義,所以多瞭一個\。這裡不需要對其轉義,所以需要使用[()]。將代碼修改為color: [(${color})];。訪問模板,發現樣式都生效瞭:
查看源碼,沒有多出\瞭:

內聯CSS也允許通過在註釋中包含內聯表達式作為CSS自然模板,使CSS可以靜態和動態的工作。將<style>的代碼修改為如下內容:
<style type="text/css" th:inline="css">
h1 {
text-align: /*[[${align}]]*/ left;
color: /*[(${color})]*/ #B60d16;
}
</style>
模板動態打開時的效果:
查看源碼:

以靜態方式打開的效果:
查看源碼:

10.國際化
這裡簡單模擬一下國際化功能,通過語言切換應用對應語言的國際化配置文件。
(1)創建國際化配置文件
在resources/i18n目錄下創建如下配置文件。
index.properties:
user.register=註冊 user.login=登錄 index.language=語言 index.language.chinese=中文 index.language.english=英文
index_en_US.properties:
user.register=Register user.login=Login index.language=Language index.language.chinese=Chinese index.language.english=English
index_zh_CN.properties:
user.register=註冊 user.login=登錄 index.language=語言 index.language.chinese=中文 index.language.english=英文
(2)新增配置
在application.yml中新增以下配置:
spring:
messages:
# 配置消息源的基本名稱,默認為messages,這裡配置為國際化配置文件的前綴
basename: i18n.index
(3)創建模板
模板i18n.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>國際化</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span><button th:text="#{user.register}">註冊</button></span>
<span><button th:text="#{user.login}">登錄</button></span>
<span th:text="#{index.language}">語言</span>
<a th:href="@{/index(lang='zn_CN')}" th:text="#{index.language.chinese}">中文</a>
<a th:href="@{/index(lang='en_US')}" th:text="#{index.language.english}">英文</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
#{}為消息表達式,用於引用消息字符串。而消息字符串通常保存在外部化文本中,消息字符串形式為key=value,通過#{key}可以引用特定的消息。而根據不同的語言從與其對應的外部化文本中獲取同一個key的消息,可以實現國際化。
(4)配置國際化解析器
package com.rtxtitanv.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import org.thymeleaf.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.util.Locale;
/**
* @author rtxtitanv
* @version 1.0.0
* @name com.rtxtitanv.config.WebConfig
* @description 配置自定義國際化解析器
* @date 2021/7/6 16:25
*/
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
/**
* 自定義LocaleResolver
*/
public static class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 接收語言參數
String lang = request.getParameter("lang");
// 使用默認語言
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
// 語言參數不為空就設置為該語言
if (!StringUtils.isEmptyOrWhitespace(lang)) {
String[] s = lang.split("_");
locale = new Locale(s[0], s[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {}
}
}
(5)Controller
@GetMapping(value = {"/index", "/"})
public String index() {
return "i18n";
}
(5)測試
訪問模板,默認語言為中文:

點擊英文鏈接切換語言為英文:

點擊中文鏈接切換語言為中文:

11.常用工具類對象
之前在文中已經簡單地總結瞭Thymeleaf中的工具類對象和它的作用。這裡結合實例來總結一下常用工具類對象具體方法的使用,由於工具類對象較多,這裡就總結Dates、Numbers和Strings的具體使用方法。至於其他對象的方法,可以參考官方文檔。
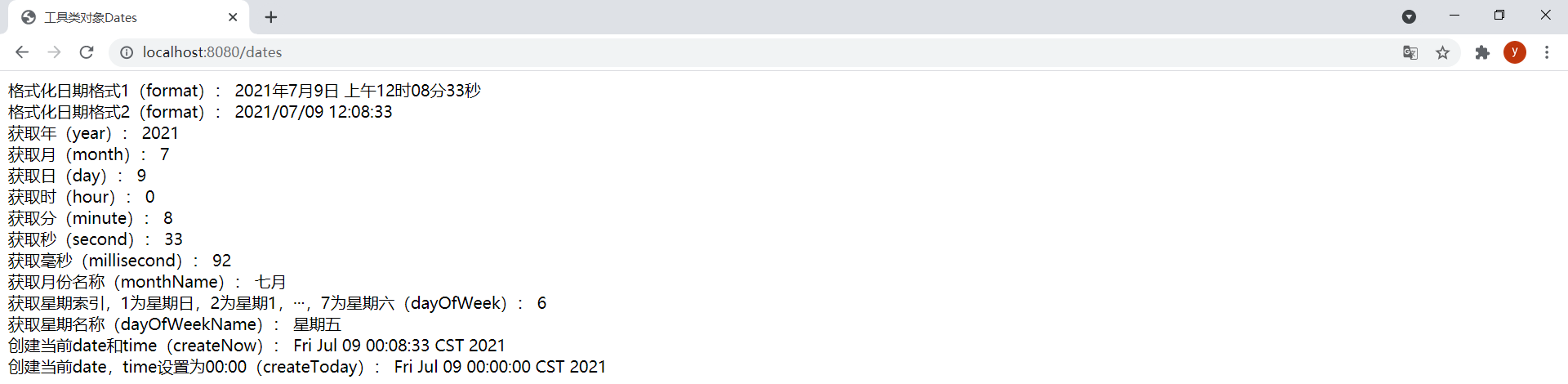
(1)Dates
模板date.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>工具類對象Dates</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>格式化日期格式1(format):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>格式化日期格式2(format):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date, 'yyyy/MM/dd hh:mm:ss')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取年(year):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.year(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取月(month):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.month(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取日(day):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.day(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取時(hour):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.hour(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取分(minute):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.minute(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取秒(second):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.second(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取毫秒(millisecond):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.millisecond(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取月份名稱(monthName):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.monthName(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取星期索引,1為星期日,2為星期1,···,7為星期六(dayOfWeek):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.dayOfWeek(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取星期名稱(dayOfWeekName):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.dayOfWeekName(date)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>創建當前date和time(createNow):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.createNow()}"></span>
<br/>
<span>創建當前date,time設置為00:00(createToday):</span>
<span th:text="${#dates.createToday()}"></span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/dates")
public String dates(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("date", new Date());
return "dates";
}
效果:
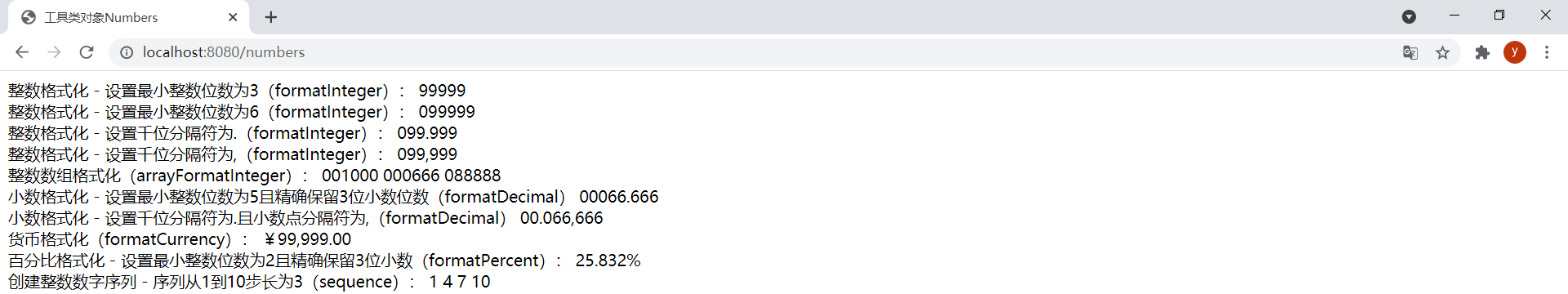
(2)Numbers
模板number.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>工具類對象Numbers</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>整數格式化 - 設置最小整數位數為3(formatInteger):</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger(num, 3)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>整數格式化 - 設置最小整數位數為6(formatInteger):</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger(num, 6)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>整數格式化 - 設置千位分隔符為.(formatInteger):</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger(num, 6, 'POINT')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>整數格式化 - 設置千位分隔符為,(formatInteger):</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatInteger(num, 6, 'COMMA')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>整數數組格式化(arrayFormatInteger):</span>
<span th:each="element:${#numbers.arrayFormatInteger(nums, 6)}">[[${element}]] </span>
<br/>
<span>小數格式化 - 設置最小整數位數為5且精確保留3位小數位數(formatDecimal)</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal(num2, 5, 3)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>小數格式化 - 設置千位分隔符為.且小數點分隔符為,(formatDecimal)</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal(num2, 5, 'POINT', 3, 'COMMA')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>貨幣格式化(formatCurrency):</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatCurrency(num)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>百分比格式化 - 設置最小整數位數為2且精確保留3位小數(formatPercent):</span>
<span th:text="${#numbers.formatPercent(0.25831694, 2, 3)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>創建整數數字序列 - 序列從1到10步長為3(sequence):</span>
<span th:each="n:${#numbers.sequence(1, 10, 3)}">[[${n}]] </span>
<br/>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/numbers")
public String numbers(Model model) {
Integer[] numArray = {1000, 666, 88888};
model.addAttribute("num", 99999);
model.addAttribute("num2", 66.6658932);
model.addAttribute("nums", numArray);
return "numbers";
}
效果:
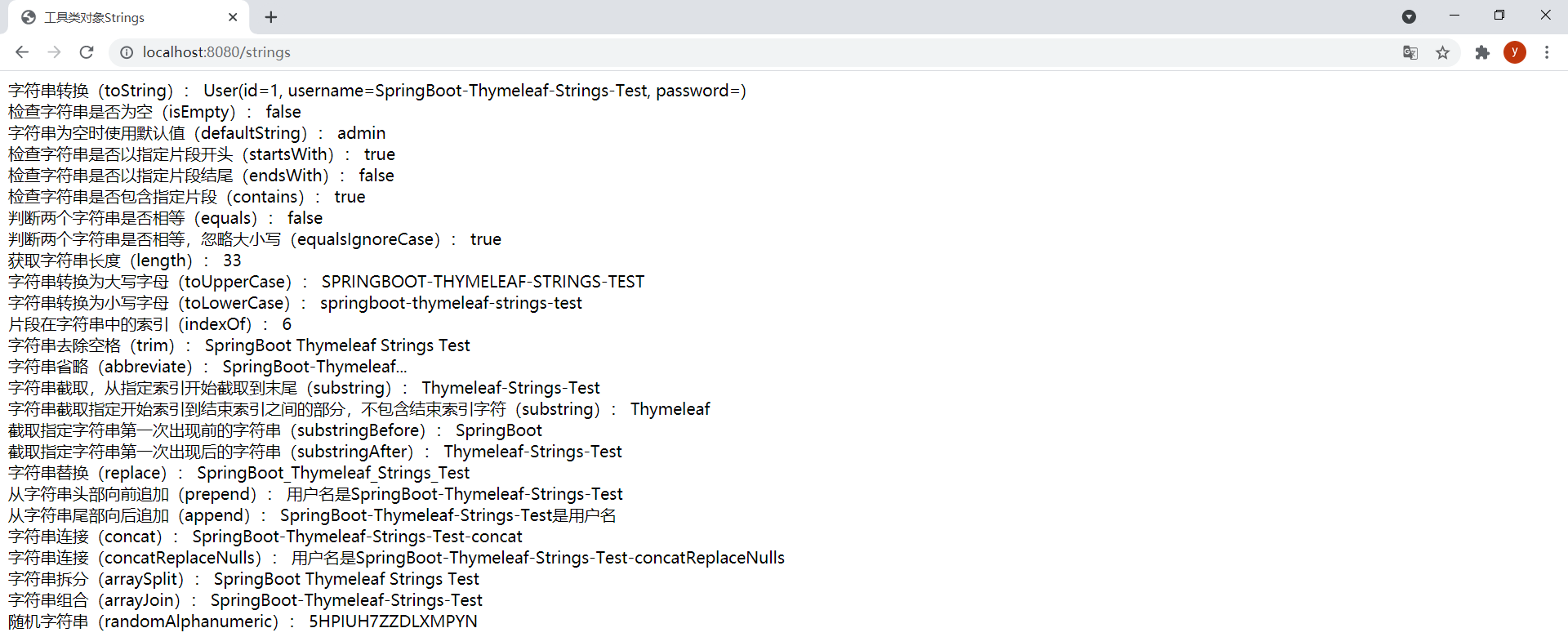
(3)Strings
模板strings.html如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>工具類對象Strings</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>字符串轉換(toString):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.toString(user)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>檢查字符串是否為空(isEmpty):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.isEmpty(user.username)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串為空時使用默認值(defaultString):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.defaultString(user.password, 'admin')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>檢查字符串是否以指定片段開頭(startsWith):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.startsWith(user.username, 'Spring')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>檢查字符串是否以指定片段結尾(endsWith):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.endsWith(user.username, 'test')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>檢查字符串是否包含指定片段(contains):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.contains(user.username, 'Thymeleaf')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>判斷兩個字符串是否相等(equals):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.equals(user.username, str)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>判斷兩個字符串是否相等,忽略大小寫(equalsIgnoreCase):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.equalsIgnoreCase(user.username, 'springboot-thymeleaf-strings-test')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>獲取字符串長度(length):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.length(user.username)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串轉換為大寫字母(toUpperCase):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.toUpperCase(user.username)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串轉換為小寫字母(toLowerCase):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.toLowerCase(user.username)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>片段在字符串中的索引(indexOf):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.indexOf(user.username, 'Boot')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串去除空格(trim):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.trim(str)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串省略(abbreviate):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.abbreviate(user.username, 23)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串截取,從指定索引開始截取到末尾(substring):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.substring(user.username, 11)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串截取指定開始索引到結束索引之間的部分,不包含結束索引字符(substring):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.substring(user.username, 11, 20)}"></span>
<br/>
<span>截取指定字符串第一次出現前的字符串(substringBefore):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.substringBefore(user.username, '-')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>截取指定字符串第一次出現後的字符串(substringAfter):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.substringAfter(user.username, '-')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串替換(replace):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.replace(user.username, '-', '_')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>從字符串頭部向前追加(prepend):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.prepend(user.username, '用戶名是')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>從字符串尾部向後追加(append):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.append(user.username, '是用戶名')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串連接(concat):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.concat(user.username, '-concat')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串連接(concatReplaceNulls):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.concatReplaceNulls(user.username, '用戶名是', null, '-concatReplaceNulls')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>字符串拆分(arraySplit):</span>
<span th:each="element:${#strings.arraySplit(user.username, '-')}">[[${element}]] </span>
<br/>
<span>字符串組合(arrayJoin):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.arrayJoin(strs, '-')}"></span>
<br/>
<span>隨機字符串(randomAlphanumeric):</span>
<span th:text="${#strings.randomAlphanumeric(16)}"></span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
ThymeleafController中新增以下方法:
@GetMapping("/strings")
public String strings(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("user", new User(1L, "SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-Strings-Test", ""));
model.addAttribute("str", "SpringBoot Thymeleaf Strings Test");
model.addAttribute("strs", new String[] {"SpringBoot", "Thymeleaf", "Strings", "Test"});
return "strings";
}
效果:
代碼示例
Github:https://github.com/RtxTitanV/springboot-learning/tree/master/springboot2.x-learning/springboot-thymeleaf
Gitee:https://gitee.com/RtxTitanV/springboot-learning/tree/master/springboot2.x-learning/springboot-thymeleaf
到此這篇關於SpringBoot2.x 集成 Thymeleaf的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關SpringBoot2.x 集成 Thymeleaf內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- Java基礎之Thymeleaf的簡單使用
- 詳解Thymeleaf的三種循環遍歷方式
- Springboot+Thymeleaf+Jpa實現登錄功能(附源碼)
- thymeleaf實現前後端數據交換的示例詳解
- SpringBoot+MyBatis實現登錄案例