Go中使用加密算法的方法
哈希算法
md5
128bit,16字節
如:md5 (“hello world!”) = fc3ff98e8c6a0d3087d515c0473f8677 // 32位16進制數字
func Test(t *testing.T) {
//方法一
str := "hello world!"
has := md5.Sum([]byte(str))
md5str1 := fmt.Sprintf("%x", has) //將[]byte轉成16進制
t.Log(md5str1)
//方法二
w := md5.New()
io.WriteString(w, str)
md5str2 := fmt.Sprintf("%x", w.Sum(nil))
t.Log(md5str2)
}
SHA1
160bit,20字節
如:SHA1 (“hello world!”) = 430ce34d020724ed75a196dfc2ad67c77772d169 // 40位16進制數字
func Test(t *testing.T) {
str := "hello world!"
//產生一個散列值得方式是 sha1.New(),sha1.Write(bytes),然後 sha1.Sum([]byte{})。
h := sha1.New()
//寫入要處理的字節。
h.Write([]byte(str))
//SHA1 值經常以 16 進制輸出,例如在 git commit 中。
t.Log(hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)))
}
RIPEMD-160
160bit,20字節
如:RIPEMD-160 (“hello world!”) = dffd03137b3a333d5754813399a5f437acd694e5 // 40位16進制數字
func Test(t *testing.T) {
str := "hello world!"
h := ripemd160.New()
h.Write([]byte(str))
t.Log(hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)))
}
SHA256
256bit,32字節
如:SHA256 (“hello world!”) = 7509e5bda0c762d2bac7f90d758b5b2263fa01ccbc542ab5e3df163be08e6ca9 // 64位16進制數字
func Test(t *testing.T) {
str := "hello world!"
// 第一種調用方法
sum := sha256.Sum256([]byte(str))
t.Logf("%x\n", sum)
// 第二種調用方法
h := sha256.New()
io.WriteString(h,str)
t.Log(hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)))
}
SHA256實現原理
SHA-256算法輸⼊報⽂的最⼤⻓度不超過2^64 bit,輸⼊按512bit分組進⾏處理,產⽣的輸出是⼀個256bit的報⽂摘要。
SHA256算法包括以下⼏步:附加填充⽐特
對報⽂進⾏填充,使報⽂⻓度與448 模512 同餘(⻓度=448 mod512),填充的⽐特數范圍是1 到512,填充⽐特串的最⾼位為1,其餘位為0。就是先在報⽂後⾯加⼀個 1,再加很多個0,直到⻓度滿⾜mod512=448。為什麼是448,因為448+64=512。第⼆步會加上⼀個64bit的原始報⽂的 ⻓度信息。附加⻓度值
將⽤64bit 表示的初始報⽂(填充前)的位⻓度附加在步驟1的結果後(低位字節優先)初始化緩存
使⽤⼀個256bit 的緩存來存放該散列函數的中間及最終結果。該緩存表示為:
A=0x6A09E667
B=0xBB67AE85
C=0x3C6EF372
D=0xA54FF53A
E=0x510E527F
F=0x9B05688C
G=0x1F83D9AB
H=0x5BE0CD19處理512bit(16 個字)報⽂分組序列
該算法使⽤瞭六種基本邏輯函數,由64 步迭代運算組成。每步都以256bit 緩存ABCDEFGH 為輸⼊,然後更新緩存內容。每步使⽤⼀個32bit 常數值Kt 和⼀個32bit Wt。
SHA512
512bit,64字節
如:SHA512 (“hello world!”) = db9b1cd3262dee37756a09b9064973589847caa8e53d31a9d142ea2701b1b28abd97838bb9a27068ba305dc8d04a45a1fcf079de54d607666996b3cc54f6b67c // 128位16進制數字
func Test(t *testing.T) {
str := "hello world!"
// 第一種調用方法
sum := sha512.Sum512([]byte(str))
t.Logf("%x\n", sum)
// 第二種調用方法
h := sha512.New()
io.WriteString(h,str)
t.Log(hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)))
}
加密模式
加密一般分為對稱加密(Symmetric Key Encryption)和非對稱加密(Asymmetric Key Encryption)。
對稱加密又分為分組加密和序列密碼。
分組密碼,也叫塊加密(block cyphers),一次加密明文中的一個塊。是將明文按一定的位長分組,明文組經過加密運算得到密文組,密文組經過解密運算(加密運算的逆運算),還原成明文組。
序列密碼,也叫流加密(stream cyphers),一次加密明文中的一個位。是指利用少量的密鑰(制亂元素)通過某種復雜的運算(密碼算法)產生大量的偽隨機位流,用於對明文位流的加密。
解密是指用同樣的密鑰和密碼算法及與加密相同的偽隨機位流,用以還原明文位流。
分組加密算法中,有ECB,CBC,CFB,OFB這幾種算法模式。
| 加密模式 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| ECB | 最基本的加密模式,也就是通常理解的加密,相同的明⽂將永遠加密成相同的密⽂,⽆初始向量,容易受到密碼本重放攻擊,⼀般情況下很少⽤ |
| CBC | 明⽂被加密前要與前⾯的密⽂進⾏異或運算後再加密,因此隻要選擇不同的初始向量,相同的密⽂加密後會形成不同的密⽂,這是⽬前應⽤最⼴泛的模式。CBC加密後的密⽂是上下⽂相關的,但明⽂的錯誤不會傳遞到後續分組,但如果⼀個分組丟失,後⾯的分組將全部作廢(同步錯誤) |
| CFB | 類似於⾃同步序列密碼,分組加密後,按8位分組將密⽂和明⽂進⾏移位異或後得到輸出同時反饋回移位寄存器,優點最⼩可以按字節進⾏加解密,也可以是n位的,CFB也是上下⽂相關的,CFB模式下,明⽂的⼀個錯誤會影響後⾯的密⽂(錯誤擴散)。 |
| OFB | 將分組密碼作為同步序列密碼運⾏,和CFB相似,不過OFB⽤的是前⼀個n位密⽂輸出分組反饋回移位寄存器,OFB沒有錯誤擴散問題 |
對稱加密
最常用的對稱加密算法DES、3DES(TripleDES)和AES,常采用的填充⽅式是NoPadding(不填充)、Zeros填充(0填充)、PKCS5Padding填充。
加密算法要求明文需要按一定長度對齊,叫做塊大小(BlockSize),比如8字節,那麼對於一段任意的數據,加密前需要對最後一個塊填充到8 字節,解密後需要刪除掉填充的數據。
| 填充⽅式 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| ZeroPadding | 數據長度不對齊時使用0填充,否則不填充 |
| PKCS7Padding | 假設數據長度需要填充n(n>0)個字節才對齊,那麼填充n個字節,每個字節都是n;如果數據本身就已經對齊瞭,則填充一塊長度為塊大小的數據,每個字節都是塊大小 |
| PKCS5Padding | PKCS7Padding的子集,塊大小固定為8字節 |
由於使用PKCS7Padding/PKCS5Padding填充時,最後一個字節肯定為填充數據的長度,所以在解密後可以準確刪除填充的數據,而使用ZeroPadding填充時,沒辦法區分真實數據與填充數據,所以隻適合以\0結尾的字符串加解密。
對稱加密需要的填充函數
func PKCS5Padding(data []byte, blockSize int) []byte {
padding := blockSize - len(data)%blockSize
padtext := bytes.Repeat([]byte{byte(padding)}, padding)
return append(data, padtext...)
}
func PKCS5UnPadding(data []byte) []byte {
length := len(data)
// 去掉最後⼀個字節 unpadding 次
unpadding := int(data[length-1])
return data[:(length - unpadding)]
}
func ZeroPadding(data []byte, blockSize int) []byte {
padding := blockSize - len(data)%blockSize
padtext := bytes.Repeat([]byte{0}, padding)
return append(data, padtext...)
}
func ZeroUnPadding(data []byte) []byte {
return bytes.TrimRightFunc(data, func(r rune) bool {
return r == rune(0)
})
}
DES
//DES加密字節數組,返回字節數組
func DesEncrypt(originalBytes, key []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, err := des.NewCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
originalBytes = PKCS5Padding(originalBytes, block.BlockSize())
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCEncrypter(block, key)
cipherArr := make([]byte, len(originalBytes))
blockMode.CryptBlocks(cipherArr, originalBytes)
return cipherArr, nil
}
//DES解密字節數組,返回字節數組
func DesDecrypt(cipherBytes, key []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, err := des.NewCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, key)
originalText := make([]byte, len(cipherBytes))
blockMode.CryptBlocks(originalText, cipherBytes)
originalText = PKCS5UnPadding(originalText)
return originalText, nil
}
//DES加密⽂本,返回加密後⽂本
func DesEncryptString(originalText string, key []byte) (string, error) {
cipherArr, err := DesEncrypt([]byte(originalText), key)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
base64str := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(cipherArr)
return base64str, nil
}
//對加密⽂本進⾏DES解密,返回解密後明⽂
func DesDecryptString(cipherText string, key []byte) (string, error) {
cipherArr, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(cipherText)
cipherArr, err := DesDecrypt(cipherArr, key)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return string(cipherArr), nil
}
3DES
// 3DES加密字節數組,返回字節數組
func TripleDesEncrypt(originalBytes, key []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, err := des.NewTripleDESCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
originalBytes = PKCS5Padding(originalBytes, block.BlockSize())
// originalBytes = ZeroPadding(originalBytes, block.BlockSize())
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCEncrypter(block, key[:8])
cipherArr := make([]byte, len(originalBytes))
blockMode.CryptBlocks(cipherArr, originalBytes)
return cipherArr, nil
}
// 3DES解密字節數組,返回字節數組
func TripleDesDecrypt(cipherBytes, key []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, err := des.NewTripleDESCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, key[:8])
originalArr := make([]byte, len(cipherBytes))
blockMode.CryptBlocks(originalArr, cipherBytes)
originalArr = PKCS5UnPadding(originalArr)
// origData = ZeroUnPadding(origData)
return originalArr, nil
}
// 3DES加密字符串,返回base64處理後字符串
func TripleDesEncrypt2Str(originalText string, key []byte) (string, error) {
block, err := des.NewTripleDESCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
originalData := PKCS5Padding([]byte(originalText), block.BlockSize())
// originalData = ZeroPadding(originalData, block.BlockSize())
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCEncrypter(block, key[:8])
cipherArr := make([]byte, len(originalData))
blockMode.CryptBlocks(cipherArr, originalData)
cipherText := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(cipherArr)
return cipherText, nil
}
// 3DES解密base64處理後的加密字符串,返回明⽂字符串
func TripleDesDecrypt2Str(cipherText string, key []byte) (string, error) {
cipherArr, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(cipherText)
block, err := des.NewTripleDESCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, key[:8])
originalArr := make([]byte, len(cipherArr))
blockMode.CryptBlocks(originalArr, cipherArr)
originalArr = PKCS5UnPadding(originalArr)
// origData = ZeroUnPadding(origData)
return string(originalArr), nil
}
AES
//AES加密字節數組,返回字節數組
func AesEncrypt(originalBytes, key []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
originalBytes = PKCS5Padding(originalBytes, blockSize)
// originalBytes = ZeroPadding(originalBytes, block.BlockSize())
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCEncrypter(block, key[:blockSize])
cipherBytes := make([]byte, len(originalBytes))
// 根據CryptBlocks⽅法的說明,如下⽅式初始化crypted也可以
// crypted := originalBytes
blockMode.CryptBlocks(cipherBytes, originalBytes)
return cipherBytes, nil
}
//AES解密字節數組,返回字節數組
func AesDecrypt(cipherBytes, key []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, key[:blockSize])
originalBytes := make([]byte, len(cipherBytes))
// origData := cipherBytes
blockMode.CryptBlocks(originalBytes, cipherBytes)
originalBytes = PKCS5UnPadding(originalBytes)
// origData = ZeroUnPadding(origData)
return originalBytes, nil
}
//AES加密⽂本,返回對加密後字節數組進⾏base64處理後字符串
func AesEncryptString(originalText string, key []byte) (string, error) {
cipherBytes, err := AesEncrypt([]byte(originalText), key)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
base64str := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(cipherBytes)
return base64str, nil
}
//AES解密⽂本,對Base64處理後的加密⽂本進⾏AES解密,返回解密後明⽂
func AesDecryptString(cipherText string, key []byte) (string, error) {
cipherBytes, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(cipherText)
cipherBytes, err := AesDecrypt(cipherBytes, key)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return string(cipherBytes), nil
}
⾮對稱加密
RSA算法也是一個塊加密算法( block cipher algorithm),總是在一個固定長度的塊上進行操作。但跟AES等不同的是,block length是跟key length有關的。
每次RSA加密的明文的長度是受RSA填充模式限制的,但是RSA每次加密的塊長度就是key length。
| 填充⽅式 | 密文長度 |
|---|---|
| PKCS1Padding | 必須 比 RSA 秘鑰模長(modulus) 短至少11個字節, 也就是RSA_SIZE(rsa) – 11 |
| OAEPPadding | RSA_SIZE(rsa) – 41 |
| NOPadding | 可以和RSA鑰模長一樣長,如果輸入的明文過長,必須切割, 然後填充 |
在不同的padding模式下,使用相同長度的密鑰可以加密的數據最大長度不同在不同密鑰長度下,使用相同的padding模式可以加密的數據最大長度也不同
因此,脫離瞭密鑰長度而討論padding模式可以加密的最大長度是不嚴謹的。常用的密鑰長度有1024bits,2048bits等,理論上1024bits的密鑰可以加密的數據最大長度為1024bits(即1024/8 = 128bytes)。2048bits的密鑰可以加密的數據最大長度為2048bits(2048/8 = 256bytes),但是RSA在實際應用中不可能使用這種“教科書式的RSA”系統。實際應用中RSA經常與填充技術(padding)一起使用,可以增加RSA的安全性。
PKCS1
// 加密字節數組,返回字節數組
func RsaEncrypt(publicKey, origData []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(publicKey)
if block == nil {
return nil, errors.New("public key error")
}
pubInterface, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pub := pubInterface.(*rsa.PublicKey)
return rsa.EncryptPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, pub, origData)
}
// 解密字節數組,返回字節數組
func RsaDecrypt(privateKey, ciphertext []byte) ([]byte, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(privateKey)
if block == nil {
return nil, errors.New("private key error!")
}
priv, err := x509.ParsePKCS1PrivateKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return rsa.DecryptPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, priv, ciphertext)
}
// 加密字符串,返回base64處理的字符串
func RsaEncryptString(publicKey []byte, origData string) (string, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(publicKey)
if block == nil {
return "", errors.New("public key error")
}
pubInterface, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
pub := pubInterface.(*rsa.PublicKey)
cipherArr, err := rsa.EncryptPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, pub, []byte(origData))
if err != nil {
return "", err
} else {
return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(cipherArr), nil
}
}
// 解密經過base64處理的加密字符串,返回加密前的明⽂
func RsaDecryptString(privateKey []byte, cipherText string) (string, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(privateKey)
if block == nil {
return "", errors.New("private key error!")
}
priv, err := x509.ParsePKCS1PrivateKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
cipherArr, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(cipherText)
originalArr, err := rsa.DecryptPKCS1v15(rand.Reader, priv, cipherArr)
if err != nil {
return "", err
} else {
return string(originalArr), nil
}
}
OAEP
// 加密
func EncryptOAEP(publicKey []byte, text string) (string, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(publicKey)
if block == nil {
return "", errors.New("public key error")
}
pubInterface, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
pub := pubInterface.(*rsa.PublicKey)
secretMessage := []byte(text)
rng := rand.Reader
cipherdata, err := rsa.EncryptOAEP(sha1.New(), rng, pub, secretMessage, nil)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
ciphertext := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(cipherdata)
return ciphertext, nil
}
// 解密
func DecryptOAEP(privateKey []byte, ciphertext string) (string, error) {
block, _ := pem.Decode(privateKey)
if block == nil {
return "", errors.New("private key error!")
}
priv, err := x509.ParsePKCS1PrivateKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
cipherdata, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(ciphertext)
rng := rand.Reader
plaintext, err := rsa.DecryptOAEP(sha1.New(), rng, priv, cipherdata, nil)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return string(plaintext), nil
}
橢圓曲線加密算法ECC
橢圓曲線密碼學(Elliptic curve cryptography,縮寫為 ECC),是基於橢圓曲線數學理論實現的⼀種⾮對稱加密算法。
ECC與RSA算法的優勢對⽐
橢圓曲線公鑰系統是代替RSA的強有⼒的競爭者。
與經典的RSA、DSA等公鑰密碼體制相⽐,橢圓密碼體制有以下優點:
(1)安全性能更⾼(ECC可以使⽤更短的密鑰):
160位ECC加密算法的安全強度相當於1024位RSA加密;
210位ECC加密算法的安全強度相當於2048位RSA加密。
(2)處理速度快:計算量⼩,處理速度快 在私鑰的處理速度上(解密和簽名),ECC遠 ⽐RSA、DSA快得多。
(3)存儲空間占⽤⼩: ECC的密鑰尺⼨和系統參數與RSA、DSA相⽐要⼩得多, 所以占⽤的存儲空間⼩得多。
(4)帶寬要求低使得ECC具有⼴泛的應⽤前景。ECC的這些特點使它必將取代RSA,成為通⽤的公鑰加密算法。
//生成ECC橢圓曲線密鑰對
func GenerateECCKey() (*ecdsa.PublicKey, *ecdsa.PrivateKey, error) {
privateKey, err := ecdsa.GenerateKey(elliptic.P521(), rand.Reader)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
publicKey := &privateKey.PublicKey
return publicKey, privateKey, nil
}
//對消息的散列值生成數字簽名
func SignECC(msg []byte) ([]byte, []byte) {
//取得私鑰
_, privateKey, err := GenerateECCKey()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
//計算哈希值
hash := sha256.New()
//填入數據
hash.Write(msg)
b := hash.Sum(nil)
//對哈希值生成數字簽名
r, s, err := ecdsa.Sign(rand.Reader, privateKey, b)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
rtext, _ := r.MarshalText()
stext, _ := s.MarshalText()
return rtext, stext
}
//驗證數字簽名
func VerifySignECC(msg []byte, rtext, stext []byte) bool {
//取得公鑰
publicKey, _, err := GenerateECCKey()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
//計算哈希值
hash := sha256.New()
hash.Write(msg)
b := hash.Sum(nil)
//驗證數字簽名
var r, s big.Int
if err := r.UnmarshalText(rtext); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
if err := s.UnmarshalText(stext); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
verify := ecdsa.Verify(publicKey, b, &r, &s)
return verify
}
//測試
func Test(t *testing.T) {
//模擬發送者
//要發送的消息
msg := []byte("hello world")
//生成數字簽名
rtext, stext := SignECC(msg)
//模擬接受者
//接受到的消息
acceptmsg := []byte("hello world")
//接收到的簽名
acceptrtext := rtext
acceptstext := stext
//驗證簽名
verifySignECC := VerifySignECC(acceptmsg, acceptrtext, acceptstext)
fmt.Println("驗證結果:", verifySignECC)
}
數字簽名
數字簽名的概念
1、簽名不可偽造性;
2、簽名不可抵賴的;
3、簽名可信性,簽名的識別和應⽤相對容易,任何⼈都可以驗證簽名的有效
性;
4、簽名是不可復制的,簽名與原⽂是不可分割的整體;
5、簽名消息不可篡改,因為任意⽐特數據被篡改,其簽名便被隨之改變,那麼
任何⼈可以驗證⽽拒絕接受此簽名。
橢圓曲線數字簽名算法ECDSA
//⽣成私鑰和公鑰,⽣成的私鑰為結構體ecdsa.PrivateKey的指針
func NewKeyPair() (ecdsa.PrivateKey, []byte) {
//⽣成secp256橢圓曲線
curve := elliptic.P256()
//產⽣的是⼀個結構體指針,結構體類型為ecdsa.PrivateKey
private, err := ecdsa.GenerateKey(curve, rand.Reader)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("私鑰:%x\n", private)
fmt.Printf("私鑰X:%x\n", private.X.Bytes())
fmt.Printf("私鑰Y:%x\n", private.Y.Bytes())
fmt.Printf("私鑰D:%x\n", private.D.Bytes())
//x坐標與y坐標拼接在⼀起,⽣成公鑰
pubKey := append(private.X.Bytes(), private.Y.Bytes()...)
//打印公鑰,公鑰⽤16進制打印出來⻓度為128,包含瞭x軸坐標與y軸坐標。
fmt.Printf("公鑰:%x \n", pubKey)
return *private, pubKey
}
//⽣成簽名的DER格式
func MakeSignatureDerString(r, s string) string {
// 獲取R和S的⻓度
lenSigR := len(r) / 2
lenSigS := len(s) / 2
// 計算DER序列的總⻓度
lenSequence := lenSigR + lenSigS + 4
// 將10進制⻓度轉16進制字符串
strLenSigR := DecimalToHex(int64(lenSigR))
strLenSigS := DecimalToHex(int64(lenSigS))
strLenSequence := DecimalToHex(int64(lenSequence))
// 拼湊DER編碼
derString := "30" + strLenSequence
derString = derString + "02" + strLenSigR + r
derString = derString + "02" + strLenSigS + s
derString = derString + "01"
return derString
}
func DecimalToHex(n int64) string {
if n < 0 {
log.Println("Decimal to hexadecimal error: the argument must be greater than zero.")
return ""
}
if n == 0 {
return "0"
}
hex := map[int64]int64{10: 65, 11: 66, 12: 67, 13: 68, 14: 69, 15: 70}
s := ""
for q := n; q > 0; q = q / 16 {
m := q % 16
if m > 9 && m < 16 {
m = hex[m]
s = fmt.Sprintf("%v%v", string(m), s)
continue
}
s = fmt.Sprintf("%v%v", m, s)
}
return s
}
//驗證簽名1
func VerifySig(pubKey, message []byte, r, s *big.Int) bool {
curve := elliptic.P256()
//公鑰的⻓度
keyLen := len(pubKey)
//前⼀半為x軸坐標,後⼀半為y軸坐標
x := big.Int{}
y := big.Int{}
x.SetBytes(pubKey[:(keyLen / 2)])
y.SetBytes(pubKey[(keyLen / 2):])
rawPubKey := ecdsa.PublicKey{curve, &x, &y}
//根據交易哈希、公鑰、數字簽名驗證成功。ecdsa.Verify func Verify(pub *PublicKey, hash[] byte, r * big.Int, s * big.Int) bool
res := ecdsa.Verify(&rawPubKey, message, r, s)
return res
}
//驗證簽名2
func VerifySignature(pubKey, message []byte, r, s string) bool {
curve := elliptic.P256()
//公鑰的⻓度
keyLen := len(pubKey)
//前⼀半為x軸坐標,後⼀半為y軸坐標
x := big.Int{}
y := big.Int{}
x.SetBytes(pubKey[:(keyLen / 2)])
y.SetBytes(pubKey[(keyLen / 2):])
rawPubKey := ecdsa.PublicKey{curve, &x, &y}
//根據交易哈希、公鑰、數字簽名驗證成功。ecdsa.Verify func Verify(pub *PublicKey, hash[] byte, r * big.Int, s * big.Int) bool
rint := big.Int{}
sint := big.Int{}
rByte, _ := hex.DecodeString(r)
sByte, _ := hex.DecodeString(s)
rint.SetBytes(rByte)
sint.SetBytes(sByte)
//fmt.Println("------", rint.SetBytes(rByte))
//fmt.Println("------", sint.SetBytes(sByte))
res := ecdsa.Verify(&rawPubKey, message, &rint, &sint)
return res
}
//驗證過程
func Test(t *testing.T) {
//1、⽣成簽名
fmt.Println("1、⽣成簽名-------------------------------")
//調⽤函數⽣成私鑰與公鑰
privKey, pubKey := NewKeyPair()
//信息的哈希
msg := sha256.Sum256([]byte("hello world"))
//根據私鑰和信息的哈希進⾏數字簽名,產⽣r和s
r, s, _ := ecdsa.Sign(rand.Reader, &privKey, msg[:])
//⽣成r、s字符串
fmt.Println("-------------------------------")
strSigR := fmt.Sprintf("%x", r)
strSigS := fmt.Sprintf("%x", s)
fmt.Println("r、s的10進制分別為:", r, s)
fmt.Println("r、s的16進制分別為:", strSigR, strSigS)
//r和s拼接在⼀起,形成數字簽名的der格式
signatureDer := MakeSignatureDerString(strSigR, strSigS)
//打印數字簽名的16進制顯示
fmt.Println("數字簽名DER格式為:", signatureDer)
fmt.Println()
//2、簽名驗證過程
fmt.Println("2、簽名驗證過程-------------------------------")
res := VerifySig(pubKey, msg[:], r, s)
fmt.Println("簽名驗證結果:", res)
res = VerifySignature(pubKey, msg[:], strSigR, strSigS)
fmt.Println("簽名驗證結果:", res)
}
字符編碼/解碼
Base64
Base64就是⼀種基於64個可打印字符來表示⼆進制數據的⽅法。Base64使⽤瞭26個⼩寫字⺟、26個⼤寫字⺟、10個數字以及兩個符號(例如“+”和“/”),⽤於在電⼦郵件這樣的基於⽂本的媒介中傳輸⼆進制數據。
Base64字符集:
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/
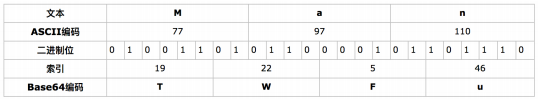
Base64的步驟
將每個字符轉成ASCII編碼(10進制)將10進制編碼轉成2進制編碼將2進制編碼按照6位⼀組進⾏平分將6位⼀組的2進制數⾼位補零,然後轉成10進制數將10進制數作為索引,從Base64編碼表中查找字符每3個字符的⽂本將編碼為4個字符⻓度(38=46)
a. 若⽂本為3個字符,則正好編碼為4個字符⻓度;
b. 若⽂本為2個字符,則編碼為3個字符,由於不⾜4個字符,則在尾部⽤⼀個“=”補⻬;
c. 若⽂本為1個字符,則編碼為2個字符,由於不⾜4個字符,則在尾部⽤兩個“=”補⻬。
巨人的肩膀
從他人的工作中汲取經驗來避免自己的錯誤重復,正如我們是站在巨人的肩膀上才能做出更好的成績。
https://github.com/rubyhan1314/Golang-100-Days
https://blog.csdn.net/luckydog612/article/details/80547758
https://www.cnblogs.com/yanzi-meng/p/9640578.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/starwolf/p/3365834.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u013073067/article/details/87086562
https://www.cnblogs.com/Terry-Wu/p/10314315.html
http://blog.studygolang.com/2013/01/go%E5%8A%A0%E5%AF%86%E8%A7%A3%E5%AF%86%E4%B9%8Bdes/
https://blog.csdn.net/kikajack/article/details/78329567
到此這篇關於Go中使用加密算法的方法的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關go 加密算法內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- Golang實現AES對稱加密的過程詳解
- Go語言使用對稱加密的示例詳解
- golang 如何獲取pem格式RSA公私鑰長度
- 通過Golang編寫一個AES加密解密工具
- GO語言創建錢包並遍歷錢包(wallet)的實現代碼
