C語言實現單鏈表的基本功能詳解
1.首先簡單瞭解一下鏈表的概念:
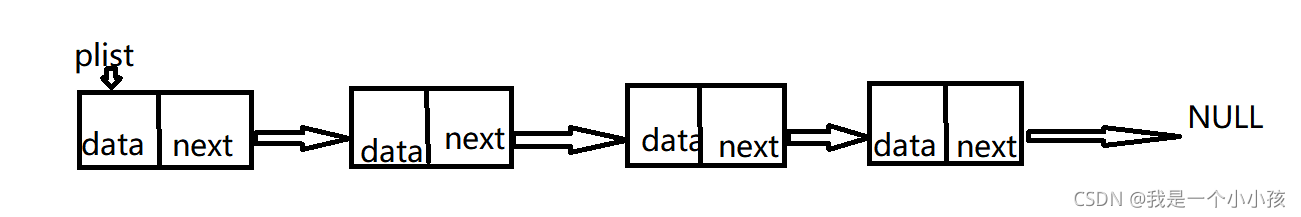
要註意的是鏈表是一個結構體實現的一種線性表,它隻能從前往後,不可以從後往前(因為next隻保存下一個節點的地址).在實現單鏈表的操作時,需要用指針來操作.很簡單,註釋寫的很詳細,歡迎大傢指正哈哈哈哈~之前寫的太爛瞭重新寫瞭一下…..
2.代碼展示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct linklist {
int data;
struct linklist* next;
}node;
//目錄
//1.動態申請節點
node* Creatnode(int x);
//2.單鏈表的尾插
void PushBack(node** plist, int x);
//3.單鏈表的打印
void Printlist(node** plist);
//4.單鏈表尾刪
void Popback(node** plist);
//5.單鏈表的頭插
void PushFront(node** plist, int x);
//6.單鏈表的頭刪
void PopFrount(node** plist);
//7.單鏈表的查找
node* Findpos(node* plist, int x);
//8.單鏈表在pos位置之後插入x
void Insertlinstafter(node* pos, int x);
//9.單鏈表刪除pos位置之後的元素
void PopPosAfter(node* pos);
//10.單鏈表的銷毀
void Destorylist(node** plist);
//1.動態申請節點
node* Creatnode(int x) {
node* t = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
if (t == NULL) {
assert(0);
return NULL;
}
else {
t->next = NULL;
t->data = x;
return t;
}
}
//2.單鏈表的尾插
void PushBack(node** plist, int x) {
assert(plist);
if (*plist == NULL) {
*plist = Creatnode(x);
}
else {
node* p = *plist;
while (p->next) {
p = p->next;
}
p->next = Creatnode(x);
}
}
//3.單鏈表的打印
void Printlist(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
node* p =* plist;
while (p) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
//4.單鏈表尾刪
void Popback(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
if (*plist == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
node* p = *plist;
node* q = NULL;
while (p->next) {
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
q->next =NULL;
free(p);
}
//5.單鏈表的頭插
void PushFront(node** plist, int x) {
assert(plist);
node* t = Creatnode(x);
if (NULL == *plist) {
*plist = t;
}
else {
t->next = *plist;
*plist = t;
}
}
//6.單鏈表的頭刪
void PopFrount(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
if (plist == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
else {
node* p = *plist;
*plist = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
//7.單鏈表的查找
node* Findpos(node* plist, int x) {
node* cur = plist;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data == x) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//8.單鏈表在pos位置之後插入x
void Insertlinstafter(node* pos, int x) {
assert(pos);
if (NULL == pos) {
return ;
}
node* t = Creatnode(x);
t->next = pos->next;
pos->next = t;
}
//9.單鏈表刪除pos位置之後的元素
void PopPosAfter(node* pos) {
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL) {
return;
}
else{
node* p = pos->next;
pos->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
//10.單鏈表的銷毀
void Destorylist(node** plist) {
assert(plist);
node* p = *plist;
while (p) {
*plist = p->next;
free(p);
p = *plist;
}
*plist = NULL;
}
void test1() {
node* plist=NULL;//創建頭指針
PushBack(&plist, 1);//尾插元素
PushBack(&plist, 2);
PushBack(&plist, 3);
PushBack(&plist, 4);
PushBack(&plist, 5);
Printlist(&plist);//打印鏈表元素 1 2 3 4 5
printf("\n");
Popback(&plist); //尾刪元素
PushFront(&plist, 0);//首插元素0
Printlist(&plist);//打印鏈表 0 1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
PopFrount(&plist);//首刪元素0
Printlist(&plist);//打印鏈表 1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
Findpos(plist,1);//尋找鏈表中1的地址,不方便演示,下面會演示
Insertlinstafter(Findpos(plist, 4), 5);//在4後面插入5,用到上面的Findpos函數
Printlist(&plist);//打印鏈表 1 2 3 4 5
printf("\n");
PopPosAfter(Findpos(plist, 4));//刪除指定位置後面的元素(刪除4後面的5)
Printlist(&plist);//打印鏈表 1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
Destorylist(&plist);//銷毀鏈表
Printlist(&plist);//打印鏈表
}
void test() {
test1();
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
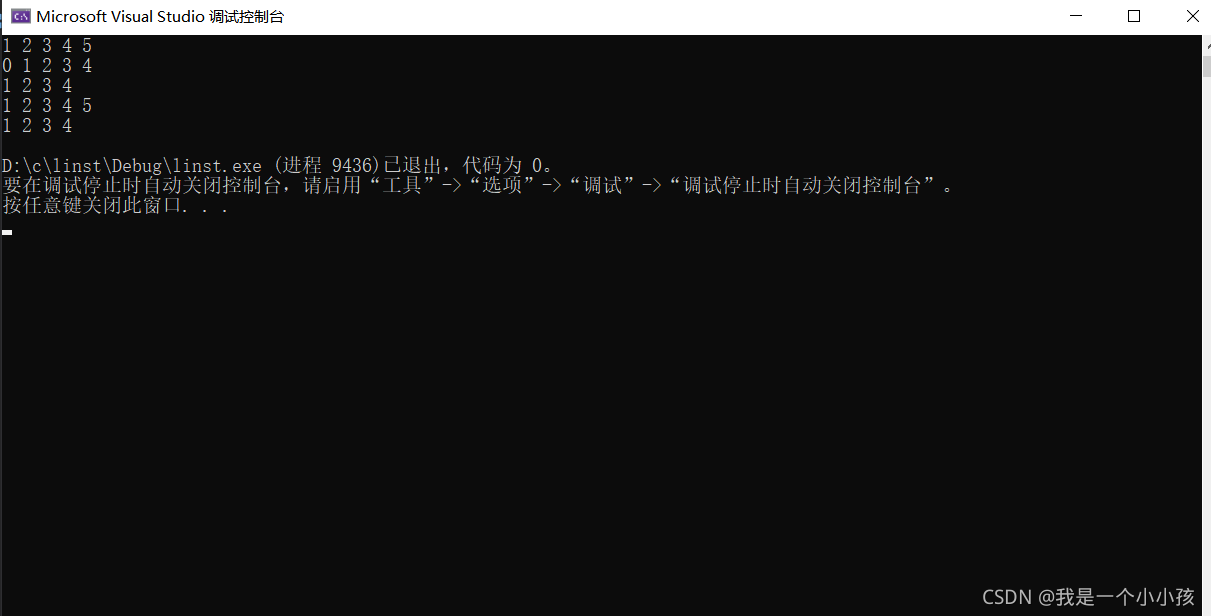
3.測試結果:
a.先創建瞭頭指針plist
b.尾插1 2 3 4 5
c. 尾刪元素5
d.首插元素0
e.首刪元素0
f.在元素4 後面插入5
g.刪除4元素後面的5
h.銷毀鏈表
到此這篇關於C語言實現單鏈表的基本功能詳解的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關單鏈表基本功能內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!