SpringMVC @RequestMapping註解詳解
一、@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping註解的源碼:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
1.@RequestMapping註解的功能
@RequestMapping的功能就是將請求和處理請求的控制器方法關聯起來,建立映射關系。
SpringMVC接收到指定的請求,就會來找到在映射關系中對應的控制器方法來處理這個請求。
2.@RequestMapping註解的位置
@RequestMapping標註在類:設置映射請求請求路徑的初始信息(通常用於表示某個模塊的信息)
@RequestMapping標註在方法:設置映射請求請求路徑的具體信息
@RequestMapping相同的請求地址一定隻有一個RequestMapping映射,否則會報錯。
瀏覽器先匹配類上標註的@Requestmapping,再匹配方法上的@Requestmapping,即請求地址url = 類請求路徑 + 方法請求路徑
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class DisplayController {
@RequestMapping("/displayTest")
//此時的請求實際就是/hello/displayTest
public String displayTest(){
return "display";
}
}
此時需要映射的請求地址實際就是http://localhost:8080/hello/display
<!--瀏覽器解析的是絕對路徑,會將"/"解析為"localhost:8080/"-->
<a th:href="@{/hello/displayTest}" rel="external nofollow" >訪問display頁面...</a>
二、@RequestMapping註解的屬性
1.value屬性(掌握)
value屬性是通過請求地址來匹配請求映射(默認是value),value屬性是一個String類型的數組,表示該請求能夠匹配多個請求地址所對應的請求,value屬性必須設設置,至少通過請求地址映射來匹配請求映射。
//表示可以通過地址testWorld或者hello/testWorld都可以訪問world.html
//@RequestMapping請求地址與方法名沒有關系,但是為瞭方便習慣上使用方法名
@RequestMapping(value = {"testWorld","hello/testWorld"})
public String testWorld(){
return "world";
}
此時需要映射的請求地址實際就是http://localhost:8080/testWorld或者http://localhost:8080/hello/testWorld
<!--瀏覽器解析的是絕對路徑,會將"/"解析為"localhost:8080/"-->
<a th:href="@{/hello/testWorld}" rel="external nofollow" >@{/hello/testWorld}訪問helloworld頁面...</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/testWorld}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >@{/testWorld}訪問helloworld頁面...</a><br>
2.method屬性(掌握)
method是通過請求方式(get/post)匹配請求映射,method屬性是一個RequestMethod[]類型的數組,表示該種請求可以匹配多種請求方式對應的請求。如果當前請求的請求映射滿足value屬性,但是不滿足method屬性,就會報錯405,報錯:Request method 'POST' not supported
get和post兩種常見的請求方式有何區別?
get:使用?將請求參數與請求地址拼接起來,格式:?請求參數名=請求參數值&請求參數名=請求參數值,不安全,傳輸速度快(請求地址也會傳輸),傳輸數據量有限,不能用於上傳文件
post:請求參數放在請求體中(格式:請求參數名=請求參數值&請求參數名=請求參數值),安全,傳輸速度慢,傳輸數據量大
//表示可以通過地址testWorld或者hello/testWorld都可以訪問world.html
@RequestMapping(value = {"testWorld","hello/testWorld"},method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String testWorld(){
return "world";
}
<!--瀏覽器解析的是絕對路徑,會將"/"解析為"localhost:8080/"-->
<a th:href="@{/testWorld}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >@{/testWorld}訪問helloworld頁面(GET請求(默認))</a><br>
<form th:action="@{/testWorld}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="@{/testWorld}訪問helloworld頁面(POST請求)">
</form>
此時訪問get請求正常,訪問post請求,請求方式不匹配(請求不支持),報錯誤405
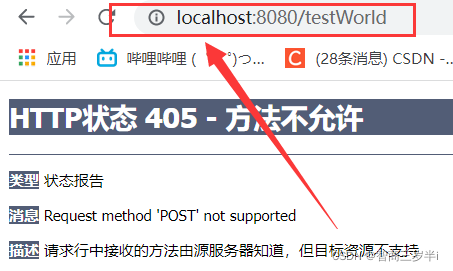
將WorldController的@RequestMapping改為@RequestMapping(value = {"testWorld","hello/testWorld"},method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST}),再次訪問post和get請求,請求成功。

3.params屬性(瞭解)
params屬性是指通過請求的參數匹配處理請求的映射,params屬性是一個String類型的數組,表示通過四種表達式設置請求參數和請求映射匹配關系。
“param”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須攜帶param請求參數
“!param”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須不能攜帶param請求參數
“param=value”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須攜帶param請求參數且param=value
“param!=value”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須攜帶param請求參數但是param!=value
//處理請求的參數隻能是username和password,且username=admin、password=12345678
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParams",params = {"username=admin","password=12345678"})
public String testParams(){
return "world";
}
<!--瀏覽器解析的是絕對路徑,會將"/"解析為"localhost:8080/"-->
<!--此處使用單引號,雙引號會報錯-->
<!--會自動轉化為?傳參-->
<a th:href="@{/testParams(username='admin',password=12345678)}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >測試params參數</a><br>
可以看到請求參數已經使用?進行瞭拼接,請求訪問成功,

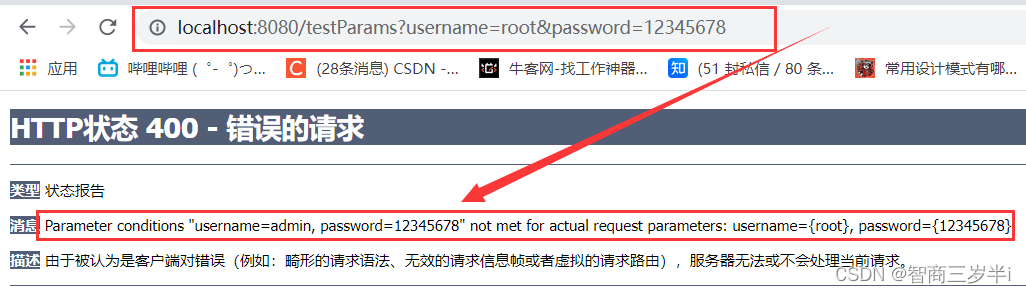
將請求改為如下,再次訪問,@RequestMapping請求參數不匹配,報400
<a th:href="@{/testParams(username='root',password=12345678)}" rel="external nofollow" >測試params參數root</a><br>
4.headers屬性(瞭解)
headers屬性通過請求的請求頭信息匹配請求映射,headers屬性是一個String類型的數組,表示可以通過四種表達式設置請求頭信息和請求映射的匹配信息。
“header”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須攜帶header請求頭信息
“!header”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須不能攜帶header請求頭信息
“header=value”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須攜帶header請求頭信息且header=value
“header!=value”:要求請求映射所匹配的請求必須攜帶header請求頭信息且header!=value
若當前請求滿足@RequestMapping註解的value和method屬性,但是不滿足headers屬性,此時頁面顯示404錯誤,即資源未找到
//此時的請求的params中username=admin,password=1234545678,並且端口號是8081才可以成功,否則報錯
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParams",
params = {"username=admin","password=12345678"},
headers = {"host=localhost:8081"})
public String testParams(){
return "world";
}
<a th:href="@{/testParams(username='admin',password=12345678)}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >測試params參數</a><br>
可以看到未找到,@RequestMapping的請求頭參數不匹配,報錯誤404
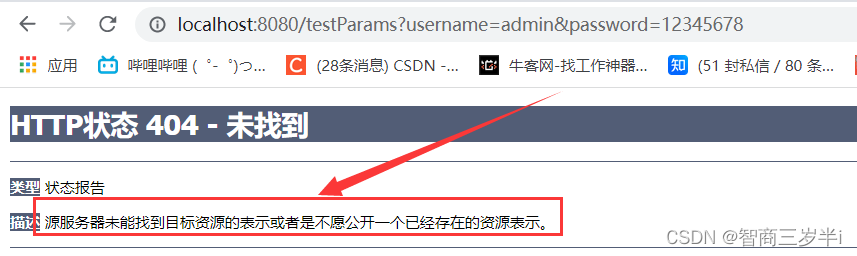
將端口號改為8080,再次測試。
//此時的請求的params中username=admin,password=1234545678,並且端口號是8080才可以成功,否則報錯
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParams",
params = {"username=admin","password=12345678"},
headers = {"host=localhost:8080"})
public String testParams(){
return "world";
}
可以看到訪問成功
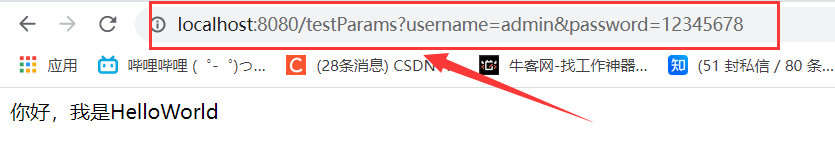
總結:
@RequestMapping沒有和任意參數匹配,報錯誤404
@RequestMapping的請求頭參數不匹配,報錯誤404
@RequestMapping請求參數(params)不匹配,報錯誤400
@RequestMapping請求方式不匹配(請求不支持),報錯誤405
5.SpringMVC支持ant風格的路徑
?:表示任意的單個字符
*:表示任意的0個或多個字符
**:表示任意的一層或多層目錄
註意:在使用**時,隻能使用/**/xxx的方式
//@RequestMapping(value = "/a?a/testAnt")
//@RequestMapping(value = "/a*a/testAnt")
@RequestMapping(value = "/**/testAnt")
public String testAnt(){
return "world";
}
<a th:href="@{/a1a/testAnt}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >測試ant風格--->?</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/a1a/testAnt}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >測試ant風格--->*</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/a1a/testAnt}" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" >測試ant風格--->**</a><br>
6.SpringMVC支持路徑中的占位符(重點)
原始方式:/deleteUser?id=1
rest方式::/deleteUser/1
SpringMVC路徑中的占位符常用於restful風格中,當請求路徑中將某些數據通過路徑的方式傳輸到服務器中,就可以在相應的@RequestMapping註解的value屬性中通過占位符{xxx}表示傳輸的數據,在通過@PathVariable註解,將占位符所表示的數據賦值給控制器方法的形參。
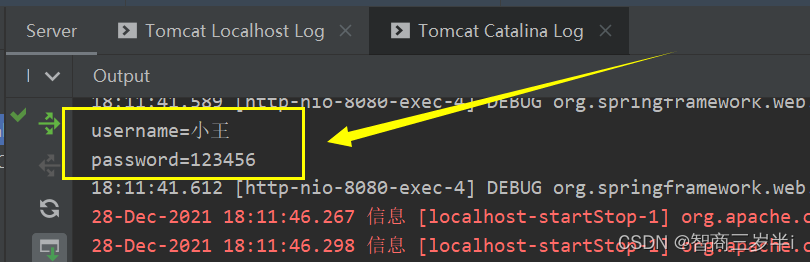
@RequestMapping("/testRest/{username}/{password}")
public String testRest(@PathVariable("username") String username,@PathVariable("password") String password){
System.out.println("username="+username);
System.out.println("password="+password);
return "world";
}
<!--瀏覽器解析的是絕對路徑,會將"/"解析為"localhost:8080/"-->
<a th:href="@{/testRest/小王/123456}" rel="external nofollow" >測試rest占位符</a><br>
可以看到沒有使用?連接,使用瞭rest方式實現瞭訪問。
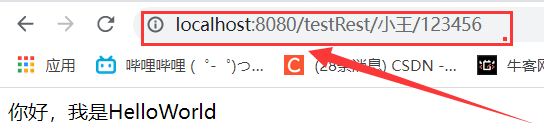
查看idea的控制臺,數據通過路徑的方式傳輸到服務器中。
三、@RequestMapping的派生類註解
對於處理指定請求方式的控制器方式,SpringMVC提供瞭@RequestMapping的派生類註解:
處理post請求的映射—>@PostMapping
處理get請求的映射—>@GetMapping
處理put請求的映射—>@PutMapping
處理delete請求的映射—>@DeleteMapping
但是目前瀏覽器隻支持get和post,若在form表單提交時,為method設置瞭其他請求方式的字符串(put或delete),則按照默認的請求方式(get)處理。
@GetMapping("testGetMapping")
public String testGetMapping(){
return "world";
}
<!--瀏覽器解析的是絕對路徑,會將"/"解析為"localhost:8080/"-->
<a th:href="@{/testGetMapping}" rel="external nofollow" >@{/testGetMapping}訪問helloworld頁面...</a><br>
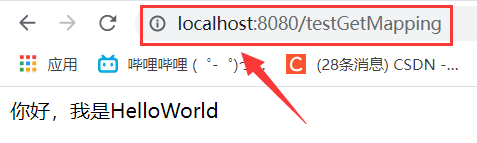
測試form表單是否支持put或delete方式的請求
當請求和請求映射的方式不匹配時就會報錯405.
//當前請求映射的請求地址是testPut,請求方式是put方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/testPut",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String testPut(){
return "world";
}
<!--測試form表單是否支持put或delete方式的請求-->
<form th:action="@{/testPut}" method="put">
<input type="submit" value="測試form表單是否支持put或delete方式的請求">
</form>
結果如下:
若在form表單提交時,為method設置瞭其他請求方式的字符串(put或delete),則按照默認的請求方式(get)處理。若要發送put和delete請求,則需要通過spring提供的過濾器HiddenHttpMethodFilter,在restful部分會講到。

到此這篇關於SpringMVC @RequestMapping註解詳解的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關SpringMVC @RequestMapping內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- 基於SpringMVC @RequestMapping的參數和用法
- 基於params、@PathVariabl和@RequestParam的用法與區別說明
- SpringMVC中RequestMapping註解(作用、出現的位置、屬性)
- SpringMVC RESTFul及REST架構風格介紹
- SpringMVC HttpMessageConverter報文信息轉換器