opencv+python識別七段數碼顯示器的數字(數字識別)
一、什麼是七段數碼顯示器
七段LCD數碼顯示器有很多叫法:段碼液晶屏、段式液晶屏、黑白筆段屏、段碼LCD液晶屏、段式顯示器、TN液晶屏、段碼液晶顯示器、段碼屏幕、筆段式液晶屏、段碼液晶顯示屏、段式LCD、筆段式LCD等。
如下圖,每個數字都由一個七段組件組成。

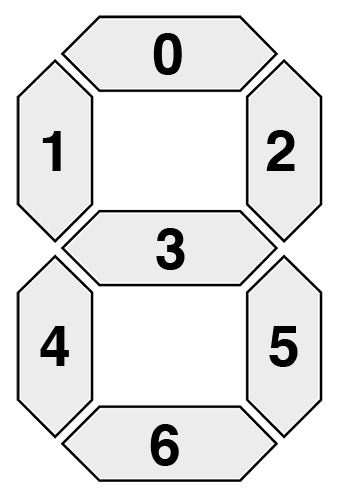
七段顯示器總共可以呈現 128 種可能的狀態:

我們要識別其中的0-9,如果用深度學習的方式有點小題大做,並且如果要進行應用還有很多前序工作需要進行,比如要確認識別什麼設備的,怎麼找到數字區域並進行分割等等。

二、創建opencv數字識別器
我們這裡進行使用空調恒溫器進行識別,首先整理下流程。
1、定位恒溫器上的 LCD屏幕。
2、提取 LCD的圖像。
3、提取數字區域
4、識別數字。
我們創建名稱為recognize_digits.py的文件,代碼如下。僅思路供參考(因為代碼中的一些參數隻適合測試圖片)
# import the necessary packages
from imutils.perspective import four_point_transform
from imutils import contours
import imutils
import cv2
# define the dictionary of digit segments so we can identify
# each digit on the thermostat
DIGITS_LOOKUP = {
(1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1): 0,
(0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0): 1,
(1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0): 2,
(1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1): 3,
(0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0): 4,
(1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1): 5,
(1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1): 6,
(1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0): 7,
(1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1): 8,
(1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1): 9
}
# load the example image
image = cv2.imread("example.jpg")#
# pre-process the image by resizing it, converting it to
# graycale, blurring it, and computing an edge map
image = imutils.resize(image, height=500)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 50, 200, 255)
# find contours in the edge map, then sort them by their
# size in descending order
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = imutils.grab_contours(cnts)
cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
displayCnt = None
# loop over the contours
for c in cnts:
# approximate the contour
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True)
# if the contour has four vertices, then we have found
# the thermostat display
if len(approx) == 4:
displayCnt = approx
break
# extract the thermostat display, apply a perspective transform
# to it
warped = four_point_transform(gray, displayCnt.reshape(4, 2))
output = four_point_transform(image, displayCnt.reshape(4, 2))
# threshold the warped image, then apply a series of morphological
# operations to cleanup the thresholded image
thresh = cv2.threshold(warped, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (1, 5))
thresh = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
# find contours in the thresholded image, then initialize the
# digit contours lists
cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = imutils.grab_contours(cnts)
digitCnts = []
# loop over the digit area candidates
for c in cnts:
# compute the bounding box of the contour
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
# if the contour is sufficiently large, it must be a digit
if w >= 15 and (h >= 30 and h <= 40):
digitCnts.append(c)
# sort the contours from left-to-right, then initialize the
# actual digits themselves
digitCnts = contours.sort_contours(digitCnts, method="left-to-right")[0]
digits = []
# loop over each of the digits
for c in digitCnts:
# extract the digit ROI
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = thresh[y:y + h, x:x + w]
# compute the width and height of each of the 7 segments
# we are going to examine
(roiH, roiW) = roi.shape
(dW, dH) = (int(roiW * 0.25), int(roiH * 0.15))
dHC = int(roiH * 0.05)
# define the set of 7 segments
segments = [
((0, 0), (w, dH)), # top
((0, 0), (dW, h // 2)), # top-left
((w - dW, 0), (w, h // 2)), # top-right
((0, (h // 2) - dHC) , (w, (h // 2) + dHC)), # center
((0, h // 2), (dW, h)), # bottom-left
((w - dW, h // 2), (w, h)), # bottom-right
((0, h - dH), (w, h)) # bottom
]
on = [0] * len(segments)
# loop over the segments
for (i, ((xA, yA), (xB, yB))) in enumerate(segments):
# extract the segment ROI, count the total number of
# thresholded pixels in the segment, and then compute
# the area of the segment
segROI = roi[yA:yB, xA:xB]
total = cv2.countNonZero(segROI)
area = (xB - xA) * (yB - yA)
# if the total number of non-zero pixels is greater than
# 50% of the area, mark the segment as "on"
if total / float(area) > 0.5:
on[i]= 1
# lookup the digit and draw it on the image
digit = DIGITS_LOOKUP[tuple(on)]
digits.append(digit)
cv2.rectangle(output, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.putText(output, str(digit), (x - 10, y - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.65, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# display the digits
print(u"{}{}.{} \u00b0C".format(*digits))
cv2.imshow("Input", image)
cv2.imshow("Output", output)
cv2.waitKey(0)

原始圖片

邊緣檢測

識別的結果圖片
到此這篇關於opencv+python識別七段數碼顯示器的數字(數字識別)的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關opencv數字識別內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- 使用Python+OpenCV進行卡類型及16位卡號數字的OCR功能
- Python如何識別銀行卡卡號?
- Python+OpenCV實現表面缺陷檢測
- python和opencv構建運動檢測器的實現
- python OpenCV實現答題卡識別判卷