Java中DataInputStream和DataOutputStream的使用方法
簡介
在 io 包中,提供瞭兩個與平臺無關的數據操作流:數據輸出流(DataOutputStream)、數據輸入流 (DataInputStream)。
通常數據輸出流會按照一定的格式將數據輸出,再通過數據輸入流按照一定的格式將數據讀入。DataOutputStream 和 DataOutputStream 用來讀寫固定字節格式數據。
DataOutputStream
創建對象
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(相接的流)
方法將一個 int 類型的數據寫到數據輸出流中,底層將 4 個字節寫到基礎輸出流中
writeInt(int i)
將一個 double 類型的數據寫到數據輸出流中,底層會將 double 轉換成 long 類型,寫到基礎輸出流中,輸出8個字節
writeDouble(double d)
以機器無關的方式使用 utf-8 編碼方式將字符串寫到基礎輸出流中。先輸出 2 個字節表示字符串的字節長度,再輸出這些字節值
writeUTF()
DataInputStream
創建對象
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(InputStream in);
方法從數據輸入流中讀取一個 int 類型數據,讀取 4 個字節
readInt()
讀取8個字節
readDouble()
先讀取 2 個字節來確定字符串的字節長度,再讀取這些字節值
readUTF()
Tips:讀取結束,再讀取會出現EOFException
栗子1:寫入數據
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/abc/f5"));
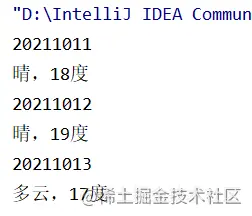
out.writeInt(20211011);
out.writeUTF("晴,18度");
out.writeInt(20211012);
out.writeUTF("晴,19度");
out.writeInt(20211013);
out.writeUTF("多雲,17度");
out.close();
}
}
運行結果:

栗子2:讀取
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:/abc/f5"));
try {
while (true) {
int date = in.readInt();
String s = in.readUTF();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
//正確讀取結束,不需要處理
}
in.close();
}
}
運行結果:
栗子3:保存學生信息
要求用如下格式保存學生信息:
學號 00 00 00 01
姓名 00 03 61 62 63
性別 00 61
年齡 00 00 00 16
xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="20dp">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="學號" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="姓名" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="性別" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="年齡" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="保存" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="讀取" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
java
public class IoActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText et1;
private EditText et2;
private EditText et3;
private EditText et4;
private Button btn1;
private Button btn2;
private TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_io);
setViews();
setListeners();
}
private void setViews() {
et1 = findViewById(R.id.et1);
et2 = findViewById(R.id.et2);
et3 = findViewById(R.id.et3);
et4 = findViewById(R.id.et4);
btn1 = findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn2 = findViewById(R.id.btn2);
tv = findViewById(R.id.tv);
}
private void setListeners() {
btn1.setOnClickListener(view -> baocun());
btn2.setOnClickListener(view -> duqu());
}
private void baocun() {
//IO操作有IO異常,所以進行try...catch...
/*
*
* ┌DataOutputStream
* ┌FileOutputStream
* sdcard
*/
try {
int id = Integer.parseInt(et1.getText().toString());
String name = et2.getText().toString();
String gender = et3.getText().toString();
int age = Integer.parseInt(et4.getText().toString());
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(getExternalFilesDir(null) + "/stu.txt", true)
);
out.writeInt(id);
out.writeUTF(name);
out.writeChar(gender.charAt(0));
out.writeInt(age);
out.close();
Toast.makeText(this, "保存成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
Toast.makeText(this, "保存失敗", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void duqu() {
//IO操作有IO異常,所以進行try...catch...
try {
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new FileInputStream(getExternalFilesDir(null) + "/stu.txt")
);
try {
tv.setText("");
while (true) {
int id = in.readInt();
String name = in.readUTF();
char gender = in.readChar();
int age = in.readInt();
tv.append("id:" + id + "\n" + "name:" + name + "\n" + "gender:" + gender + "\n" + "age:" + age + "\n");
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
}
in.close();
Toast.makeText(this, "讀取成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
Toast.makeText(this, "讀取失敗", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
運行程序:

點擊讀取按鈕:

其中getExternalFilesDir(null)得到以下路徑
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/yourPackageName/files
這個目錄會在應用被卸載的時候刪除,而且訪問這個目錄不需要動態申請STORAGE 權限。
所以運行程序會在這個路徑下生成一個 stu.txt 的文件
到此這篇關於Java中DataInputStream和DataOutputStream的使用方法的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關DataInputStream和DataOutputStream內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- Android studio實現簡易的計算器功能
- Android生成隨機數的方法實例
- Android開發手冊TextInputLayout樣式使用示例
- android I/0流操作文件(文件存儲)
- Android ListView仿微信聊天界面