python中字典的常見操作總結2
判斷字典中的元素是否存在
in 與 not in判斷元素是否存在
key in dict # 返回True或False key not in dict # 返回True或False
get()函數判斷元素是否存在
bool(dict.get(key)) # 返回True或False
註意:如果key對應的value是False,0,'',None等,那麼就會返回false,這樣的不準確瞭
例子:

字典中的popitem()函數
刪除字典末尾一組鍵值對,並將其返回
dict.popitem() # 無需傳參,返回被刪除的鍵值對,用元組包裹,0索引是key,1索引是value
註意:如果字典為空,會報錯
例子:
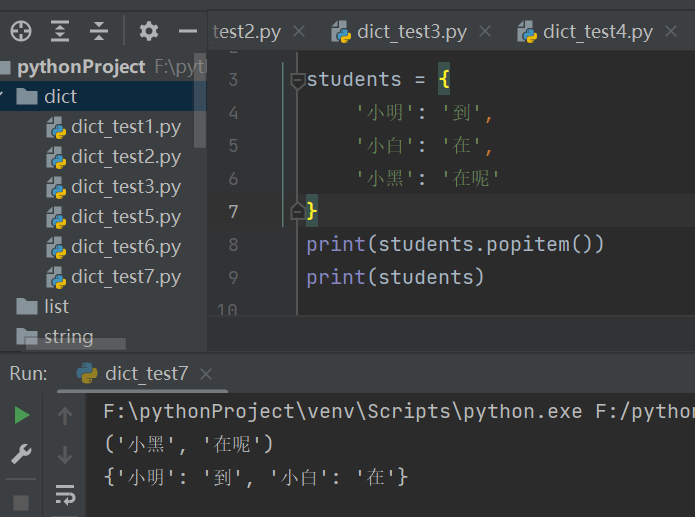
students = {
'小明': '到',
'小白': '在',
'小黑': '在呢'
}
print(students.popitem())
print(students)
print(students.popitem()))
print(students)
所有數據類型與其佈爾值

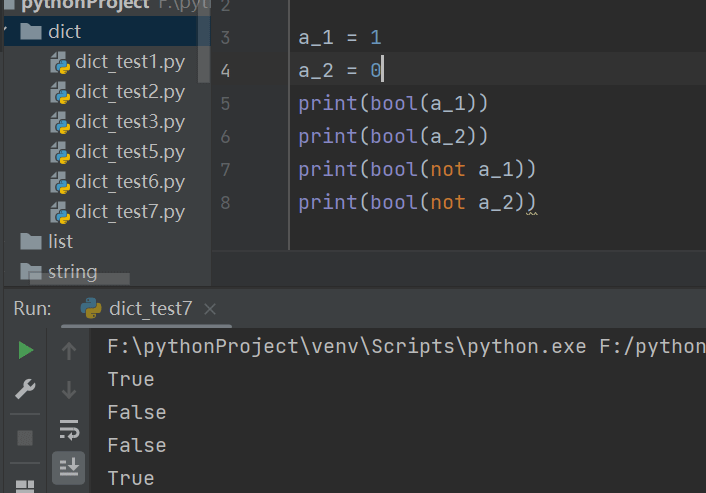
例子:
a_1 = 1 a_2 = 0 print(bool(a_1)) print(bool(a_2)) print(bool(not a_1)) print(bool(not a_2))
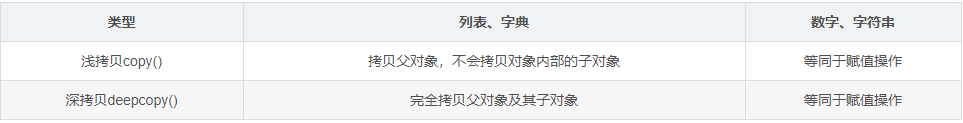
深拷貝與淺拷貝總結
例子:
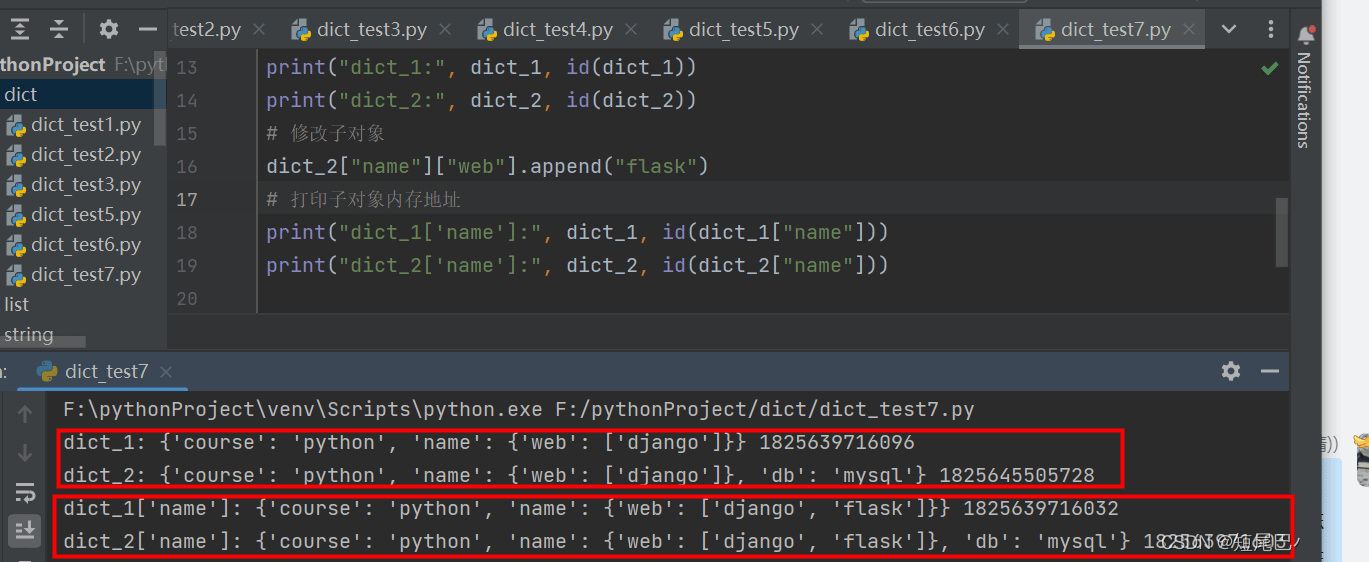
淺拷貝:
import copy
dict_1 = {
"course": "python",
"name": {"web": ["django"]}
}
dict_2 = copy.copy(dict_1)
# 修改父對象
dict_2["db"] = "mysql"
# 打印父對象內存地址
print("dict_1:", dict_1, id(dict_1))
print("dict_2:", dict_2, id(dict_2))
# 修改子對象
dict_2["name"]["web"].append("flask")
# 打印子對象內存地址
print("dict_1['name']:", dict_1, id(dict_1["name"]))
print("dict_2['name']:", dict_2, id(dict_2["name"]))
運行結果:
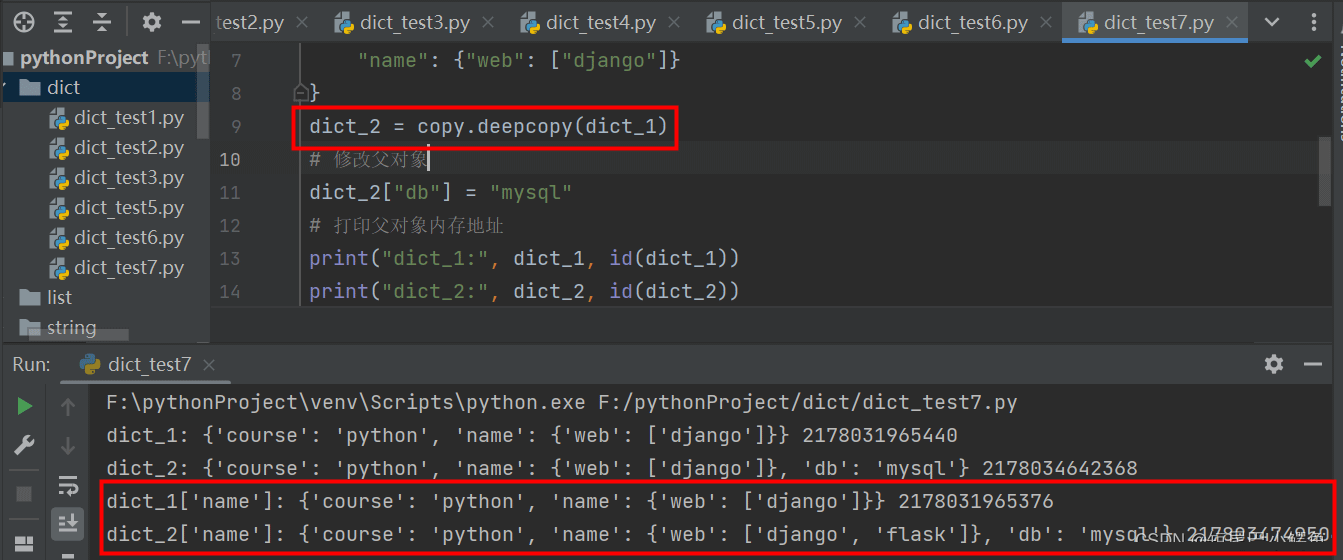
將淺拷貝換成深拷貝後,運行結果:
到此這篇關於python中字典的常見操作總結2的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關python字典操作內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- Python中淺拷貝的四種實現方法小結
- Python學習之列表常用方法總結
- Python解析JSON對象的全過程記錄
- Python函數進階與文件操作詳情
- Python字典刪除鍵值對和元素的四種方法(小結)