react中使用forEach或map兩種方式遍歷數組
使用forEach或map兩種方式遍歷數組
之前寫代碼,從後臺提取數據並渲染到前臺,由於有多組數據,用map遍歷會相對方便一點,但是
map不能遍歷array數組,隻能遍歷object對象。
所以如果遇到這樣的問題可以采用forEach試一下
forEach
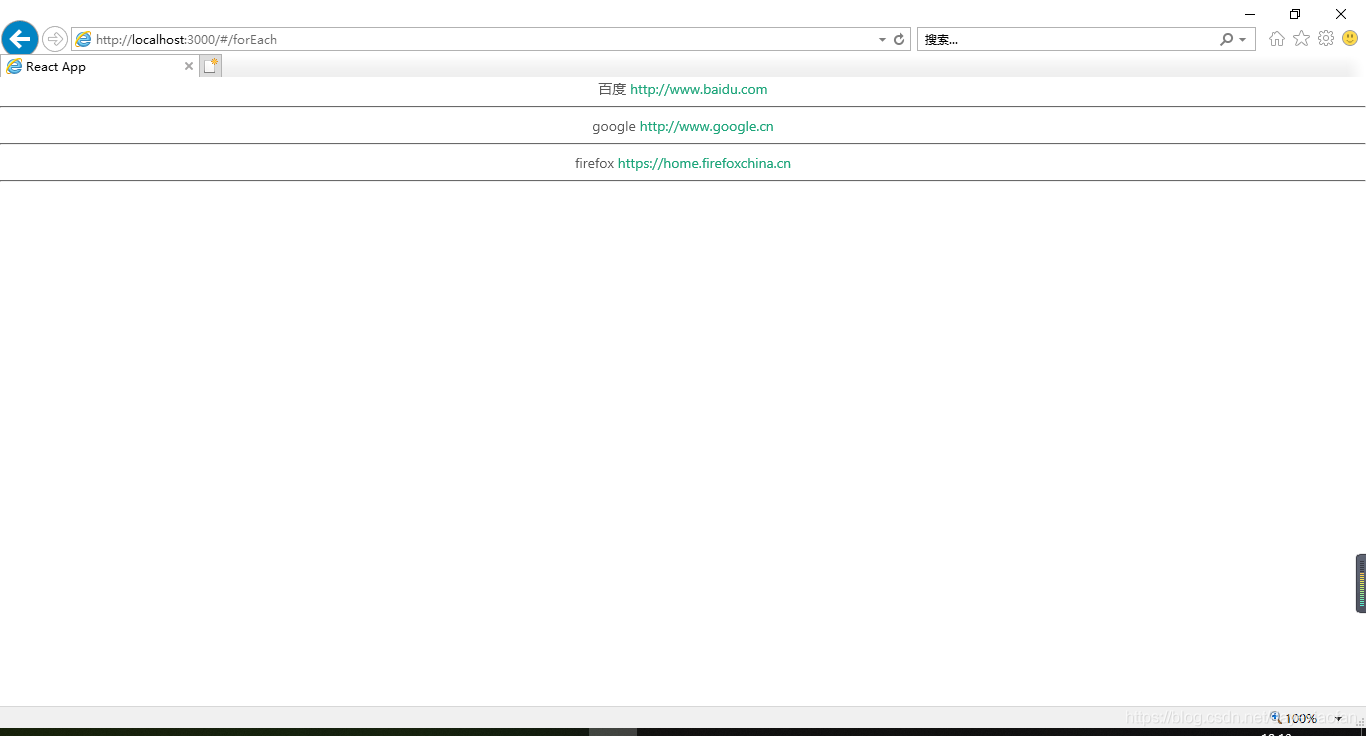
import React,{Component} from 'react';
let list=[
{
name:"百度",
address:"http://www.baidu.com"
},
{
name:"google",
address:"http://www.google.cn"
},
{
name:"firefox",
address:"https://home.firefoxchina.cn"
}
];
class forEach extends Component{
render(){
//定義一個數組,將數據存入數組
const elements=[];
list.forEach((item)=>{
elements.push(
<div>
{item.name}
<a>{item.address}</a>
<hr/>
</div>
)
});
return(
<div>
{elements}
</div>
)
}
}
export default forEach;
map
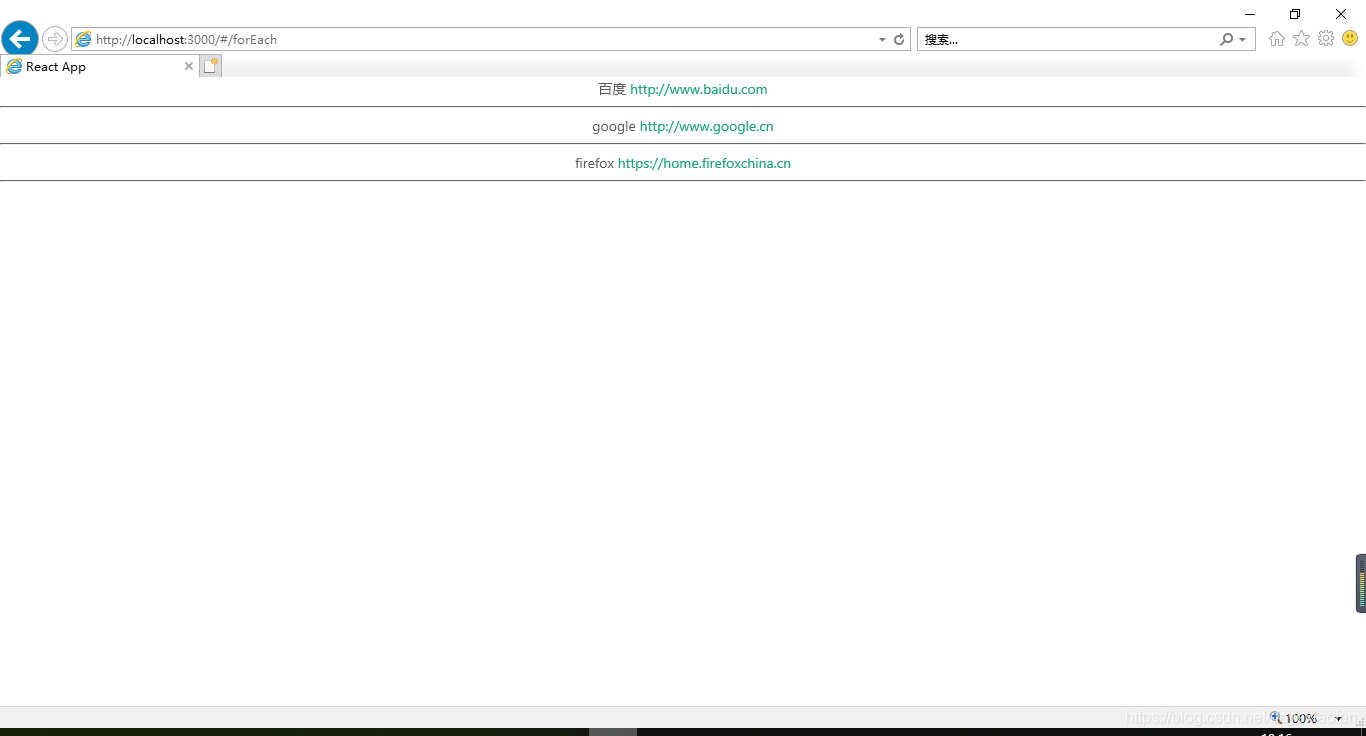
import React,{Component} from 'react';
let list=[
{
name:"百度",
address:"http://www.baidu.com"
},
{
name:"google",
address:"http://www.google.cn"
},
{
name:"firefox",
address:"https://home.firefoxchina.cn"
}
];
class forEach extends Component{
render(){
return(
list.map((item)=>
<div>
{item.name}
<a>{item.address}</a>
<hr/>
</div>
)
)
}
}
export default forEach;
循環遍歷數組時map和forEach的區別
1. map函數返回一個新的數組,在map的回調函數裡,迭代每一項的時候也必須有返回值。
2. forEach 沒有返回值
forEach情況
import React, { Component } from "react"
import ListItem from './ListItem'
class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
inputValue: '',
list: ['bb', 'ccc']
};
this.changeInput = this.changeInput.bind(this);
}
changeInput(e) {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value
})
}
commitInput = () => {
const newList = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.state.list));
newList.push(this.state.inputValue);
this.setState({
list: newList,
inputValue: ''
})
}
deleteItem = index => {
this.state.list.splice(index, 1);
this.setState ({
list: this.state.list
})
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('parent didmount')
}
render() {
console.log('parent render')
const elements = []
this.state.list.forEach((item, index) => {
elements.push(
<ListItem
key={index}
content={item}
index={index}
deleteItem={(index) => { this.deleteItem(index) }}
/>
)
})
{
console.log('zzz')
}
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={this.state.inputValue} onChange={this.changeInput} />
<button onClick={this.commitInput}>提交</button>
<ul>
{
console.log('mmm')
}
{
elements
}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
export default TodoList
map 情況
import React, { Component } from "react"
import ListItem from './ListItem'
class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
inputValue: '',
list: ['bb', 'ccc']
};
this.changeInput = this.changeInput.bind(this);
}
changeInput(e) {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value
})
}
commitInput = () => {
const newList = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.state.list));
newList.push(this.state.inputValue);
this.setState({
list: newList,
inputValue: ''
})
}
deleteItem = index => {
this.state.list.splice(index, 1);
this.setState ({
list: this.state.list
})
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('parent didmount')
}
render() {
console.log('parent render')
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={this.state.inputValue} onChange={this.changeInput} />
<button onClick={this.commitInput}>提交</button>
<ul>
{
this.state.list.map((item, index) => {
return(
<ListItem
key={index}
content={item}
index={index}
deleteItem={(index) => { this.deleteItem(index) }}
/>
)
})
}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
export default TodoList
以上為個人經驗,希望能給大傢一個參考,也希望大傢多多支持WalkonNet。
推薦閱讀:
- 入門React的這些重要知識點你都知道嗎
- React setState是異步還是同步原理解析
- React Class組件生命周期及執行順序
- React 原理詳解
- React父子組件傳值(組件通信)的實現方法