C/C++中多重繼承詳解及其作用介紹
概述
多重繼承 (multiple inheritance): 一個派生類有兩個或多個基類, 派生類從兩個或多個基類中繼承所需的屬性. C++ 為瞭適應這種情況, 允許一個派生類同時繼承多個基類. 這種行為稱為多重繼承.
優缺點
優點
- 自然地做到瞭對單繼承的擴展
- 可以繼承多個類的功能
缺點
- 結構復雜化
- 優先順序模糊
- 功能沖突
聲明多重繼承的方法
格式
多重繼承的格式:
派生類構造函數名(總形式參數表列):
基類1構造函數(實際參數表列),
基類2構造函數(實際參數表列),
基類3構造函數(實際參數表列)
{
派生類中新增數成員據成員初始化語句
}
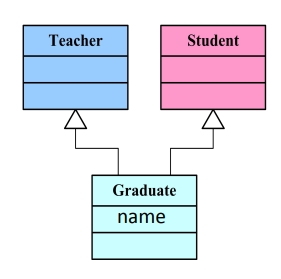
例子
Teacher 類:
#ifndef PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#define PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher {
protected:
string name;
int age;
string title;
public:
Teacher(string n, int a, string t);
void display_teacher();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_TEACHER_H
Teacher.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Teacher.h"
using namespace std;
Teacher::Teacher(string n, int a, string t) : name(n), age(a), title(t) {}
void Teacher::display_teacher() {
cout << "Teacher name: " << name << endl;
cout << "age: " << age << endl;
cout << "title: " << title << endl;
}
Student 類:
#ifndef PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#define PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student {
protected:
string name;
char gender;
double score;
public:
Student(string n, char g, double s);
void display_student();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_STUDENT_H
Student.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "Student.h"
using namespace std;
Student::Student(string n, char g, double s) : name(n), gender(g), score(s) {}
void Student::display_student() {
cout << "Student name: " << name << endl;
cout << "gender: " << gender << endl;
cout << "score: " << score << endl;
}
Graduate 類:
#ifndef PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#define PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
#include "Teacher.h"
#include "Student.h"
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Graduate : public Teacher, public Student{
private:
double wage;
public:
Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s);
void display_graduate();
};
#endif //PROJECT5_GRADUATE_H
Graduate.cpp:
#include "Graduate.h"
Graduate::Graduate(string t_n, int t_a, string t_t, string s_n, char s_g, double s_s) :
Teacher(t_n, t_a, t_t),
Student(s_n, s_g, s_s) {}
void Graduate::display_graduate() {
display_teacher();
display_student();
}
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Graduate.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Graduate graduate1("王叔叔", 18, "隔壁老王", "我是小白呀", 'f', 99);
graduate1.display_graduate();
return 0;
}
輸出結果:
Teacher name: 王叔叔 age: 18 title: 隔壁老王 Student name: 我是小白呀 gender: f score: 99
二義性
二義性 (Ambiguity) 指在多重繼承中, 兩個基類中的數據成員名相同.
二義性在派生類中的解決方法:
- 在標識符前用類名做前綴: Teacher::name 和 Student::name
- 基類和派生類需要有一個完整的設計, 不能隨意而為
兩個基類有同名成員
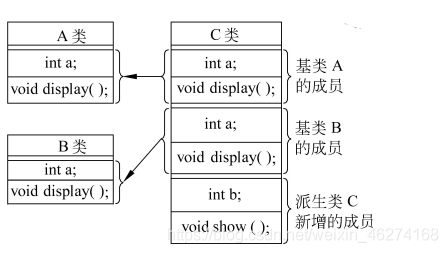
A 類:
#ifndef PROJECT5_A_H
#define PROJECT5_A_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_A_H
B 類:
#ifndef PROJECT5_B_H
#define PROJECT5_B_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class B {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_B_H
C 類:
#ifndef PROJECT5_C_H
#define PROJECT5_C_H
#include <iostream>
#include "A.h"
#include "B.h"
using namespace std;
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int c;
void display() {cout << c << endl;};
};
#endif //PROJECT5_C_H
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
C c1;
c1.A::num = 1; // 用基類名限定
c1.B::num = 2; // 用基類名限定
c1.A::display();
c1.B::display();
return 0;
}
輸出結果:
A's num:1 B's num:2
錯誤的寫法
#include <iostream>
#include "C.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
C c1;
c1.num = 1;
c1.display();
return 0;
}
基類和派生類有同名成員
A 類:
class A {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "A's num:" << num << endl;};
};
B 類:
class B {
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "B's num:" << num << endl;};
};
C 類:
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int num;
void display() {cout << "C's num:" << num << endl;};
};
main:
int main() {
C c1;
c1.num = 3;
c1.A::num = 1;
c1.B::num = 2;
c1.display();
c1.A::display();
c1.B::display();
return 0;
}
輸出結果:
C's num:3 A's num:1 B's num:2
同名覆蓋:
- 基類的同名成員在派生類中被屏蔽, 成為 “不可見”的
- 對成員函數, 限於函數名和參數個數相同, 類型相匹配. 若隻有函數名相同而參數不同, 屬於函數重載
兩個基類從同一個基類派生
N 類:
class N {
public:
int a;
void display(){
cout << "A::a=" << a <<endl;
}
};
A 類:
class A : public N {
public:
int a1;
};
B 類:
class B : public N {
public:
int a2;
};
C 類:
class C: public A, public B{
public:
int a3;
void display() {cout << "a3=" << a3 << endl;};
};
main:
int main() {
C c1;
// 合法訪問
c1.A::a = 3;
c1.A::display();
return 0;
}
輸出結果:
A::a=3
到此這篇關於C/C++中多重繼承詳解及其作用介紹的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關C++多重繼承內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- C/C++中虛基類詳解及其作用介紹
- C++中繼承(inheritance)詳解及其作用介紹
- C++中對象&類的深入理解
- C/C++中組合詳解及其作用介紹
- C++ 組合 (Composition)的介紹與實例