一文搞懂Codec2解碼組件
1 前言
在本篇中,我們將關註Codec 2.0以下幾個問題:
1.從頂而下,一個解碼組件是如何創建的
2.組件的接口有哪些,分別是什麼含義
3.組件是如何運行的,輸入與輸出的數據流是怎樣的
2 組件的創建
CCodec在allocate中,通過CreateComponentByName創建瞭具體的解碼組件。
//android/frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplguin/CCodec.cpp
void CCodec::allocate(const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &codecInfo) {
...
AString componentName = codecInfo->getCodecName();
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client;
// set up preferred component store to access vendor store parameters
//從CCodec調用到component是通過HAL層服務的,默認谷歌的原生服務為
//android.hardware.media.c2@IComponentStore/software,默認廠商的服務為
//android.hardware.media.c2@IComponentStore/default,在android小機shell中通過lshal|grep media可以查詢
//到正在運行的codec2服務,如果廠商已支持codec2,則可以查詢到default服務。如果CCodec中能夠創建到default
//服務,則可以將該服務設置為Preferred Codec2 ComponentStore,也就是將其作為目標組件。
client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService("default");
if (client) {
ALOGI("setting up '%s' as default (vendor) store", client->getServiceName().c_str());
SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(
std::make_shared<Codec2ClientInterfaceWrapper>(client));
}
//創建具體的解碼組件或者編碼組件,譬如c2.android.avc.decoder
//所有omx與codec2的編解碼組件支持列表可以在libstagefright/data目錄下的xml中查詢得到,它們的加載與
//排序情況可以在libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp中追蹤
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> comp =
Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
componentName.c_str(),
mClientListener,
&client);
...
ALOGI("Created component [%s]", componentName.c_str());
mChannel->setComponent(comp);
auto setAllocated = [this, comp, client] {
Mutexed<State>::Locked state(mState);
if (state->get() != ALLOCATING) {
state->set(RELEASED);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
state->set(ALLOCATED);
state->comp = comp;
mClient = client;
return OK;
};
...
// initialize config here in case setParameters is called prior to configure
Mutexed<Config>::Locked config(mConfig);
status_t err = config->initialize(mClient, comp);
...
config->queryConfiguration(comp);
mCallback->onComponentAllocated(componentName.c_str());
}
繼續追蹤Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName接口。
//android/frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component>
Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
const char* componentName,
const std::shared_ptr<Listener>& listener,
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client>* owner,
size_t numberOfAttempts) {
std::string key{"create:"};
key.append(componentName);
std::shared_ptr<Component> component;
c2_status_t status = ForAllServices(
key,
numberOfAttempts,
[owner, &component, componentName, &listener](
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> &client)
-> c2_status_t {
//調用Codec2Client類的createComponent接口,獲取component
c2_status_t status = client->createComponent(componentName,
listener,
&component);
...
return status;
});
...
return component;
}
追蹤Codec2Client類的createComponent接口。
\\av\media\codec2\hidl\client\client.cpp
c2_status_t Codec2Client::createComponent(
const C2String& name,
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Listener>& listener,
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component>* const component) {
c2_status_t status;
sp<Component::HidlListener> hidlListener = new Component::HidlListener{};
hidlListener->base = listener;
//這裡的mBase是什麼?這裡調用的是IComponentStore的createComponent接口
Return<void> transStatus = mBase->createComponent(
name,
hidlListener,
ClientManager::getInstance(),
[&status, component, hidlListener](
Status s,
const sp<IComponent>& c) {
status = static_cast<c2_status_t>(s);
if (status != C2_OK) {
return;
}
*component = std::make_shared<Codec2Client::Component>(c);
hidlListener->component = *component;
});
...
return status;
}
我們先看一下IComponentStore的createComponent接口。
\\av\media\codec2\hidl\1.0\utils\include\codec2\hidl\1.0\ComponentStore.h
struct ComponentStore : public IComponentStore {
ComponentStore(const std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentStore>& store);
virtual ~ComponentStore() = default;
// Methods from ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore.
virtual Return<void> createComponent(
const hidl_string& name,
const sp<IComponentListener>& listener,
const sp<IClientManager>& pool,
createComponent_cb _hidl_cb) override;
virtual Return<void> createInterface(
const hidl_string& name,
createInterface_cb _hidl_cb) override;、
...
}
該接口的實現為:
\\av\media\codec2\hidl\1.0\utils\ComponentStore.cpp
// Methods from ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore
Return<void> ComponentStore::createComponent(
const hidl_string& name,
const sp<IComponentListener>& listener,
const sp<IClientManager>& pool,
createComponent_cb _hidl_cb) {
sp<Component> component;
std::shared_ptr<C2Component> c2component;
//C2PlatformComponentStore的createComponent調用
//調用C2PlatformComponentStore的createComponent接口,返回的是一個C2Component對象
//譬如,這個對象可以是C2SoftAvcDec Component對象,也可以是VendorHwAvcDec Component對象
Status status = static_cast<Status>(
mStore->createComponent(name, &c2component));
if (status == Status::OK) {
onInterfaceLoaded(c2component->intf());
//把前面創建的C2SoftAvcDec“裝載”到Component類中,Client調用Component
//Component內部會調用到C2SoftAvcDec
//Component相當於對原生編解碼組件/廠商編解碼組件的統一封裝
component = new Component(c2component, listener, this, pool);
if (!component) {
status = Status::CORRUPTED;
} else {
reportComponentBirth(component.get());
if (component->status() != C2_OK) {
status = static_cast<Status>(component->status());
} else {
component->initListener(component);
if (component->status() != C2_OK) {
status = static_cast<Status>(component->status());
}
}
}
}
_hidl_cb(status, component);
return Void();
}
關於C2PlatformComponentStore的createComponent調用,它的實現在C2Store.cpp中,它繼承於C2ComponentStore類,有幾個重要成員對象,ComponentModule,ComponentLoader,有幾個重要的接口,listComponents(),createComponent(),createInterface()。ComponentLoader包含ComponentModule對象,而ComponentModule主要提供兩個接口,createComponent()與createInterface(),內部也包含著C2ComponentFactory成員以及它的創建與銷毀接口,分別是C2ComponentFactory::CreateCodec2FactoryFunc,C2ComponentFactory::DestroyCodec2FactoryFunc。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
class C2PlatformComponentStore : public C2ComponentStore {
public:
virtual std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits>> listComponents() override;
...
virtual c2_status_t createInterface(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> *const interface) override;
virtual c2_status_t createComponent(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<C2Component> *const component) override;
virtual ~C2PlatformComponentStore() override = default;
private:
/**
* An object encapsulating a loaded component module.
*/
struct ComponentModule : public C2ComponentFactory,
public std::enable_shared_from_this<ComponentModule> {
virtual c2_status_t createComponent(
c2_node_id_t id, std::shared_ptr<C2Component> *component,
ComponentDeleter deleter = std::default_delete<C2Component>()) override;
virtual c2_status_t createInterface(
c2_node_id_t id, std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> *interface,
InterfaceDeleter deleter = std::default_delete<C2ComponentInterface>()) override;
...
protected:
...
void *mLibHandle; ///< loaded library handle
C2ComponentFactory::CreateCodec2FactoryFunc createFactory; ///< loaded create function
C2ComponentFactory::DestroyCodec2FactoryFunc destroyFactory; ///< loaded destroy function
C2ComponentFactory *mComponentFactory; ///< loaded/created component factory
};
/**
* An object encapsulating a loadable component module.
*/
struct ComponentLoader {
/**
* Load the component module.
*
* This method simply returns the component module if it is already currently loaded, or
* attempts to load it if it is not.
*/
c2_status_t fetchModule(std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
c2_status_t res = C2_OK;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> localModule = mModule.lock();
if (localModule == nullptr) {
localModule = std::make_shared<ComponentModule>();
res = localModule->init(mLibPath);
if (res == C2_OK) {
mModule = localModule;
}
}
*module = localModule;
return res;
}
/**
* Creates a component loader for a specific library path (or name).
*/
ComponentLoader(std::string libPath)
: mLibPath(libPath) {}
private:
std::weak_ptr<ComponentModule> mModule; ///< weak reference to the loaded module
};
struct Interface : public C2InterfaceHelper {
...
};
/**
* Retrieves the component module for a component.
*/
c2_status_t findComponent(C2String name, std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module);
/**
* Loads each component module and discover its contents.
*/
void visitComponents();
std::map<C2String, ComponentLoader> mComponents; ///< path -> component module
std::map<C2String, C2String> mComponentNameToPath; ///< name -> path
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits>> mComponentList;
...
};
C2PlatformComponentStore::createComponent調用findComponent(name, &module)找到擁有component的ComponentModule,再通過module->createComponent(0, component)調用,找到相應的component。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t C2PlatformComponentStore::createComponent(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<C2Component> *const component) {
// This method SHALL return within 100ms.
component->reset();
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> module;
c2_status_t res = findComponent(name, &module);
if (res == C2_OK) {
// TODO: get a unique node ID
res = module->createComponent(0, component);
}
return res;
}
findComponent(name, &module)有兩步,先通過visitComponents()列舉出所有可用的components,再調用ComponentLoader的fetchModule(),找到擁有component的ComponentModule。module可以看作是組件,加載某個module,也就是加載對應的組件,module提供的 createComponent()接口就是用來創建具體component的,譬如C2SoftAvcDec。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t C2PlatformComponentStore::findComponent(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
(*module).reset();
visitComponents();
auto pos = mComponentNameToPath.find(name);
if (pos != mComponentNameToPath.end()) {
return mComponents.at(pos->second).fetchModule(module);
}
return C2_NOT_FOUND;
}
visitComponents()訪問mComponents對象(這是一個map對象,將path與component module映射關聯,這一映射工作在C2PlatformComponentStore初始化時進行),遍歷所有的mComponents,即pathAndLoader對象,如果一個對象的loader能夠加載成功,則添加到mComponentNameToPath對象中。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
void C2PlatformComponentStore::visitComponents() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
if (mVisited) {
return;
}
//參考定義 std::map<C2String, ComponentLoader> mComponents; ///< path -> component module
for (auto &pathAndLoader : mComponents) {
const C2String &path = pathAndLoader.first;
ComponentLoader &loader = pathAndLoader.second;
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> module;
if (loader.fetchModule(&module) == C2_OK) {
std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits> traits = module->getTraits();
if (traits) {
mComponentList.push_back(traits);
mComponentNameToPath.emplace(traits->name, path);
for (const C2String &alias : traits->aliases) {
mComponentNameToPath.emplace(alias, path);
}
}
}
}
mVisited = true;
}
loader.fetchModule(&module)這個函數定義在ComponentLoader類中,在這裡再貼一次代碼。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t fetchModule(std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
c2_status_t res = C2_OK;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> localModule = mModule.lock();
if (localModule == nullptr) {
localModule = std::make_shared<ComponentModule>();
res = localModule->init(mLibPath);
if (res == C2_OK) {
mModule = localModule;
}
}
*module = localModule;
return res;
}
對於module,會調用初始化函數,初始化成功就算是fetch到瞭。初始化作瞭什麼工作,參見C2PlatformComponentStore::ComponentModule::init函數,也就是對編解碼庫dlopen成功,可獲得相應的函數地址,譬如,C2SoftAvcDec.cpp中的C2ComponentFactory* CreateCodec2Factory()與void DestroyCodec2Factory()。當然還有其他,不面面俱道瞭。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t C2PlatformComponentStore::ComponentModule::init(
std::string libPath) {
ALOGV("in %s", __func__);
ALOGV("loading dll");
mLibHandle = dlopen(libPath.c_str(), RTLD_NOW|RTLD_NODELETE);
createFactory =
(C2ComponentFactory::CreateCodec2FactoryFunc)dlsym(mLibHandle, "CreateCodec2Factory");
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(createFactory == nullptr,
"createFactory is null in %s", libPath.c_str());
destroyFactory =
(C2ComponentFactory::DestroyCodec2FactoryFunc)dlsym(mLibHandle, "DestroyCodec2Factory");
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(destroyFactory == nullptr,
"destroyFactory is null in %s", libPath.c_str());
mComponentFactory = createFactory();
...
std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> intf;
c2_status_t res = createInterface(0, &intf);
...
return mInit;
}
那麼問題來瞭,為什麼谷歌對它自己的codec2插件組C2PlatformComponentStore設計得這麼復雜,能不能簡化一點。
3 組件接口
在codec2/components目錄下,有base, avc, aom, hevc, aac等文件夾,base目錄下是SimpleC2Component.cpp與SimpleC2Interface.cpp以及對應的頭文件,avc目錄下是C2SoftAvcDec.cpp,C2SoftAvcEnc.cpp以及對應的頭文件,其他編解碼器文件夾亦同樣道理。C2SoftAvcDec,C2SoftHevcDec等編解碼器類都是繼承於SimpleC2Component類的,也就是說,SimpleC2Component是components的頂層類,它對接瞭component類的接口,實現瞭編解碼器的公共流程部分,C2SoftAvcDec,C2SoftHevcDec等子類繼承SimpleC2Component的一些接口,實現各自的編解碼操作。
SimpleC2Component實現的component的接口如下:
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\include\SimpleC2Component.h
// C2Component
// From C2Component
//設置回調
virtual c2_status_t setListener_vb(
const std::shared_ptr<Listener> &listener, c2_blocking_t mayBlock) override;
//送數據到component,數據打包成某種對象,叫C2Work,這個對象很關鍵,它包含input與output
virtual c2_status_t queue_nb(std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>>* const items) override;
//暫時沒有多大用處,不管它
virtual c2_status_t announce_nb(const std::vector<C2WorkOutline> &items) override;
//跳播使用,將當前數據沖刷掉
virtual c2_status_t flush_sm(
flush_mode_t mode, std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>>* const flushedWork) override;
//渲染可用的幀
virtual c2_status_t drain_nb(drain_mode_t mode) override;
virtual c2_status_t start() override;
virtual c2_status_t stop() override;
virtual c2_status_t reset() override;
virtual c2_status_t release() override;
virtual std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> intf() override;
而C2SoftAvcDec,C2SoftHevcDec等子類繼承SimpleC2Component的接口如下:
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\include\SimpleC2Component.h
virtual c2_status_t onInit() = 0;
virtual c2_status_t onStop() = 0;
virtual void onReset() = 0;
virtual void onRelease() = 0;
virtual c2_status_t onFlush_sm() = 0;
//最重要的處理函數,處理的對象是C2Work,它包含著輸入輸出,交互配置方面的類。
virtual void process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) = 0;
virtual c2_status_t drain(
uint32_t drainMode,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) = 0;
4 組件運行原理
SimpleC2Component有一個成員對象WorkHandler,這個類繼承於AHandler,也就是說,SimpleC2Component內部運行一個線程,來自上層的接口調用,都可以發送消息到onMessageReceived中排隊處理,譬如初始化、停止、重置、釋放以及數據處理等工作,都在隊列中排隊處理,相應的處理都是調用到子類的實現,譬如,onInit(),onStop(),onReset(),onRelease(),以及processQueue()。
我們可以看一下onMessageReceived的實現。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
void SimpleC2Component::WorkHandler::onMessageReceived(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
std::shared_ptr<SimpleC2Component> thiz = mThiz.lock();
...
switch (msg->what()) {
case kWhatProcess: {
if (mRunning) {
if (thiz->processQueue()) {
(new AMessage(kWhatProcess, this))->post();
}
} else {
ALOGV("Ignore process message as we're not running");
}
break;
}
case kWhatInit: {
int32_t err = thiz->onInit();
Reply(msg, &err);
[[fallthrough]];
}
case kWhatStart: {
mRunning = true;
break;
}
case kWhatStop: {
int32_t err = thiz->onStop();
Reply(msg, &err);
break;
}
case kWhatReset: {
thiz->onReset();
mRunning = false;
Reply(msg);
break;
}
case kWhatRelease: {
thiz->onRelease();
mRunning = false;
Reply(msg);
break;
}
default: {
ALOGD("Unrecognized msg: %d", msg->what());
break;
}
}
}
我們看一下AVC解碼器內部是如何處理輸入與輸出數據的,在這個process中,處理完輸入,解碼,處理輸出,在處理output buffer時,process的思路是這樣的:從內存池申請一個GraphicBlock,對應地設置給解碼器Buffer地址以供解碼輸出,如果解碼後有幀輸出,則將當前的GraphicBlock轉換為C2Buffer對象,返回給上層。類似於FFMPEG,你給它一個output frame,它就將解碼圖片填充到frame,你取走顯示。可以推斷,軟解碼器內部應該也有申請一個隊列的buffer,這個隊列維護著解碼所需要的參考圖像。
\\av\media\codec2\components\avc\C2SoftAvcDec.cpp
//省略瞭部分不影響理解主要流程的代碼
void C2SoftAvcDec::process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) {
// Initialize output work
work->result = C2_OK;
work->workletsProcessed = 0u;
work->worklets.front()->output.flags = work->input.flags;
size_t inOffset = 0u;
size_t inSize = 0u;
uint32_t workIndex = work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku() & 0xFFFFFFFF;
C2ReadView rView = mDummyReadView;
if (!work->input.buffers.empty()) {
//為瞭得到輸入數據,層層訪問,真正放數據的地址在rView.data()[]中
//把work這個對象用思維導圖畫出來,我們可以更容易的理解work,到底擁有哪些成員,如何訪問
rView = work->input.buffers[0]->data().linearBlocks().front().map().get();
inSize = rView.capacity();
...
}
bool eos = ((work->input.flags & C2FrameData::FLAG_END_OF_STREAM) != 0);
bool hasPicture = false;
ALOGV("in buffer attr. size %zu timestamp %d frameindex %d, flags %x",
inSize, (int)work->input.ordinal.timestamp.peeku(),
(int)work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku(), work->input.flags);
size_t inPos = 0;
while (inPos < inSize) {
//ensureDecoderState會從內存池中fetch一個GraphicBlock
//實質上也就是調用Gralloc接口取得一個output buffer
if (C2_OK != ensureDecoderState(pool)) {
mSignalledError = true;
work->workletsProcessed = 1u;
work->result = C2_CORRUPTED;
return;
}
ivd_video_decode_ip_t s_decode_ip;
ivd_video_decode_op_t s_decode_op;
{
//mOutBlock即是上述fetch到的output buffer,通過map映射可以得到一個wView,類似於rView
//wView.data()[]指向out buffer的真正地址
//wView.data()[C2PlanarLayout::PLANE_Y]就是要存在Y變量的地址
//wView.data()[C2PlanarLayout::PLANE_U]就是要存在U變量的地址
C2GraphicView wView = mOutBlock->map().get();
...
//setDecodeArgs所作的主要工作是,告訴解碼器,輸入數據的地址是什麼,輸出地址包括Y/U/V
//分量的地址是什麼,輸入數據的長度是多少
if (!setDecodeArgs(&s_decode_ip, &s_decode_op, &rView, &wView,
inOffset + inPos, inSize - inPos, workIndex)) {
mSignalledError = true;
work->workletsProcessed = 1u;
work->result = C2_CORRUPTED;
return;
}
if (false == mHeaderDecoded) {
/* Decode header and get dimensions */
setParams(mStride, IVD_DECODE_HEADER);
}
//解碼器庫是用瞭第三方的,已經被谷歌收購
(void) ivdec_api_function(mDecHandle, &s_decode_ip, &s_decode_op);
}
if (s_decode_op.i4_reorder_depth >= 0 && mOutputDelay != s_decode_op.i4_reorder_depth) {
//目前不清楚把這個重排序長度告訴上層有什麼作用,TODO
mOutputDelay = s_decode_op.i4_reorder_depth;
ALOGV("New Output delay %d ", mOutputDelay);
C2PortActualDelayTuning::output outputDelay(mOutputDelay);
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<C2SettingResult>> failures;
c2_status_t err =
mIntf->config({&outputDelay}, C2_MAY_BLOCK, &failures);
if (err == OK) {
work->worklets.front()->output.configUpdate.push_back(
C2Param::Copy(outputDelay));
}
continue;
}
if (0 < s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd && 0 < s_decode_op.u4_pic_ht) {
if (mHeaderDecoded == false) {
mHeaderDecoded = true;
setParams(ALIGN64(s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd), IVD_DECODE_FRAME);
}
if (s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd != mWidth || s_decode_op.u4_pic_ht != mHeight) {
mWidth = s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd;
mHeight = s_decode_op.u4_pic_ht;
CHECK_EQ(0u, s_decode_op.u4_output_present);
C2StreamPictureSizeInfo::output size(0u, mWidth, mHeight);
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<C2SettingResult>> failures;
c2_status_t err = mIntf->config({&size}, C2_MAY_BLOCK, &failures);
if (err == OK) {
work->worklets.front()->output.configUpdate.push_back(
C2Param::Copy(size));
}
continue;
}
}
(void)getVuiParams();
hasPicture |= (1 == s_decode_op.u4_frame_decoded_flag);
if (s_decode_op.u4_output_present) {
//通過createGraphicBuffer調用,將mOutBlock"轉換"成C2Buffer對象
//把C2Buffer添加到work對象的輸出隊列中
//通過listener->onWorkDone_nb回調,可以將work返回到CCodec層
//以上是這個函數以及其內部調用的主要實現內容,內部調用的finish()函數屬於SimpleC2Component
finishWork(s_decode_op.u4_ts, work);
}
inPos += s_decode_op.u4_num_bytes_consumed;
}
if (eos) {
drainInternal(DRAIN_COMPONENT_WITH_EOS, pool, work);
mSignalledOutputEos = true;
} else if (!hasPicture) {
fillEmptyWork(work);
}
work->input.buffers.clear();
}
在Component中,輸入與輸出對象都封裝在work對象中,甚至上下層的配置交互對象也包括在work對象中,與OMX是不一樣的,OMX的數據對象是BufferHeader,輸入是一個Input BufferHeader,輸出是一個Output BufferHeader,對象中包括buffer地址,分配的buffer大小,有效數據長度,有效數據長度的偏移量,buffer標志等。 那麼,work對象也應該會包括類似的成員。
我們來看兩張思維導圖,全局觀察work對象。
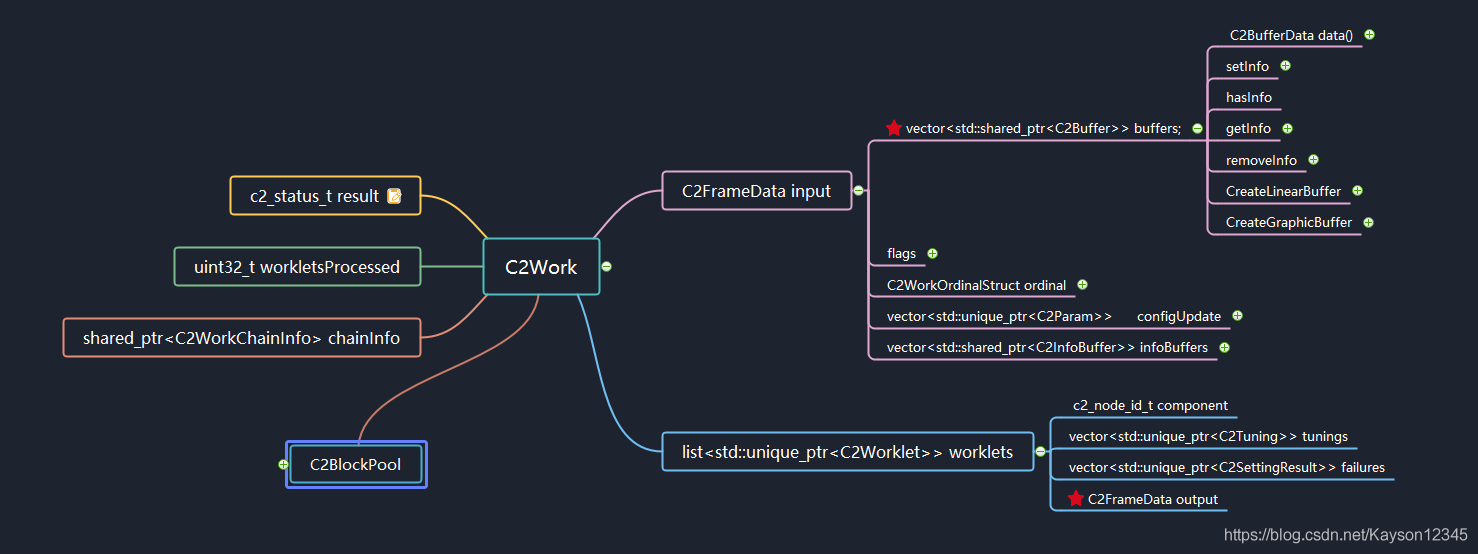
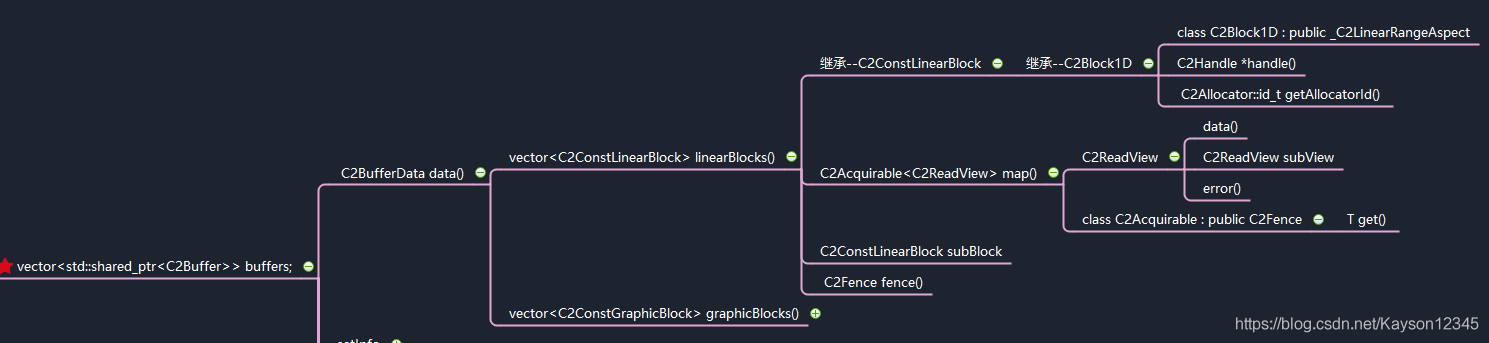
C2SoftAvcDec::process中有一句代碼,從work中訪問rView。
rView = work->input.buffers[0]->data().linearBlocks().front().map().get();
從上述兩圖中,我們可以追蹤這一條訪問線路,訪問C2Work對象的成員C2FrameData,繼續訪問C2FrameData對外的成員vector linearBlocks(),C2ConstLinearBlock有一個方法C2Acquirable map(),這個映射方法返回一個C2ReadView對象,這個C2ReadView對象有一個data()[]數組,指向瞭Y/U/V的向量地址,也就是真正存放解碼數據的內存地址。而Input與Output都是以C2FrameData來描述,Output並非像Input一樣,直接作為C2Work的成員,而是作為C2Work->worklets的成員。worklet是一個list類型,C2SoftAvcDec在存放output buffer的時候,總是存放在第一個worklets的output中,參見思維導圖,output是C2FrameData類型,它擁有一個C2Buffer容器,C2SoftAvcDec總是將新的output buffer丟進容器中,它可以一次丟很多個output buffer,然後一次性通過work回送到上層,上層可以一次性從work中取到多個output buffer去作渲染。C2WorkOrdinalStruct ordinal包括著buffer的pts與frameIndex信息。這裡有個疑問待解決,為什麼output buffer總是存放在第一個worklets的output中,worklets作為一個隊列對象,有什麼其他的意義?
上面我們分析瞭兩個點,一個是模塊的消息處理機制,另一個是如何送數據到解碼器再取出幀數據回送到上層,接下來看第三點,CCodec每次送多少輸入數據下來,component每次處理多少數據,回送輸出數據給CCodec作渲染在哪些地方。
上層是調用SimpleC2Component::queue_nb接口送數據下來的。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
c2_status_t SimpleC2Component::queue_nb(std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>> * const items) {
{
Mutexed<ExecState>::Locked state(mExecState);
if (state->mState != RUNNING) {
return C2_BAD_STATE;
}
}
bool queueWasEmpty = false;
{
Mutexed<WorkQueue>::Locked queue(mWorkQueue);
queueWasEmpty = queue->empty();
while (!items->empty()) {
queue->push_back(std::move(items->front()));
items->pop_front();
}
}
if (queueWasEmpty) {
(new AMessage(WorkHandler::kWhatProcess, mHandler))->post();
}
return C2_OK;
}
觀察上面的代碼,入參是一個列表對象,也就是說,每次送多個work,一個work可以包括一個C2Buffer容器,碼流都是放在容器的第一個元素,雖然一個容器可以放多個C2Buffer,但它就隻放瞭一個C2Buffer。我們可以從下面的代碼中發現,每一次的process,都隻從work中取一個C2Buffer。
\\av\media\codec2\components\avc\C2SoftAvcDec.cpp
void C2SoftAvcDec::process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) {
...
uint32_t workIndex = work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku() & 0xFFFFFFFF;
C2ReadView rView = mDummyReadView;
if (!work->input.buffers.empty()) {
//關註buffers[0]
rView = work->input.buffers[0]->data().linearBlocks().front().map().get();
inSize = rView.capacity();
}
}
SimpleC2Component::processQueue()每次隻處理一個work,處理完就把work回送上去。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
bool SimpleC2Component::processQueue() {
....
ALOGV("start processing frame #%" PRIu64, work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku());
//處理work
process(work, mOutputBlockPool);
ALOGV("processed frame #%" PRIu64, work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku());
Mutexed<WorkQueue>::Locked queue(mWorkQueue);
if (work->workletsProcessed != 0u) {
queue.unlock();
Mutexed<ExecState>::Locked state(mExecState);
ALOGV("returning this work");
std::shared_ptr<C2Component::Listener> listener = state->mListener;
state.unlock();
//回送work
listener->onWorkDone_nb(shared_from_this(), vec(work));
}
...
}
在沒有新送下來的work需要處理的時候,processQueue()會調用drain接口作“渲染”操作,它會看解碼器是否有幀數據生成,有的話,就填充到work中回送到上層。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
bool SimpleC2Component::processQueue() {
....
if (!work) {
c2_status_t err = drain(drainMode, mOutputBlockPool);
if (err != C2_OK) {
Mutexed<ExecState>::Locked state(mExecState);
std::shared_ptr<C2Component::Listener> listener = state->mListener;
state.unlock();
listener->onError_nb(shared_from_this(), err);
}
return hasQueuedWork;
}
...
}
另一個渲染的地方是在process()中,解碼完發現有幀數據的時候,就調用finishWork()將work回送。
\\av\media\codec2\components\avc\C2SoftAvcDec.cpp
void C2SoftAvcDec::process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) {
...
if (s_decode_op.u4_output_present) {
finishWork(s_decode_op.u4_ts, work);
}
...
}
5 小結
Component內部的邏輯還是比較好理解的,重點在於它是如何申請buffer的,如何將buffer“送”給解碼器,解碼完後是如何取得buffer並返回上層,難點在於work對象層層封裝,當你要訪問實際內存地址時,如何訪問,如果要取得內存的handle,又要如何訪問,這一點通過將work對象一層一層的“繪制”出來,就好懂得多。接下來問題來瞭,在OMX中,上下層的交互配置是通過setParamerter/getParamerter等接口進行的,那麼在Codec2中是如何進行的?Codec2中到底有沒有像OMX一樣的BufferCountActual設計?Codec2在調用nativewindow的setMaxDequeuedBufferCount時是如何確定maxDequeueBufferCount的?GraphicBuffer的生命周期是如何控制的?
到此這篇關於一文搞懂Codec2解碼組件的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關Codec2解碼組件內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- 一文搞懂Codec2框架解析
- 詳解c++ libuv工作隊列
- Android音視頻開發Media FrameWork框架源碼解析
- C#使用遠程服務調用框架Apache Thrift
- postgresql 性能參數配置方式