人工智能-Python實現多項式回歸
1、概述
1.1 有監督學習
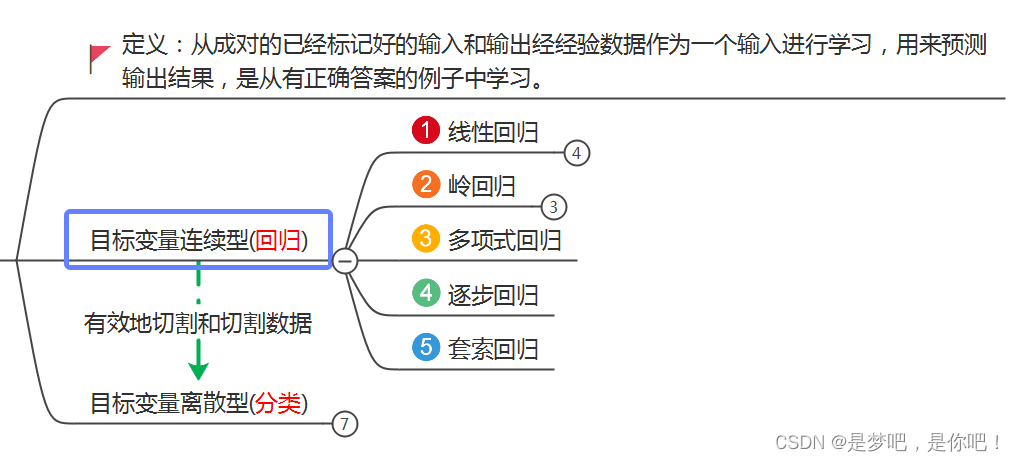
1.2 多項式回歸
上一次我們講解瞭線性回歸,這次我們重點分析多項式回歸。
多項式回歸(Polynomial Regression) 是研究一個因變量與一 個或多個自變量間多項式的回歸分析方法。如果自變量隻有一個 時,稱為一元多項式回歸;如果自變量有多個時,稱為多元多項 式回歸。

(1)在一元回歸分析中,如果依變量 y 與自變量 x 的關系為非線性的,但 是又找不到適當的函數曲線來擬合,則可以采用一元多項式回歸。
(2)多項式回歸的最大優點就是可以通過增加 x 的高次項對實測點進行逼 近,直至滿意為止。
(3)事實上,多項式回歸可以處理相當一類非線性問題,它在回歸分析 中占有重要的地位,因為任一函數都可以分段用多項式來逼近。
2 概念
之前提到的線性回歸實例中,是運用直線來擬合數據輸入與輸出之間的線性關系。不同於線性回歸, 多項式回歸是使用曲線擬合數據的輸入與輸出的映射關系 。

3 案例實現——方法1
3.1 案例分析
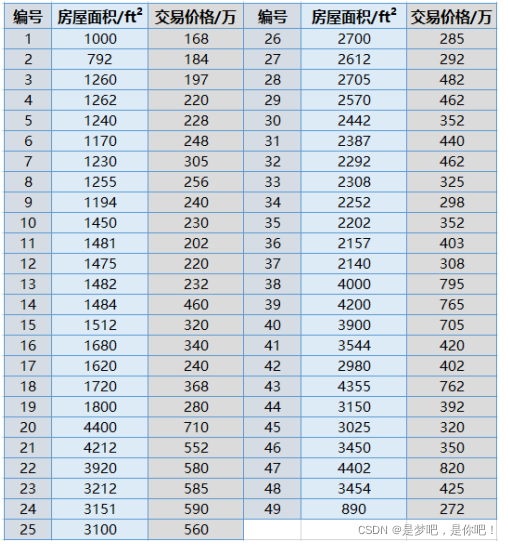
應用背景:我們在前面已經根據已知的房屋成交價和房屋的尺寸進行瞭線性回歸,繼而可以對已知房屋尺寸,而未知房屋成交價格的實例進行瞭成交價格的預測,但是在實際的應用中這樣的擬合往往不夠好,因此我們在此對該數據集進行多項式回歸。
目標:對房屋成交信息建立多項式回歸方程,並依據回歸方程對房屋價格進行預測。
成交信息包括房屋的面積以及對應的成交價格:
- (1)房屋面積單位為平方英尺( ft 2 )
- (2)房屋成交價格單位為萬
3.2 代碼實現

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
# 讀取數據集
datasets_X = []
datasets_Y = []
fr = open('多項式線性回歸.csv','r')
lines = fr.readlines()
for line in lines:
items = line.strip().split(',')
datasets_X.append(int(items[0]))
datasets_Y.append(int(items[1]))
length = len(datasets_X)
datasets_X = np.array(datasets_X).reshape([length,1])
datasets_Y = np.array(datasets_Y)
minX = min(datasets_X)
maxX = max(datasets_X)
X = np.arange(minX,maxX).reshape([-1,1])
poly_reg = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 2) #degree=2表示建立datasets_X的二次多項式特征X_poly。
X_poly = poly_reg.fit_transform(datasets_X) #使用PolynomialFeatures構造x的二次多項式X_poly
lin_reg_2 = linear_model.LinearRegression()
lin_reg_2.fit(X_poly, datasets_Y) #然後創建線性回歸,使用線性模型(linear_model)學習X_poly和y之間的映射關系
print(X_poly)
print(lin_reg_2.predict(poly_reg.fit_transform(X)))
print('Coefficients:', lin_reg_2.coef_) #查看回歸方程系數(k)
print('intercept:', lin_reg_2.intercept_) ##查看回歸方程截距(b)
print('the model is y={0}+({1}*x)+({2}*x^2)'.format(lin_reg_2.intercept_,lin_reg_2.coef_[0],lin_reg_2.coef_[1]))
# 圖像中顯示
plt.scatter(datasets_X, datasets_Y, color = 'red') #scatter函數用於繪制數據點,這裡表示用紅色繪制數據點;
#plot函數用來繪制回歸線,同樣這裡需要先將X處理成多項式特征;
plt.plot(X, lin_reg_2.predict(poly_reg.fit_transform(X)), color = 'blue')
plt.xlabel('Area')
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.show()
3.3 結果
[[1.0000000e+00 1.0000000e+03 1.0000000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 7.9200000e+02 6.2726400e+05]
[1.0000000e+00 1.2600000e+03 1.5876000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.2620000e+03 1.5926440e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.2400000e+03 1.5376000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.1700000e+03 1.3689000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.2300000e+03 1.5129000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.2550000e+03 1.5750250e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.1940000e+03 1.4256360e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.4500000e+03 2.1025000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.4810000e+03 2.1933610e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.4750000e+03 2.1756250e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.4820000e+03 2.1963240e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.4840000e+03 2.2022560e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.5120000e+03 2.2861440e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.6800000e+03 2.8224000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.6200000e+03 2.6244000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.7200000e+03 2.9584000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 1.8000000e+03 3.2400000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 4.4000000e+03 1.9360000e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 4.2120000e+03 1.7740944e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.9200000e+03 1.5366400e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.2120000e+03 1.0316944e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.1510000e+03 9.9288010e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 3.1000000e+03 9.6100000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.7000000e+03 7.2900000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.6120000e+03 6.8225440e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.7050000e+03 7.3170250e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.5700000e+03 6.6049000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.4420000e+03 5.9633640e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.3870000e+03 5.6977690e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.2920000e+03 5.2532640e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.3080000e+03 5.3268640e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.2520000e+03 5.0715040e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.2020000e+03 4.8488040e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.1570000e+03 4.6526490e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 2.1400000e+03 4.5796000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 4.0000000e+03 1.6000000e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 4.2000000e+03 1.7640000e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.9000000e+03 1.5210000e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.5440000e+03 1.2559936e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 2.9800000e+03 8.8804000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 4.3550000e+03 1.8966025e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.1500000e+03 9.9225000e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 3.0250000e+03 9.1506250e+06]
[1.0000000e+00 3.4500000e+03 1.1902500e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 4.4020000e+03 1.9377604e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 3.4540000e+03 1.1930116e+07]
[1.0000000e+00 8.9000000e+02 7.9210000e+05]]
[231.16788093 231.19868474 231.22954958 … 739.2018995 739.45285011
739.70386176]
Coefficients: [ 0.00000000e+00 -1.75650177e-02 3.05166076e-05]
intercept: 225.93740561055927
the model is y=225.93740561055927+(0.0*x)+(-0.017565017675036532*x^2)
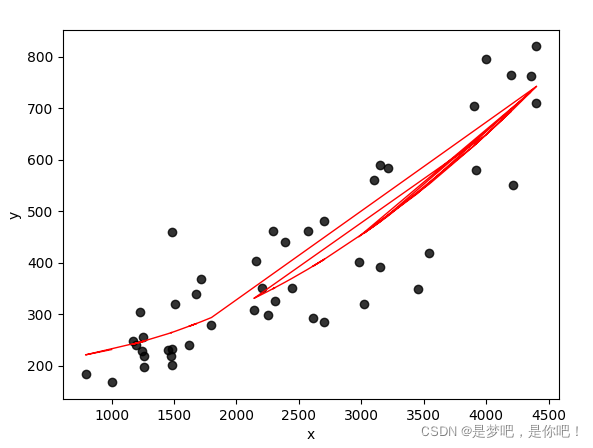
3.4 可視化

4 案例實現——方法2
4.1 代碼
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(action="ignore", module="sklearn")
dataset = pd.read_csv('多項式線性回歸.csv')
X = np.asarray(dataset.get('x'))
y = np.asarray(dataset.get('y'))
# 劃分訓練集和測試集
X_train = X[:-2]
X_test = X[-2:]
y_train = y[:-2]
y_test = y[-2:]
# fit_intercept 為 True
model1 = Pipeline([('poly', PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)), ('linear', LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True))])
model1 = model1.fit(X_train[:, np.newaxis], y_train)
y_test_pred1 = model1.named_steps['linear'].intercept_ + model1.named_steps['linear'].coef_[1] * X_test
print('while fit_intercept is True:................')
print('Coefficients: ', model1.named_steps['linear'].coef_)
print('Intercept:', model1.named_steps['linear'].intercept_)
print('the model is: y = ', model1.named_steps['linear'].intercept_, ' + ', model1.named_steps['linear'].coef_[1],
'* X')
# 均方誤差
print("Mean squared error: %.2f" % mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred1))
# r2 score,0,1之間,越接近1說明模型越好,越接近0說明模型越差
print('Variance score: %.2f' % r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred1), '\n')
# fit_intercept 為 False
model2 = Pipeline([('poly', PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)), ('linear', LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False))])
model2 = model2.fit(X_train[:, np.newaxis], y_train)
y_test_pred2 = model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[0] + model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[1] * X_test + \
model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[2] * X_test * X_test
print('while fit_intercept is False:..........................................')
print('Coefficients: ', model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_)
print('Intercept:', model2.named_steps['linear'].intercept_)
print('the model is: y = ', model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[0], '+', model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[1], '* X + ',
model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[2], '* X^2')
# 均方誤差
print("Mean squared error: %.2f" % mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred2))
# r2 score,0,1之間,越接近1說明模型越好,越接近0說明模型越差
print('Variance score: %.2f' % r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred2), '\n')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
# 畫訓練集的散點圖
plt.scatter(X_train, y_train, alpha=0.8, color='black')
# 畫模型
plt.plot(X_train, model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[0] + model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[1] * X_train +
model2.named_steps['linear'].coef_[2] * X_train * X_train, color='red',
linewidth=1)
plt.show()
4.2 結果
如果不用框架,需要自己手動對數據添加高階項,有瞭框架就方便多瞭。sklearn 使用 Pipeline 函數簡化這部分預處理過程。
當 PolynomialFeatures 中的degree=1時,效果和使用 LinearRegression 相同,得到的是一個線性模型,degree=2時,是二次方程,如果是單變量的就是拋物線,雙變量的就是拋物面。以此類推。
這裡有一個 fit_intercept 參數,下面通過一個例子看一下它的作用。
當 fit_intercept 為 True 時,coef_ 中的第一個值為 0,intercept_ 中的值為實際的截距。
當fit_intercept 為 False 時,coef_ 中的第一個值為截距,intercept_ 中的值為 0。
如圖,第一部分是 fit_intercept 為 True 時的結果,第二部分是 fit_intercept 為 False 時的結果。
while fit_intercept is True:................ Coefficients: [ 0.00000000e+00 -3.70858180e-04 2.78609637e-05] Intercept: 204.25470490804574 the model is: y = 204.25470490804574 + -0.00037085818009180454 * X Mean squared error: 26964.95 Variance score: -3.61 while fit_intercept is False:.......................................... Coefficients: [ 2.04254705e+02 -3.70858180e-04 2.78609637e-05] Intercept: 0.0 the model is: y = 204.2547049080572 + -0.0003708581801012066 * X + 2.7860963722809286e-05 * X^2 Mean squared error: 7147.78 Variance score: -0.22
4.3 可視化
到此這篇關於人工智能-Python實現多項式回歸的文章就介紹到這瞭,更多相關Python實現多項式回歸內容請搜索WalkonNet以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大傢以後多多支持WalkonNet!
推薦閱讀:
- 人工智能-Python實現嶺回歸
- Python之Sklearn使用入門教程
- python機器學習基礎線性回歸與嶺回歸算法詳解
- 詳解Bagging算法的原理及Python實現
- 一文搞懂Python Sklearn庫使用