OpenCV+MediaPipe實現手部關鍵點識別
可視化輔助函數
在下面的代碼的註釋內有大致的操作
基本操作與前面的人臉檢測的操作相似,增加瞭可視化的輔助函數
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 使用ipython的魔法方法,將繪制出的圖像直接嵌入在notebook單元格中
import cv2
# 定義可視化圖像函數
def look_img(img):
'''opencv讀入圖像格式為BGR,matplotlib可視化格式為RGB,因此需將BGR轉RGB'''
img_RGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img_RGB)
plt.show()
#調用攝像頭拍照
time.sleep(2) # 運行本代碼後兩秒拍照
# 獲取攝像頭,0為電腦默認攝像頭,1為外接攝像頭
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 從攝像頭捕獲一幀畫面
success, image = cap.read()
# 關閉攝像頭
cap.release()
# 關閉圖像窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.imwrite('photo.jpg', image)
#調用攝像頭拍視頻
import cv2
import time
# 定義逐幀處理函數,可不進行任何處理,直接將攝像頭捕獲的畫面寫入視頻幀
def process_frame(img):
return img
output_name = 'record_video.mp4'
# 獲取攝像頭,傳入0表示獲取系統默認攝像頭
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 打開cap
cap.open(0)
frame_size = (cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH), cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_name, fourcc, fps, (int(frame_size[0]), int(frame_size[1])))
# 無限循環,直到break被觸發
while cap.isOpened():
# 獲取畫面
success, frame = cap.read()
if not success:
break
# 對捕獲的幀進行圖像處理
frame = process_frame(frame)
## 將幀寫入視頻文件中
out.write(frame)
# 展示處理後的三通道圖像
cv2.imshow('press q to break', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) in [ord('q'), 27]: # 按鍵盤上的q或esc退出(在英文輸入法下)
break
# 關閉圖像窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
out.release()
# 關閉攝像頭
cap.release()
print('視頻已保存', output_name)
單張圖片
import cv2 as cv
import mediapipe as mp
import tqdm
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def look_img(img):
img_RGB=cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img_RGB)
plt.show()
# 手部關鍵點檢測模型
mp_hand=mp.solutions.hands
# 導入模型
hands=mp_hand.Hands(static_image_mode=False,
max_num_hands=5,
min_detection_confidence=0.3,
min_tracking_confidence=0.3
)
# 導入繪圖函數
mpDraw=mp.solutions.drawing_utils
img=cv.imread('hand2.png')
# look_img(img)
img_RGB=cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
results=hands.process(img_RGB)
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
for hand_idx in range(len(results.multi_hand_landmarks)):
hand_21=results.multi_hand_landmarks[hand_idx]
mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, hand_21, mp_hand.HAND_CONNECTIONS) # 可視化
look_img(img)
cv.imwrite('hands2.jpg',img)
# 在三維坐標系中可視化索引為0的手
mpDraw.plot_landmarks(results.multi_hand_landmarks[0], mp_

攝像頭檢測
import cv2
# mediapipe人工智能工具包
import mediapipe as mp
# 進度條庫
from tqdm import tqdm
# 時間庫
import time
# 導入模型
# 導入solution
mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
# 導入模型
hands = mp_hands.Hands(static_image_mode=False, # 是靜態圖片還是連續視頻幀
max_num_hands=2, # 最多檢測幾隻手
min_detection_confidence=0.7, # 置信度閾值
min_tracking_confidence=0.5) # 追蹤閾值
# 導入繪圖函數
mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
# 處理單幀函數
# 處理幀函數
def process_frame(img):
# 水平鏡像翻轉圖像,使圖中左右手與真實左右手對應
# 參數 1:水平翻轉,0:豎直翻轉,-1:水平和豎直都翻轉
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
# BGR轉RGB
img_RGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 將RGB圖像輸入模型,獲取預測結果
results = hands.process(img_RGB)
if results.multi_hand_landmarks: # 如果有檢測到手
# 遍歷每一隻檢測出的手
for hand_idx in range(len(results.multi_hand_landmarks)):
hand_21 = results.multi_hand_landmarks[hand_idx] # 獲取該手的所有關鍵點坐標
mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, hand_21, mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS) # 可視化
# 在三維坐標系中可視化索引為0的手
# mpDraw.plot_landmarks(results.multi_hand_landmarks[0], mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
return img
# 導入opencv-python
import cv2
import time
# 獲取攝像頭,傳入0表示獲取系統默認攝像頭
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
# 打開cap
cap.open(0)
# 無限循環,直到break被觸發
while cap.isOpened():
# 獲取畫面
success, frame = cap.read()
if not success:
print('Error')
break
## !!!處理幀函數
frame = process_frame(frame)
# 展示處理後的三通道圖像
cv2.imshow('my_window', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) in [ord('q'), 27]: # 按鍵盤上的q或esc退出(在英文輸入法下)
break
# 關閉攝像頭
cap.release()
# 關閉圖像窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
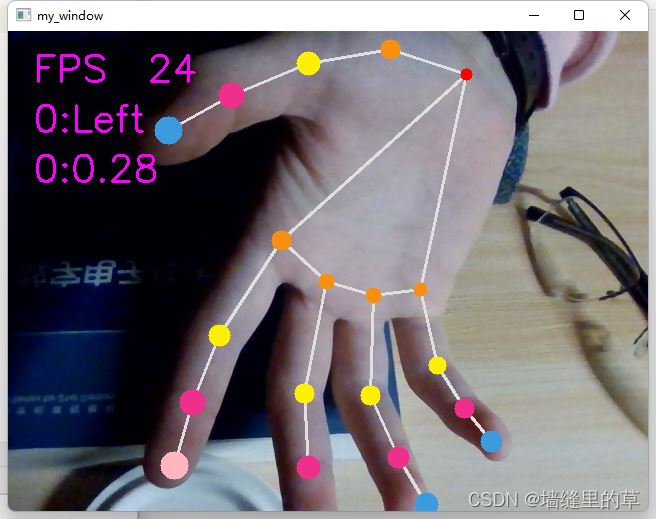
改變關鍵點數據特征
import cv2
# mediapipe人工智能工具包
import mediapipe as mp
# 進度條庫
from tqdm import tqdm
# 時間庫
import time
# 導入solution
mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
# 導入模型
hands = mp_hands.Hands(static_image_mode=False, # 是靜態圖片還是連續視頻幀
max_num_hands=2, # 最多檢測幾隻手
min_detection_confidence=0.7, # 置信度閾值
min_tracking_confidence=0.5) # 追蹤閾值
# 導入繪圖函數
mpDraw = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
def process_frame(img):
# 記錄該幀開始處理的時間
start_time = time.time()
# 獲取圖像寬高
h, w = img.shape[0], img.shape[1]
# 水平鏡像翻轉圖像,使圖中左右手與真實左右手對應
# 參數 1:水平翻轉,0:豎直翻轉,-1:水平和豎直都翻轉
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
# BGR轉RGB
img_RGB = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 將RGB圖像輸入模型,獲取預測結果
results = hands.process(img_RGB)
if results.multi_hand_landmarks: # 如果有檢測到手
handness_str = ''
index_finger_tip_str = ''
for hand_idx in range(len(results.multi_hand_landmarks)):
# 獲取該手的21個關鍵點坐標
hand_21 = results.multi_hand_landmarks[hand_idx]
# 可視化關鍵點及骨架連線
mpDraw.draw_landmarks(img, hand_21, mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS)
# 記錄左右手信息
temp_handness = results.multi_handedness[hand_idx].classification[0].label
handness_str += '{}:{} '.format(hand_idx, temp_handness)
# 獲取手腕根部深度坐標
cz0 = hand_21.landmark[0].z
for i in range(21): # 遍歷該手的21個關鍵點
# 獲取3D坐標
cx = int(hand_21.landmark[i].x * w)
cy = int(hand_21.landmark[i].y * h)
cz = hand_21.landmark[i].z
depth_z = cz0 - cz
# 用圓的半徑反映深度大小
radius = max(int(6 * (1 + depth_z * 5)), 0)
if i == 0: # 手腕
img = cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), radius, (0, 0, 255), -1)
if i == 8: # 食指指尖
img = cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), radius, (193, 182, 255), -1)
# 將相對於手腕的深度距離顯示在畫面中
index_finger_tip_str += '{}:{:.2f} '.format(hand_idx, depth_z)
if i in [1, 5, 9, 13, 17]: # 指根
img = cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), radius, (16, 144, 247), -1)
if i in [2, 6, 10, 14, 18]: # 第一指節
img = cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), radius, (1, 240, 255), -1)
if i in [3, 7, 11, 15, 19]: # 第二指節
img = cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), radius, (140, 47, 240), -1)
if i in [4, 12, 16, 20]: # 指尖(除食指指尖)
img = cv2.circle(img, (cx, cy), radius, (223, 155, 60), -1)
scaler = 1
img = cv2.putText(img, handness_str, (25 * scaler, 100 * scaler), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.25 * scaler,
(255, 0, 255), 2 * scaler)
img = cv2.putText(img, index_finger_tip_str, (25 * scaler, 150 * scaler), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1.25 * scaler, (255, 0, 255), 2 * scaler)
# 記錄該幀處理完畢的時間
end_time = time.time()
# 計算每秒處理圖像幀數FPS
FPS = 1 / (end_time - start_time)
# 在圖像上寫FPS數值,參數依次為:圖片,添加的文字,左上角坐標,字體,字體大小,顏色,字體粗細
img = cv2.putText(img, 'FPS ' + str(int(FPS)), (25 * scaler, 50 * scaler), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1.25 * scaler, (255, 0, 255), 2 * scaler)
return img
# 獲取攝像頭,傳入0表示獲取系統默認攝像頭
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 打開cap
cap.open(0)
# 無限循環,直到break被觸發
while cap.isOpened():
# 獲取畫面
success, frame = cap.read()
if not success:
break
frame = process_frame(frame)
# 展示處理後的三通道圖像
cv2.imshow('my_window', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) in [ord('q'), 27]: # 按鍵盤上的q或esc退出(在英文輸入法下)
break
# 關閉攝像頭
cap.release()
# 關閉圖像窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
以上就是OpenCV+MediaPipe實現手部關鍵點識別的詳細內容,更多關於OpenCV MediaPipe手部關鍵點識別的資料請關註WalkonNet其它相關文章!
推薦閱讀:
- python+mediapipe+opencv實現手部關鍵點檢測功能(手勢識別)
- Python+OpenCV手勢檢測與識別Mediapipe基礎篇
- Python+OpenCV實戰之拖拽虛擬方塊的實現
- 基於Mediapipe+Opencv實現手勢檢測功能
- opencv+mediapipe實現人臉檢測及攝像頭實時示例